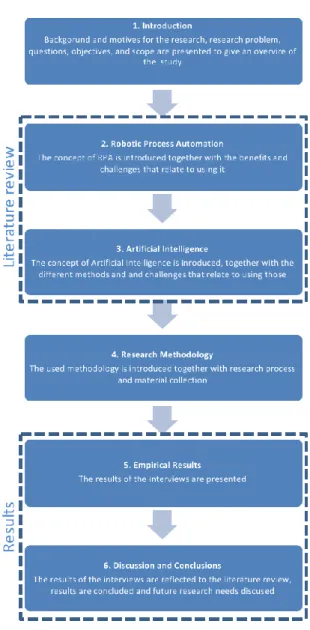
The goal of this study was to determine how AI capabilities could complement robotic process automation in business process automation. The outcome of this study showed that artificial intelligence capabilities can complement robotic process automation in business process automation in several ways.
INTRODUCTION
- Research background and motives
- Research problem, research questions and objective
- Research scope
- Research structure
The purpose of this thesis is to provide insight into how AI capabilities can complement RPA in a bigger picture. Then, the main objective of this thesis is to provide an understanding of how AI capabilities can address these challenges and limitations related to the use of RPA.
ROBOTIC PROCESS AUTOMATION
- Robotic process automation concept
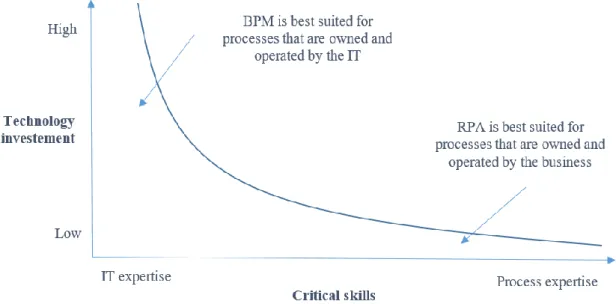
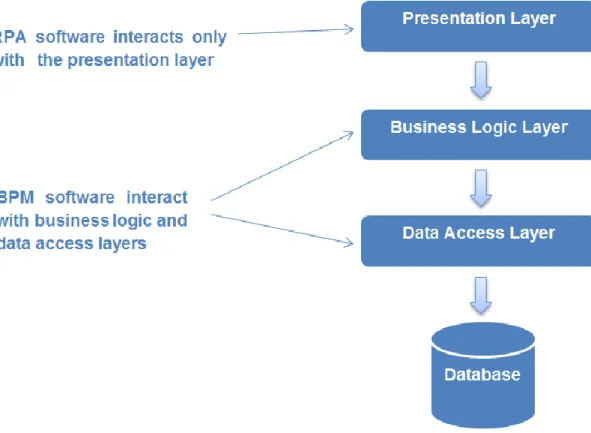
- Robotic process automation vs. traditional IT development
- Adoption of robotic process automation
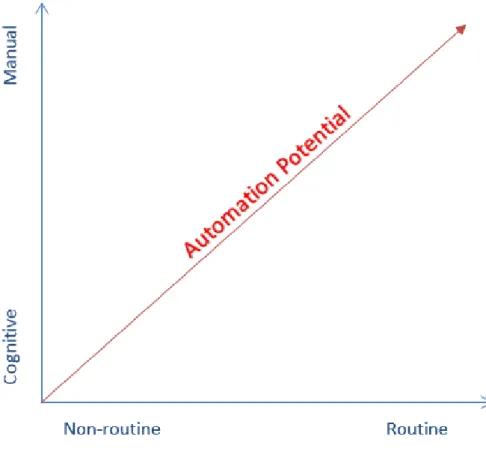
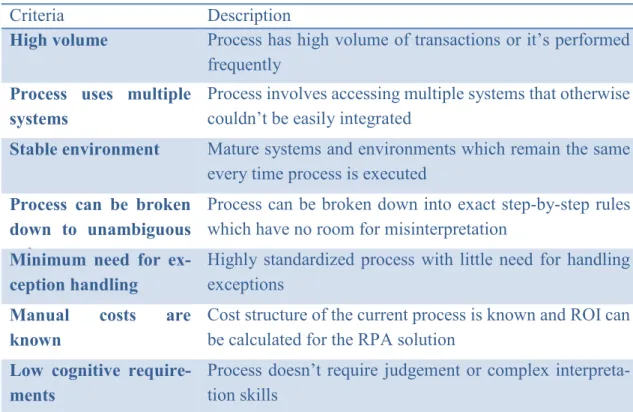
- Benefits and limitations of robotic process automation
- Robotic process automation vs. Intelligent automation
This is due to the fact that RPA is relatively easy technology to understand and learn as it performs the processes in the same way as the human counterpart would. Predictable results here are very important, as the robot needs accurate and unambiguous rules to work with, as all possible steps in the process must be taught to the robot so that the execution of the process can be error-free (Fehrst & Slaby 2012).
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
Concept of artificial intelligence
Similar to this are the Oxford Reference (2018) definition: "the theory and development of computer systems that can perform tasks that normally require human intelligence", the Everest Group definition: "AI is the ability of machines to exhibit human-like intelligence (Burnett 2017) and Harvard Journal of Law. All of these definitions refer to very similar definitions, but are perhaps a bit circular in that they contain the word "intelligence", and therefore raise the question of what intelligence and being intelligent actually mean.
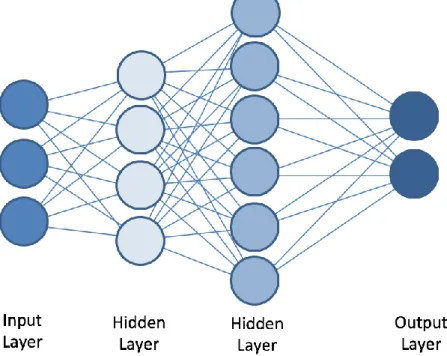
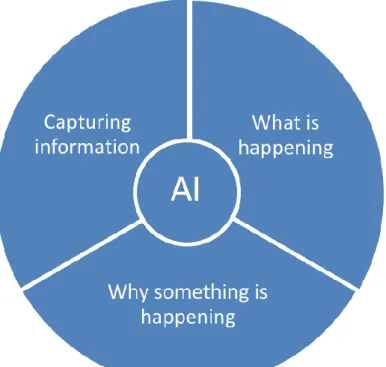
Artificial intelligence capabilities
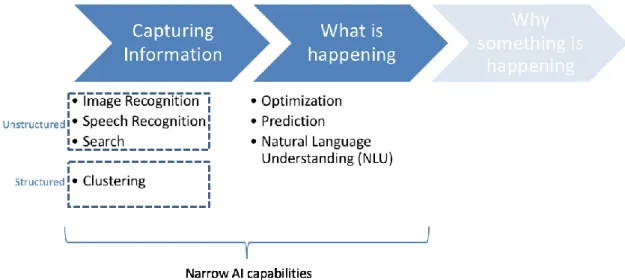
- Capturing Information
- What is happening
For example, many everyday applications used today in people's everyday lives actually benefit from AI capabilities (Burgess 2017, p. 2; Rossi 2016; Snow 2017). Using supervised learning AI system would learn with large amounts of training data which are intrinsic characteristics of the object X (Burgess 2017, p. 7; Ng 2016). Points worth noting are also the fact that when AI is actually used, it is most often implemented as a combination of several options (Burgess 2017, p. 4; Burnett 2017).
Speech recognition then uses supervised learning to match the transcripts with tagged training data (Burgess 2017, pp. 33-34; Ng 2016). By prediction is meant the ability of AI to match new data points to an identified group based on the historical data (Burgess 2017, .p 46;. When the prediction model is then fed with new data, it correlates the variables with historical data and provides a prediction with a probability of correct answer (Burgess 2017, p. 47).
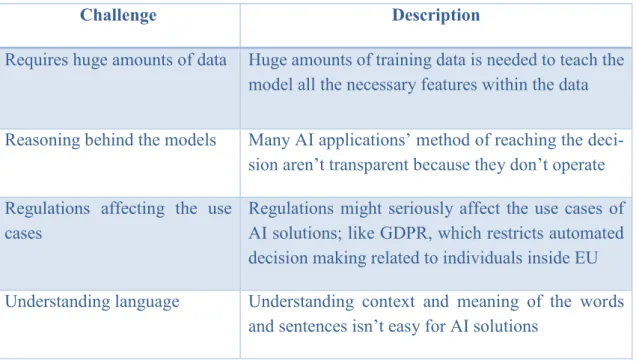
Challenges and limitations
However, what is really the problem with many of today's AI systems is the ambiguity of decision making. This in turn may mean that the systems cannot be used in many cases where transparency and the possibility of validating decisions are crucial. After all, the reliability of the results that AI systems provide are only as good as the data they feed on.
So the other way that can creep into the systems is the above situation where biases of the developers who built the algorithm end up in the model. This is extremely critical, as it is not even enough for the AI system to understand all possible variations in the meaning of the words if it still gets the context wrong. Regulations can seriously affect the use of AI solutions; such as GDPR, which restricts automated decision-making related to individuals within the EU. Understanding of language Understanding of context and meaning of the words.
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
Methodology
This is important because the chosen research philosophy shows how researchers look at the world and how they approach knowledge during research. It is important to know that the chosen research philosophy also affects the research strategy and methods that are chosen as part of this strategy. Positivism here means that the research is done from a very objective point of view, which can result in almost generalized theories.
When starting a research, another important factor is how the researcher approaches knowledge about the research topic. In this thesis, all research questions also concern "What?" and "How?", and in this sense, this dissertation's research strategy can be categorized as a case study from this point of view as well (Yin 2003). Next in the research is to choose the data collection method and time horizon for the research.
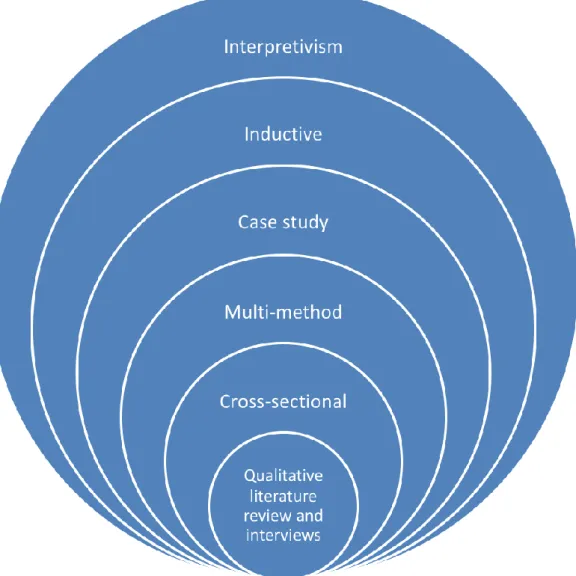
Collection of material
- Literature review
- Empirical part
Two out of three of these methods, literature review and subject matter expert interviewing, are used in this thesis. In this thesis, the data collection methods were the literature review and thematic interviews. The theoretical part of this thesis, which was carried out as a literature review, consists of two chapters: robotic process automation and artificial intelligence capabilities.
Thus, the literature search portion of this thesis was a continuous, iterative process throughout the writing of the literature review section, allowing for an ever-increasing insight into the topics. The purpose of the diploma thesis is research and thus combines relatively new literary fields with interviews. The interviewees for the empirical part were chosen as experts in the fields of this thesis in order to gain a deeper understanding of the topics as well as new insight.
Research process
These interview questions and key topics can be found in the appendices as shown later. To summarize briefly, the first interview was conducted with Tuom Pursiainen, who is a senior consultant at CGI focusing on process automation, robotic process automation and intelligent automation. The interview with Samu Paajanen then focused more on the use of artificial intelligence technologies; what different technologies exist, what benefits and challenges are associated with them, and what use cases currently exist.
After completing the literature research, a literature review was written for the diploma thesis, and based on the findings, the process of finding suitable candidates for interviews was carried out. Once suitable interview candidates were found, interview questions, interview frameworks and interview dates were set. Finally, the results of the interviews were combined and used in the literature review and the conclusions of the entire dissertation were written.
RESULTS
Intelligent automation expert interview
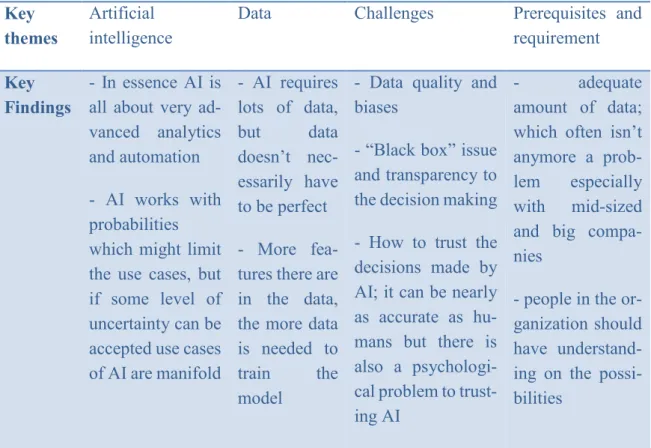
In terms of quality, Pursiainen noted that the importance of good quality becomes more important when there is only a small amount of data to train on, as this can affect the model. Then, when the model is trained with biased data, the model inherits the same biases. One can then simply hope that in the model something is connected in an unexpected way so that the data affecting it can be identified.
This is because in many cases AI's decision making is somewhat of a 'black box' and there is no transparency as to how the model arrived at the decision. Even if the model can be trained without using any of these data, problems may arise related to the datasets to be kept. One approach here to validate the results of a system, which is not transparent, might be to test the model after removing the labels from the data and then test the model again against earlier results, if they are available. and see if the model behaves the same and gives expected results.

Data Science expert interview
AI requires lots of data, but data doesn't necessarily have to be perfect - The more features there are in the data, the more data is needed to train the model. So at the end of the day, even a self-driving car is nothing more than advanced analytics and automation. In relation to business processes, Paajanen pointed out that he doesn't think there are really areas where AI could not be useful.
However, AI systems will never arrive at definitive results, but similarly, humans rarely do. With AI the approach is just the opposite, decisions are almost always in the gray area and very rarely anything can be said with 100% certainty. In the end the results are only as good as the data, if the data is of poor quality the results will be.
DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSIONS
Discussion
- Artificial intelligence in business processes
- Intelligent automation
However, as Paajanen pointed out in the interview, it really also depends on the case in which the AI solution is implemented. As found in the literature review, the basic models of AI solutions are taught based on the data they are fed. As for the actual use of intelligent automation, the interview with Pursiainen also mentioned some specific use cases for combining RPA with artificial intelligence.
Chatbots were also brought up in the interviews as one of the most used solutions together with RPA. While the chatbot would initially be used to collect information, it could for example also collect unstructured input, i.e. then the trained model could be used to make new decisions based on the historical data and so that the 'weak' points in the RPA process could be filled.
Summary and conclusions
That said, it can be clearly identified that there are certain limitations that limit the scope of automated processes with RPA. However, there are aspects and objectives related to human decision-making as well as AI through which the concept can be examined. Then within these objectives the AI can be further divided into different abilities that are used to achieve these objectives.
The concept of AI can therefore be approached from the perspective of its capabilities, which means what kind of tasks AI can be used for. These criteria limit the implementation possibilities of RPA to certain types of processes, and still only sub-processes can be fully automated. Looking then at the AI's goals of capturing information and understanding "what's going on" and the capabilities within these goals, it can quickly be seen that they aim to address similar kinds of problems.
Critical evaluation of the research
This means that validating the results can be very difficult or even impossible if the logic in how the AI model makes its decisions is not transparent. This in turn can be a spectacle, as the reasons behind those outcomes are sometimes as essential a part of the outcome as the results. This means that there is always some uncertainty with the results - as they are simply probabilities.
Therefore, the validity of the results can be considered credible as no major differences were found between the theoretical and empirical works (Saunders et al. 2009, p. 156). Thus, most of the results are such that they would probably also be shown in similar research. The main results were obtained through a combination of the results of the literature review and the results of the interviews.
Future research
What artificial intelligence can and cannot do now. https://hbr.org/2016/11/what-artificial-intelligence-can-and-cant-do-right-now. What do you think are the most critical problems with robotic process automation where artificial intelligence can help and how. What kind of prerequisites are there to start using artificial intelligence technologies with robotic process automation.
What challenges and problems can arise when implementing artificial intelligence technologies with robotic process automation. How do you think the new General Data Protection Regulation will affect the use of artificial intelligence technologies? What do you think would be a good starting point for organizations to start using artificial intelligence technologies with robotic process automation?