Hélicase du syndrome de Werner RPA70168–308 Région acide N-terminale, extrémité C-terminale et hélicase du syndrome de Bloom RPA70168–308 Région acide N-terminale, extrémité C-terminale abd. ADN polymérase B (Pol B) Stimulation de l'activité polymérase Élongation de la réplication ADN polymérase D (Pol D) Stimulation de l'activité polymérase Élongation de la réplication Facteur de réplication C (RF-C) Chargement de PCNA sur l'ADN Initiation de la réplication.
An extended network of genomic maintenance in the archaeon Pyrococcus abyssi highlights unexpected associations between
However, none of the proteins responsible for the lesion recognition step have been found in archaeal genomes (Kelman and White 2005). Production and purification of bait proteins have either already been reported (see Table 1 for a list of protein baits used and relevant references) or is described in the supplementary materials. Insert sequences were checked and recombinant clones were used to transform E.
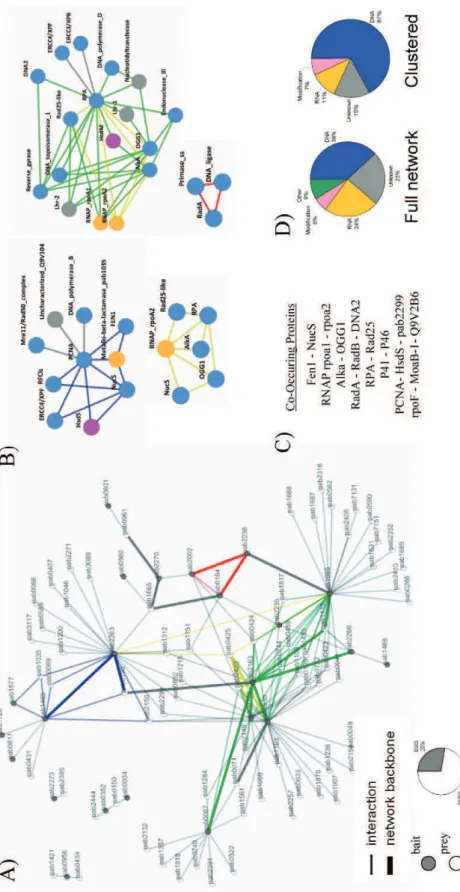
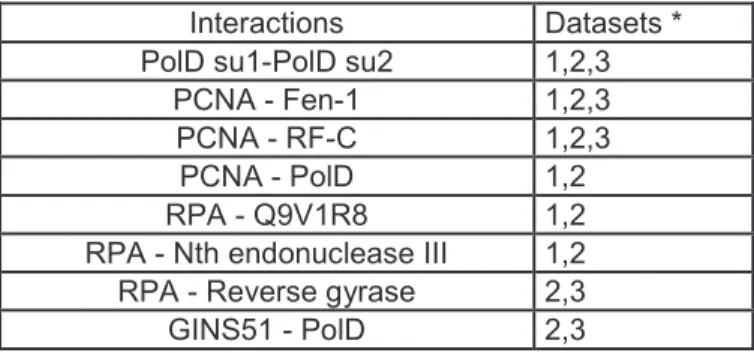
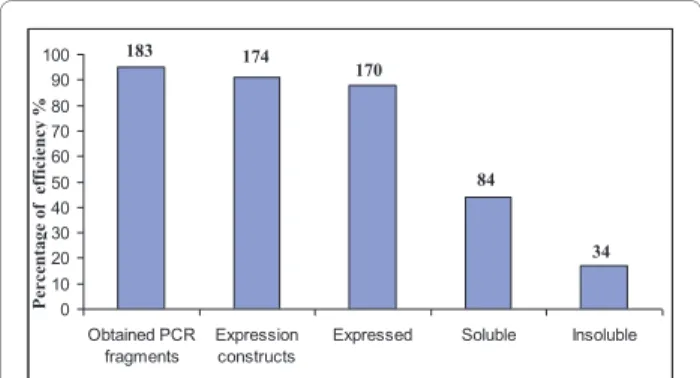
We found that the PCNA replication clamp interacted with the small subunit of the loading factor RF-C, the replicative DNA polymerase B and the. We found that the GINS51 subunit of the GINS complex interacts with the exonuclease subunit of DNA polymerase D (PolD). The interaction between the polymerase subunit of PolD and GINS51 was also detected, although it showed higher SR scores (SR-:0.22; SR+:0.41). Subunits RPA32 and RPA41 of the RPA complex were co-purified with the HIS-tagged Polymerase D complex (PolD).
The eukaryotic Mre11 complex is composed of the meiotic recombination 11 (Mre11), Rad50 and Nbs1 (Nijmegen breakage syndrome 1). However, it has been shown that the eukaryotic Mre11 complex colocalizes with the PCNA at replication foci during S phase and that the eukaryotic Mre11 complex plays a primary role in the maintenance of the replication fork during DNA replication (Huertas, Cortes-Ledesma et et al. 2008). Since numerous client proteins of the PCNA interact with the replication clamp via a PIP box (Beattie and Bell 2011), we searched for the occurrence of such a motif in the sequence of Pab0431.
We demonstrated that Pab0431 is a new partner of PCNA and is therefore probably involved in the process of DNA metabolism. The putative PIP motif appears to be conserved only in the sequence of representatives of the order Thermococcales. Pab1035 belongs to COG0595 and arCog00547 (Makarova, Sorokin et al. 2007), which comprise putative hydrolases of the metallo-beta-lactamase superfamily.
However, recent functional characterizations of RNases from the β-CASP family indicate a lack of discrimination between RNA and DNA, which may be common among members of this family (Clouet-d'Orval, Rinaldi et al. 2010). Indeed, quantitative proteomic analyzes highlighted the yeast RPA complex as an interaction partner of the transcription machinery (Sikorski, Ficarro et al. 2011). The eukaryotic XPB is a component of the TFIIH complex and is essential for both NER and transcription initiation (Coin, Oksenych et al. 2007; Oksenych, Bernardes de Jesus et al. 2009).
Indeed, DinG is a bacterial representative of the SF2 family of helicases and translocates in the 5'-3' direction on ssDNA. GINS, GAN and MCM form a complex that appears to be a key component of the DNA replication machinery in all Archaea (Makarova, Koonin et al. 2012).
When targeting the 3D structure of the protein of interest, a second hurdle is encountered in the crystallization step of these proteins. Selection and Bioinformatic Analysis of Target Genes A subset of 200 target genes was selected from various partners involved in the program to assess the potential for heterologous expression of marine organism genes in E. Nucleotide sequences were screened for the absence of selected sites. limiting for gene cloning strategy.
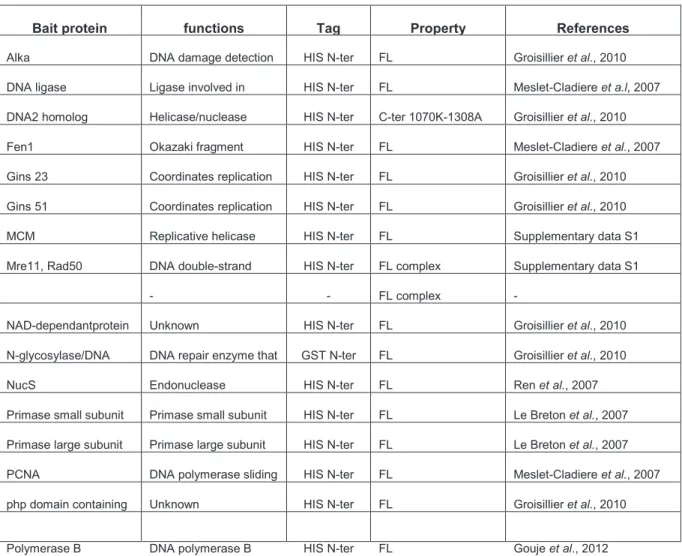
Crucial choices of the N- and C-terminal boundaries of each module were refined using Hydrophobic Cluster Analysis (HCA) [ 18 ]. For 167 of the 183 cloned constructs containing inserts of the expected size small-scale experiments for soluble protein expression were examined. A key step in automating the small-scale experimental setup is the development of auto-induction media (the ZYP5052 medium used in the present study), which contains differently metabolized carbon sources that promote growth at relatively high cell densities. and then automatic. -induced by the use of lactose.
Furthermore, in this study, 24-well plates were used instead of the usual 96-well plates [14] to achieve better aeration of the cells [22]. The scale-up was performed using culture volumes of 200 ml and based on the medium flow strategy protocols. One of the goals of the follow-up study based on genome data from P.
This challenge involves techniques to elucidate the structure and function of the gene products, interactions between proteins and/or global protein changes. The general concept of the MARINE-EXPRESS program can be divided into three main parts: .. i) the bioinformatics analysis of the target genes selected by different partners, ii) the cloning of target genes in. GST fusions help obtain soluble products of the entire fusion protein simply by its presence.
Indeed, for direct detection of the His-tagged product in the soluble fraction, a dot blot procedure with an anti-His antibody is often applied [ 35 – 37 ]. The sources and relevant genotypes of the bacterial strains as well as of the plasmids used are listed in Table 3. Targets were scored as positive for expression and solubility if a detectable fusion protein of the correct molecular weight was observed after Coomassie staining.