Mobile payment technology
- SMS
- USSD
- IVR
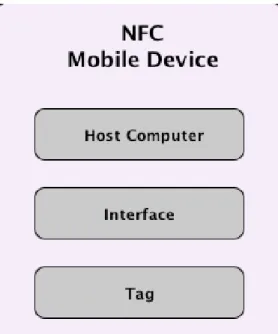
- Near Field Communication Technology
- NFC Applications
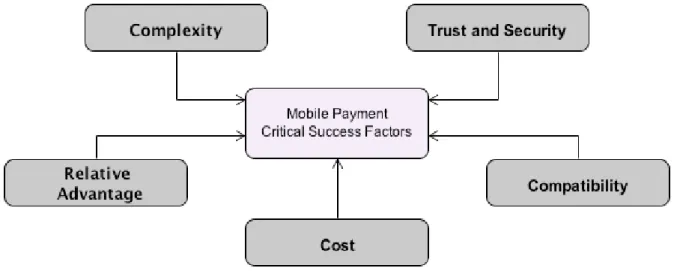
Compatibility is “the extent to which [NFC-enabled mobile payments are] consistent with the existing values, past experiences, and [mobile payments] needs of potential adopters,” Rogers (1983, p. 223). As long as banks are the issuers of the chips that enable the payment function, they control the entire payment process and “own” the customer (essential from a Customer Relationship Management perspective).
Critical Success Factors
- Complexity
- Trust and Security
- Relative Advantage
- Cost
- Regulations
In this section of the research, several of these NFC-based mobile payment trials will be reviewed. The stakeholders took advantage of the dual-chip approach for the NFC-enabled mobile payment solution that involved MasterCard action.
NFC Stakeholders
- Consumers
- Mobile Network Operator
- Financial Institutions
It should also be noted that Philips was one of the organizations that first promoted NFC technology. Some of the local financial institutions that offer MasterCard products include ABSA Bank, Nedbank and Standard Bank.
Benefits and Challenges
One interviewee described it as the "nightmare scenario" and the only thing they could imagine derailing the growth of mobile financial services. We discuss this in the next section as one of the four most important uncertainties for the next decade.
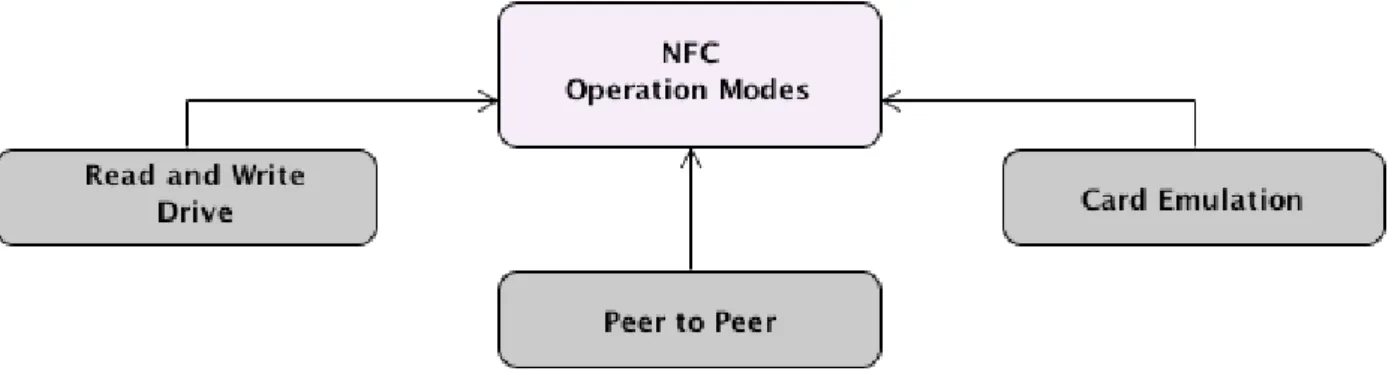
NFC enabled Mobile Payments
The speed and convenience of mobile payments with NFC can generate additional revenue through more transactions. NFC service providers may also charge consumers for the ability to make NFC-based mobile payments, creating an alternative source of revenue.
PAYMENT USE, COSTS, AND PRICING
- Payment Use
- Payment Costs
The NFC Forum's efforts have made it possible for the highly regulated Western world to adopt contactless mobile payment solutions through the standardization of NFC technology. Using OTA (over the air) capabilities, mobile payment services can be turned on in minutes instead of the days associated with physical payment solutions such as credit cards.
Payment transactions
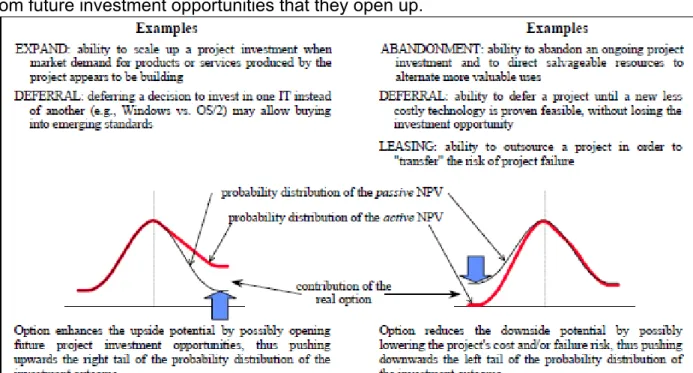
Next, two of the real options used here in the analysis are discussed: the postponement (delay) option and the expansion option. Only with an appropriate modification that includes an estimate of the investor's (management's) utility function can DTA be adequately applied to projects involving options (see [Smith and Nau, 1995] for details).
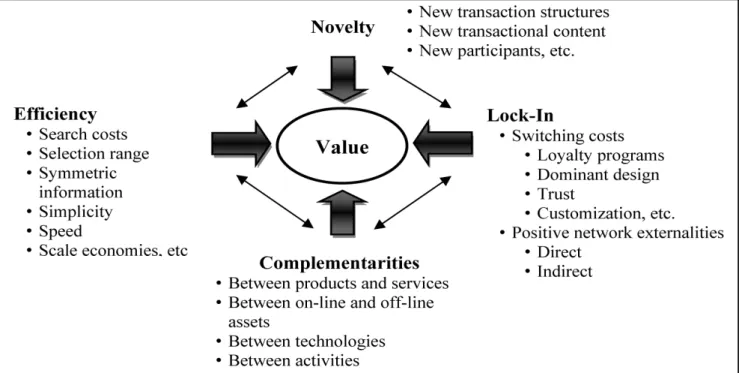
Value Creation in Virtual Transactions
- Eficiency
- Complementarities
- Lock-in
- Novelty
Pay-By-Mobile Stakeholders
Nav Bains (2008, p. 14), director of the Pay-By-Mobile project, introduces a new role of Trusted Service Manager (TSM) that is unique to a single-chip approach to NFC-enabled mobile payments. Some other mobile phone manufacturers that have produced NFC-enabled mobile devices include Sagem and Motorola.
Pay-By-Mobile Business Model
Another important stakeholder in the single-chip approach to NFC mobile payments is the merchant. This means that TSM will have a business relationship with both the MNO and the card issuing banks.
Benefits and challenges
However, banks would no longer be involved in the consumer-to-merchant or consumer-to-consumer side of the payment. To be sure, the consequences of the financial crisis that emerged from the United States and the United Kingdom have been severe in many countries.
North America
- Canada
- USA
During the trial, Canadian consumers were already able to use the PayPass solution at establishments such as Rabba Fine Foods, Cineplex Odeon and Petro-Canada. To reward the use of an NFC-enabled mobile payment solution, MasterCard used the same rewards and loyalty programs as traditional MasterCard products.
Europe
- United Kingdom
- Switzerland
In Switzerland, Visa Europe conducted an NFC-enabled mobile payment trial with the help of Credit Suisse, PostFinance, Swisscard, Swisscom and Telekurs. The unique aspect of this trial was the use of the partners' employees as the participants.
Asia
- Malaysia
- Japan
- Philippines
First, 85% of participants felt that the model and brand of NFC-enabled mobile device offered would influence their decision to adopt NFC-enabled mobile payment, and second, the importance of speed and persuasiveness outweighed the importance of security. The NFC-enabled SIM was developed with the help of one of the founders of the NFC Forum, NXP.
Middle East
- UAE
Both major mobile network providers in the Philippines, SMART and Globe, have developed large-scale m-banking offerings. According to representatives from Dubai First, the purpose of the trial was to examine how participants used the new mobile payment technology.
Africa
Its value corresponds to the active NPV, equal to the passive NPV plus the value of the deferral flexibility. In the m-payments sector, there has already been one intervention by the competition authorities to ensure open access.

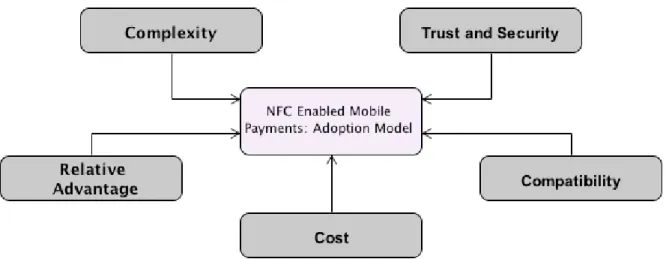
Adoption Model
- Complexity
- Trust and security
- Relative advantage
- Cost
- Compatibility
Mobile payments aim to increase convenience for consumers and the same applies to NFC-based mobile payments. NFC-based mobile payments can offer cost savings, but due to the different stakeholders, the savings will depend on the business model adopted.
Problem Statement
- Consumer Perceptions
- Complexity Characteristics
- Trust and Security Characteristics
- Relative Advantage Characteristics
- Compatibility Characteristics
The consumer survey also found that only about 4% of the population would not let their trust and security concerns influence their decision to adopt NFC-enabled mobile payments. Subject matter experts provided some of the trust and security concerns they predict will cause problems for NFC-enabled mobile payments.
Cooperation Models for the Development of Mobile Payment Solutions
- Key inputs of a mobile phone solution
This failure is perhaps one of the biggest obstacles to the growth of m-banking, at least of the transformational kind. The NPV is the difference between the present value of the future cash flows and the initial investment cost.
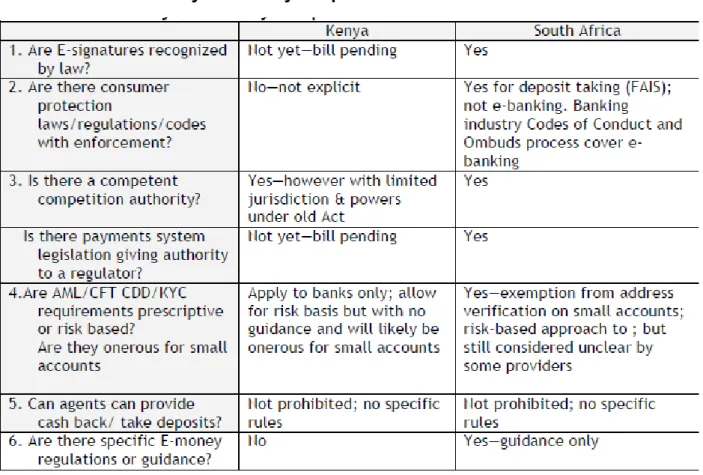
Issues for ICT Policy makers: are e-signatures recognized legally?
It is therefore necessary to give electronic transactions at least a status equivalent to that obtained by physical signature. Establishing e-signature legality is therefore a necessity to grow the m-payments/m-banking market at scale.
Issues for Financial Regulators
The soundness of the banking system and the national payment system are central to the mandate of most financial regulators. In effect, these arrangements amount to outsourcing the front-end of deposit-taking activities.
Issues for Competition regulators
Although there may be higher risks involved, international AML-CFT frameworks do not rule this out and suggest using a risk-based approach. However, if national regulators do not provide guidance on what are acceptable risk-based approaches, banks may be vulnerable to subsequent retaliation; and this can encourage unnecessary conservatism.
Issues for Telco regulators
Bank accounts are arguably subject to the same stickiness as cell phone numbers, but bank number portability has yet to be required. Models that involve special downloads for the SIM card may restrict the customer to the SIM issuing network.
Developed country financial regulator approaches
The possibility of the central bank losing control over the money supply as a result of widespread e-money issuance. The interaction of the new payment systems with existing bank payment systems in order to avoid the transfer of systemic risk.
Monitoring
As long as e-money is issued in exchange for central bank money, and until e-money is used on a large scale, crowding out the demand for central bank money, this concern is usually exaggerated. After all, issuers such as telecommunications companies do not create e-money, but rather exchange it for bank money.
Beyond monitoring: facilitation & co-ordination?
In addition, new payment systems may cause changes in usage patterns that may affect the viability of existing payment platforms.
Beyond monitoring: new legislation?
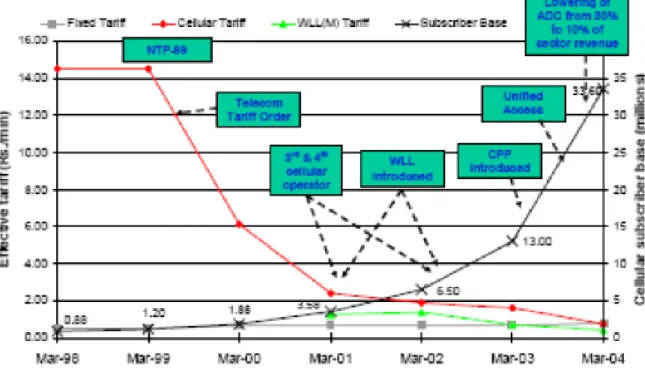
For example, the OECD paper on "Regulatory reform as a tool for bridging the digital divide" shows how the timing of several facilitative actions by the Indian telecom regulator has led to a sharp fall in the effective mobile rate since 1999, and a related showing huge increase in Indian mobile subscribers since 2001.
Other Regulatory Issues
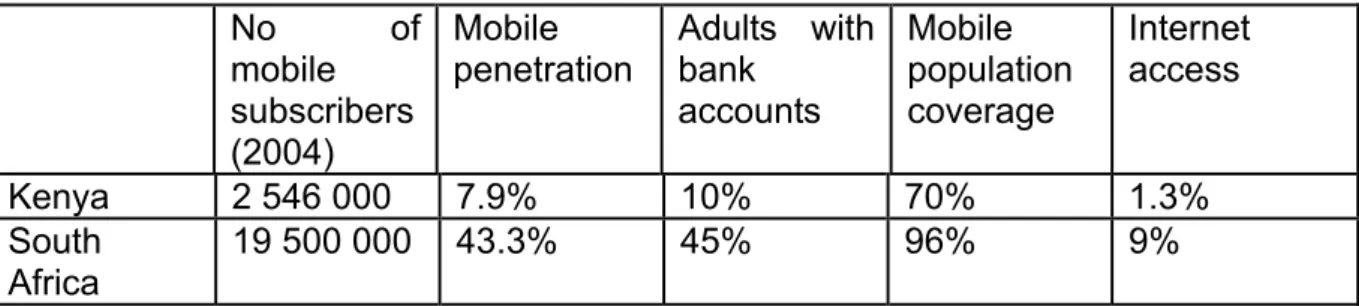
We will then examine specific issues arising in the legal and policy environment in the two pilot countries—Kenya and South Africa; and barriers reported by providers there.
Legal & policy environment
In both countries, high-level strategy and policy documents have been developed and released for the development of the National Payment Systems. They were chosen for this project because of the new m-banking models that emerged in each.
Provider obstacles reported
The company can capture the value of the operational project through an immediate investment, V - X, or retain the investment opportunity. Depending on the size of these two tendencies, the value of the exercised option at time t, Ct, can be higher or lower.
The Enabling Environment
Financial stability: That the safety and soundness of the banking and payment system is not compromised; Financial Integrity: That the financial system is not compromised by misuse for criminal or terrorist financing purposes.
Industry Growth Trajectories
Economic efficiency: That the efficiency of the financial system as a payment mechanism and mediation system is maximized and in turn contributes to overall economic growth;. Mobile banking offers the prospect of increasing efficiency of the payment system; and possibly expanding access to financial services.
Openness and certainty at the early stage
Therefore, enabling a new market can be understood as a movement in the direction of the arrows from the starting point, towards greater openness and security. To be sure, openness and security remain important even in later stages of market development, but are essential if a market is to develop at all.
Additive and transformational approaches to banking
However, in the absence of other fast, secure and cheap ways to transfer money, it is at least plausible that airtime transfer could take on some of the characteristics of money transfer or remittances. In addition, sales or value added tax is often charged on the face value of the airtime.
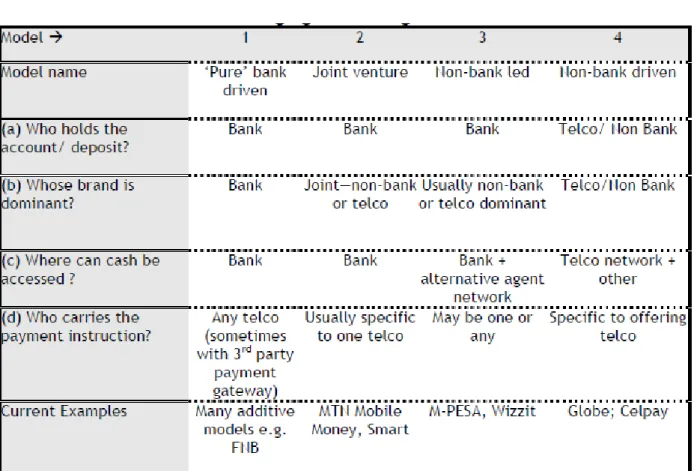
Categorization of m-banking models
It is therefore much more likely that airtime can function as a de facto e-money in developing countries. These African m-payment providers are all at a relatively early stage; a number of different models, platforms and approaches are being tested.
Categorization of m-banking models
Traditional DCF analysis values an investment in present values, assuming that future cash flows are known and discounted by a risk-adjusted factor, eg the firm's weighted average cost of capital (WACC) (Damodaran, 2002). The time the company can wait is the time of maturity T, and the risk of the project is reflected in the volatility (standard deviation) of the assets.
Financial options
If K is the strike price and ST is the final price of the underlying asset, the payoff of a long position in a European call option is: maximum (ST - K, 0). The payoff to the holder of a long position in a European put option is maximum (K - ST, 0).
Real options
- The Black– Scholes model
The Black-Scholes closed-loop solution for European options can be used as an approximation. It is not uncommon to use the Black-Scholes formula as an approximation in real option valuations.

Real options in telecommunications
Pricing Real m-banking Investment Options
- Value of Managerial Flexibility and Project Evaluation Methods
- Option Pricing Concepts Applied to Real Deferral Options
- Option-Based Decision Rule for Investment Timing
Given the similarity between a deferral option and a financial option, we should be able to apply the Black-Scholes model to real IT options. However, we will later see a specific variant of the Black-Scholes model, which can be directly used with the above decision rule.
A Planning Retrospective for m-banking
- Moblie operators are starting to offer m-banking
- Settlement with other Telcos
Consequently, the following decision rule leads to the optimal investment strategy given today's information set. Of course, this decision rule must be reapplied each time new information arrives during the grace period to see how the optimal investment strategy might change based on the new information.
M-Payments and competition in reatail payments
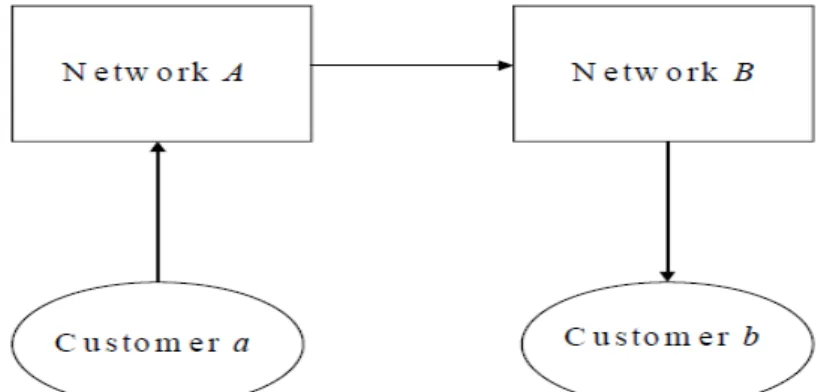
The Wholesale (Telco to Telco) side: Growing Interdepedence
Some phone companies will be more active on the buying side, others on the issuing side. Telephone companies with a large merchant base (such as S1 in Figure 17) will receive net payments in the settlement process, while telephone companies with a small merchant base will be net payers.
The bank – dominated model
Especially if an increasing proportion of the income goes to risk sharing, the telecommunications companies will also have to consider clearing and settlement more carefully. However, a bank-dominated set-up would leave the competitive situation in the payment system roughly as it is.
The emergence of new payment service providers
As recent investigations into the payment system found evidence of anti-competitive practices, this would be a clear disadvantage. It should also be remembered that banks have so far been slow to come up with effective solutions for cross-border retail payments, and it is not clear that further involvement in m-payments would change this.
The role of network effects
- Case Study Movilpago
The growth of the mobile Internet may lead to the rise of a new generation of mobile banking providers, raising important questions about the risks to consumers, as well as the future shape of the competitive landscape, one of the uncertainties discussed in the next section. 34; The Economics of Mobile Payments: Understanding Stakeholder Issues for Emerging Financial Technology, Research, and E-Commerce Applications.".
The future of NFC and mobile banking
On the supply side, governments will shape the scope of opportunity through their supply-side policies, either by using state-owned banks (as in Brazil), moral suasion and setting rate caps (as in India), or by bidding in general. (as in South Africa). SIM-resident applications can provide end-to-end security for messages, but require the cooperation of the MNO.
Four uncertainties
However, there is also reason to believe that it is much weaker with mobile banking and the poor. The ability to place cash close to consumers in many distributed service points (agents) is a defining feature of mobile banking.