Emotional intelligence as a key factor for successful leadership in the work environment: a critical review and analysis of the. Many scientists have studied the impact of emotional intelligence on leadership processes in various fields. A positive correlation has been found between emotional intelligence and various leadership styles, such as transformational leadership and contingent reward (part of the transactional leadership theory).
Introduction
Overview
Scope and methodology of dissertation
Objectives and structure of dissertation
Theoretical Background
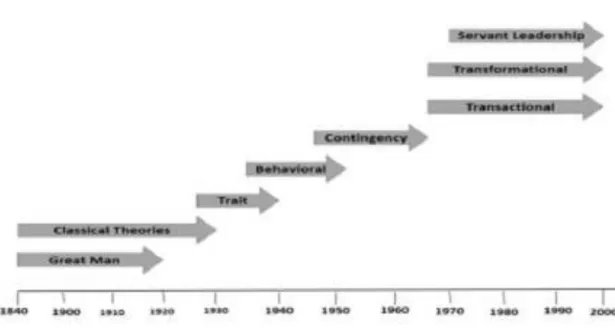
Leadership theories and styles of leaders
- Leadership theories
- Styles of leaders
According to Lamb (2013), effective leadership depends on a percentage of a leader's skills that match the needs of the environment and existing situations. Therefore, it is easily understood that the adaptability of a leader plays a crucial role for his/her effectiveness according to this theory (Zakeer et al., 2016). According to Chow et al. 2017), this theory does not emphasize the development of employees but rather the achievement of goals.
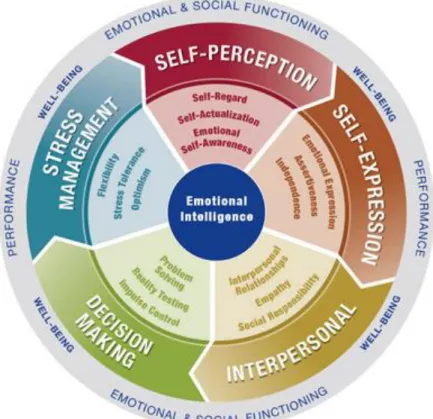
Emotional intelligence and the dimensions of it
- Bar-On’s Model
- Mayer-Salovey-Caruso’s Model
- Petride’s trait EI Model
- Goleman, Boyatzis & McKee’s Model
EI defined as the ability to observe one's own and others' feelings and emotions, to distinguish between them, and to use this information to guide the thinking and actions of others. Some other versions of the EQ-i are the EQ-360, which takes into account the feedback of others and thus extracts the final result, and the EQ-i YV, which is a youth version for ages 8 to 18 and highlights positive areas of functioning and areas that need for development (Badri, 2013). According to Salovey & Mayer (1990), EI is defined as the acceptance and use of one's own and others' emotions to solve problems and control behavior and the subset of social intelligence that includes the ability to observe one's own and others' emotions and feelings. to distinguish between them and use this information to control one's thinking and actions rather than a general sense of self and judgment of others.
The test that measures EI according to this model is Mayer-Salovey-Caruso Emotional Intelligence Test (MSCEIT) which was introduced in 2002 (Mayer et al. 2002). According to Petrides and Furnham (2001), there should be a differentiation between trait EI and ability EI. The model's questionnaire called Trait Emotional Intelligence Questionnaire (TEIQue) (Petrides, 2009) consists of four factors and fifteen facets that are connected to the personality domain (Petrides & Mavroveli, 2018).
Daniel Goleman (1998) in his book "working with emotional intelligence" defined EI as the ability to perceive our own feelings and those of others, self-management, and handling emotions both in ourselves and in our relationships . According to Boyatzis (2009) competence is defined as a skill or ability which is a set of interrelated but. Empathy: Understanding the emotions and perspective of others and actively caring about their concerns.
According to this model, to rate EI in an individual, a 360-degree feedback data must be collected.
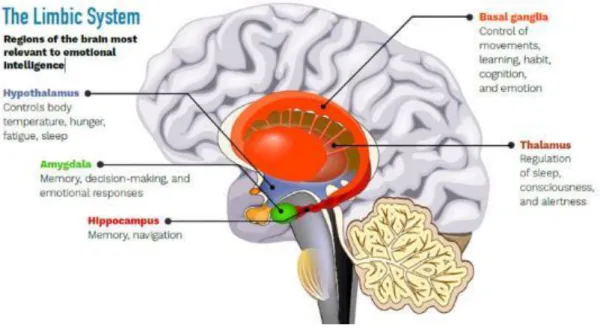
Connection between neuroscience, emotions and leadership
The EIQ, Emotional Intelligence Questionnaire developed by Dulewicz and Higgs (1999), provides self-assessment and a 360o evaluation of an individual's performance from peers, colleagues and managers. Regulation of emotion (ROE), the ability of emotion regulation to recover from distress. 1998) mentioned that neurogenesis, a process of creating hippocampal stem cells into new neural tissue, is thought to occur in PEA status.
Boyatzis (2008) also mentioned that "the growth of new nerve tissue allows more spines to grow on neurons, creating more space for the neurotransmitters and neuroreceptors that are the basis of learning". In summary, if leaders want to instill a vision, implement change, or motivate subordinates to perform better, they need to create a PEA status. When the SNS is activated, blood flow is diverted to large muscle groups and the potential for new nerve tissue growth is inhibited.
Although a long stay in NEA status is not indicated, it is sometimes beneficial for better functioning. Results revealed in the case of dissonant leaders, negative activation in the right inferior frontal gyrus, left posterior cingulate cortex, right medial frontal gyrus, and right anterior cingulate cortex. In addition, significant activation was found in the bilateral inferior frontal gyrus, bilateral posterior gyrus, bilateral inferior frontal gyrus, and right thalamus.
In the case of resonant leaders, activation right inferior frontal gyrus, left dorsal region of the anterior cingulate cortex, bilateral insula, left middle frontal gyrus, right putamen, right inferior parietal lobe and bilateral thalamus.
Methodology, Sources and Literature Review
Methodology of Dissertation
Identification of Sources
The author had participated in the free online educational program entitled "Inspirational Leadership through Emotional Intelligence", guided by R.E. Papers that were cited by a satisfactory number of researchers (over 150) were selected for review. Some of the references that were used for this dissertation were found by reviewing the references from the previously mentioned sources.
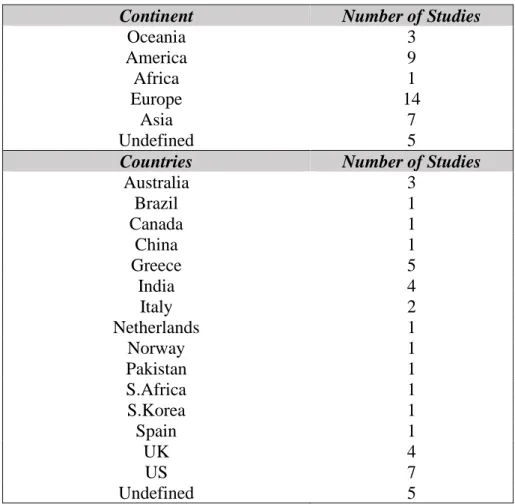
The author felt that it would be useful to review some of the cited references, which appear to be relative. Of these, 35 derived their findings after analyzing data collected from questionnaires completed by multiple samples of managers or subordinates. Below, in table 2, we can see the distribution according to the organizations' geographical area, of the studies where the results are extracted from analysis data from samples of managers and subordinates.
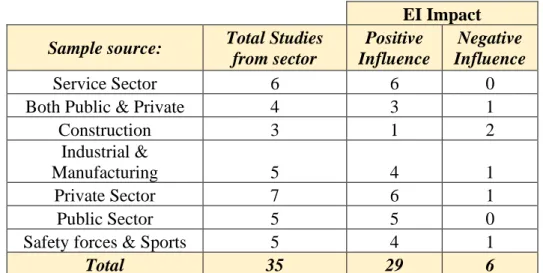
In addition, Table 3 shows the distribution of the studies that analyzed the samples according to the work sector.
Literature Review
Rubin et.al (2005) mentioned that leader's emotion recognition ability is positively related to transformational leadership behavior, while Daus and Ashkanasy (2005) argued that there is a relationship between ability-based models of EI and leadership ability, especially on transformational leadership. Similarly, Downey et.al (2006) investigated the relationship between EI and leadership in 176 female managers from several industries in Australia. Also, Kerr et.al (2006), in their study of 38 supervisors of a large manufacturing company in the UK, using the MSCEIT to test EI, found a partial correlation between EI and management effectiveness ratings from subordinates.
In 2006, Barbuto et.al found several links between EI and leadership in their study of 388 US public sector leader-follower dyads. In contrast, it did not reveal a significant relationship between EI and transformational leadership from the followers' perspective. Finally, Hur et.al (2011) also found a positive relationship between EI and transformational leadership in their study of 55 teams consisting of a total of 859 employees in the South Korean public sector.
In contrast, Cavaotte et.al (2012) in their study of 134 Brazilian energy sector managers failed to establish a link between EI and transformational leadership and. Butler and Chinowsky (2006) studied the relationship between EI and transformational leadership in 130 US construction managers. The results of their studies showed that there is a positive relationship between EI and transformational leadership.
Similarly, Lopez-Zafra et.al (2012) in their study found a correlation between EI and transformational leadership.
Findings, discussion and commentary
Transformational leadership appears to be positively influenced when leaders are characterized by developed EI skills. The interesting finding from the literature review is that 5 studies mentioned that EI is positively related to contingent rewards, a characteristic of transactional leadership. 2006) explained this discrepancy by claiming that contingent rewards are agreements between leaders and subordinates, and the success of these agreements "is mediated by leaders' regulation of mood and accurate recognition of follower emotions" (p.260). Although the purpose of this dissertation is to examine the effect of EI on leadership effectiveness, we cannot overlook the fact that EI (either of the leader or of subordinates) is enhancing subordinates.
Coetzee and Schaap (2005) mentioned that EI leaders are able to inspire followers to put in extra effort, which leads to an increased level of satisfaction of followers. From the reviewed studies, we summarize that EI positively affects transformational leaders (Barbuto et al. (2006), Hur et al. 2011)) and increases their effectiveness (Hur et al. We can conclude from the above that EI could have a positive impact on the leadership process in organizations.
2018) noted that critical emotional intelligence skills increase leader effectiveness, while Udod et al. 2020) mentioned that EI leaders are able to achieve desired outcomes for the organization. In the field of education, Koukoli (2018) mentioned that EI positively impacts leader effectiveness and relationship management. Transformational leadership in particular is based on EI skills and improving them will certainly help transformational leaders to be effective.
Therefore, we can argue that EI will definitely help organizations build effective transformational leaders.
Conclusions
Implications and advantages of dissertation
When EI skills are combined with cognitive skills, this results in optimal decision-making, which is of great importance for any organization that wants to develop and implement its strategy. Finally, an adequate training program for its managers, based on EI, would be important for any organization to achieve the desired changes and results.
Limitations of the review
Another goal of this study is to reveal the direction in which organizations should recruit and develop managers and employees even at lower levels. Modern leadership styles, such as transformational, charismatic or servant leadership, need EI as a factor for their effectiveness. The theoretical development of many of these measures is unclear and there is considerable variation in content between EI measures (Conte suggested that common measures such as the MEIS or EQ-i should not be used and argued that EI measures should be used for occupational questions only after they are specially developed, standardized and verified to prove professional applicability.
2001) suggested that unless a clear definition of EI as well as its domain elements is provided, it is futile to attempt to measure EI. They also asserted that “EI tasks generally lack sufficient reliability to provide meaningful profile interpretations and that consensus and expert rating systems are impractical for clinical assessment” (p.274). They asserted that it will be problematic to conceptualize EI as a unique intelligence and to prove its validity to personality constructs if self-report instruments are used to assess it.
Similarly to Roberts et al. 2008) argued that self-report measures should not be used because they do not accurately assess EI. They added that “to achieve the goal of accurate and systematic measurement of EI, instrumentation must be expanded beyond a single paradigm to provide a more reliable estimate of the generalizability of the construct” (p.477).
Future directions