The role of the board of directors and the audit committee in constraining earnings management: analysis of Russian firms. To identify board of directors characteristics related to the level of earnings management for Russian firms;
Earnings management and corporate governance: theoretical review
Definition of earnings management
According to neutral accounting, managers do not intend to influence the decision-making process of external stakeholders, so earnings management does not occur. However, while fraudulent accounting practices are usually investigated by external auditors and government bodies, researchers focus more on legal earnings management.
Earnings management strategies and methods
Accrual-based earnings management (AEM) is achieved by changing the accounting methods or estimates used in presenting a particular transaction in the financial statements (Zang 2012). In contrast, real earnings management (REM) involves changing the timing or structure of operating, investment, or financial decisions in an attempt to influence the results of the accounting system (Gunny 2010).
Consequences of earnings management
One of the most researched areas of earnings management consequences is the post-IPO stock underperformance for the companies involved in earnings manipulations. Feroz, Park and Pastena (1991) showed in their paper that the first announcement about a disclosed fact of earnings management leads on average to the drop of 13% in the share price of the company.
Restraining earnings management: the role of the board of directors and its audit
Davidson, Goodwin-Stewart and Kent (2005) outline two functions of corporate governance mechanisms in relation to the financial reporting process. In most companies, the audit committee of the board of directors is formed to oversee the preparation of the financial statements.
Board and audit committee composition and earnings management. Hypotheses
The presence of the audit committee can theoretically affect the financial reporting process in two ways (Piot and Janin 2007). Thus, it is reasonable to theorize that the presence of the audit committee may help curb earnings management. As with the board of directors, independence is also an important characteristic of the audit committee.
There are many previous studies that analyzed the relationship between the presence of the independent directors on the board and in the audit committee and the level of earnings management. The empirical evidence for the relationship between legal earnings management and board and audit committee size is mixed. The evidence for the activity of the board and the audit committee is thus mixed.
Another characteristic of the audit committee is the presence of members who possess financial expertise. This evidence supports the idea that the presence of financial experts on the audit committee can contribute to the quality of financial supervision.
Literature review conclusion and research gap
Bowen, Rajgopal, and Venkatachalam (2008) presented some of the first evidence that executive busyness is positively related to the level of earnings management (the study was conducted for the US market). For example, the use of earnings management can result in a subsequent decline in market capitalization, which harms shareholders. An important characteristic of the board of directors and the audit committee is the independence of its members: independent directors can exercise more objective supervision as they are not psychologically or economically dependent on management.
The level of activity of the board of directors or the audit committee can also play a role in the quality of supervision. Even for the US, several existing studies provide conflicting evidence on the relationship between the level of earnings management and the independence of both the board and the audit committee. So far, no research has examined the relationship between board and audit committee characteristics and legal earnings management in Russian companies.
How does the composition of the board (eg, presence of the independent directors on board) affect the level of accrual-based earnings management of Russian firms. How does the presence and composition of the audit committee (eg, its size) affect the level of accrual-based earnings management of Russian firms.
Methodology and empirical results
Sample
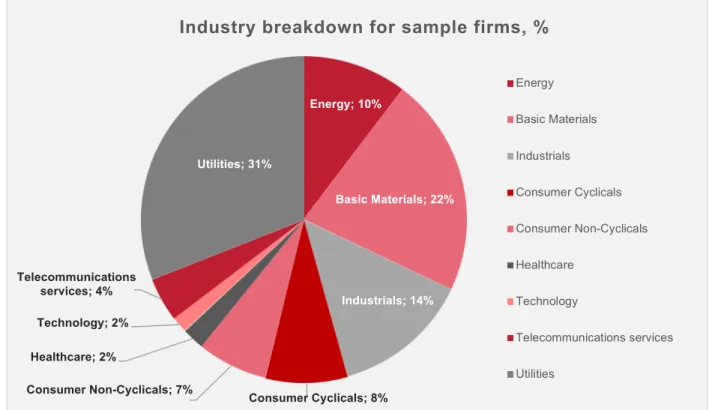
The industry breakdown of the sample is shown in Figure 2 (Thomson Reuters Business Classification was used). Utility companies represent the largest proportion of companies in the sample, accounting for 31% of all companies. This category mainly consists of the companies involved in the production, transmission and distribution of electricity.
Akron (agricultural chemicals) or MMK (iron and steel producer) are examples of Basic Materials companies in the sample. The industrial sector accounts for 14% of the final sample and includes companies that manufacture and/or distribute capital goods, for example airlines, construction companies or manufacturers of industrial machinery. Aeroflot, an airline, or NMTP (Novorossiysk Commercial Sea Port), a port operator, are representatives of the industrial sector.
One of the most important sectors of the Russian economy, energy, is represented by companies that represent a tenth of the sample. The rest of the sample consists of consumer cyclicals, consumer non-cyclicals, telecommunications, technology and healthcare companies.
Methodology
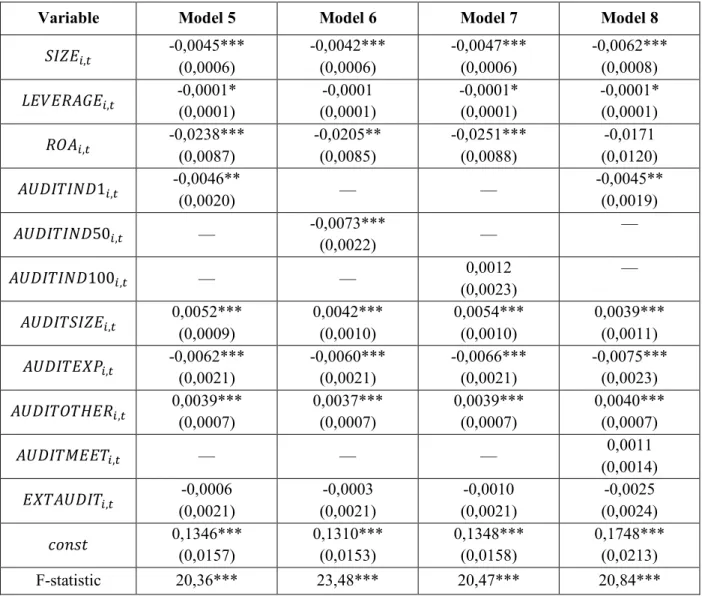
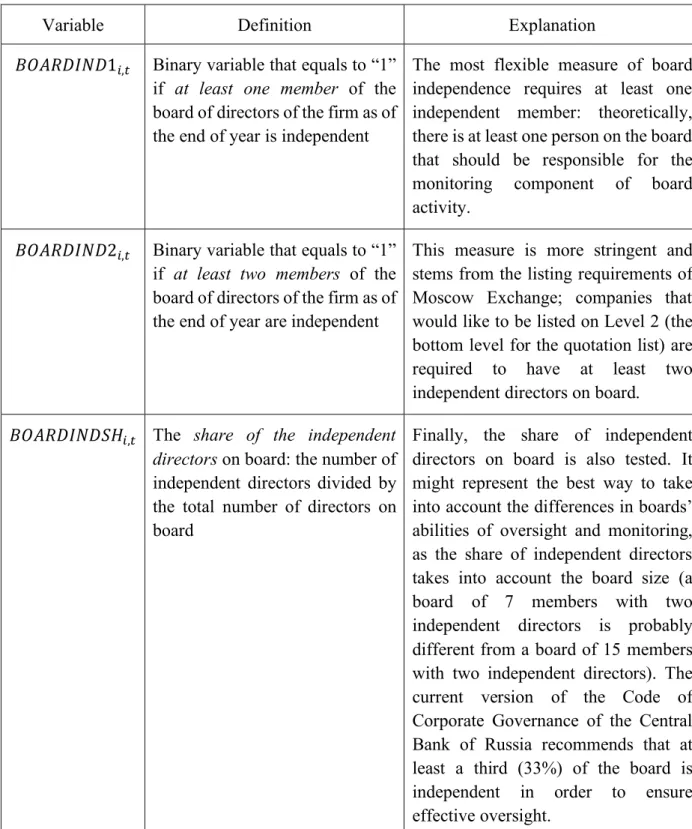
Another board characteristic analyzed in the study is board size. As with the board of directors, one of the key characteristics of the audit committee is the independence of its members. For example, the results of Klein (2002) show that the most significant relationship between audit committee independence and earnings management is observed when less than a majority (50%) of the audit committee is not independent.
In line with existing research, this study also deals with the financial knowledge of audit committee members ('RNS!Kj2,.). Similar to the board of directors model, the audit committee model has the variable of outside directorship of the members. The average number of other directorates of audit committee members is used to measure occupancy.
The annual number of meetings as a measure of the audit committee activity has also previously been tested in many studies (Xie, Davidson and DaDalt 2003; Bedard, Chtourou and Courteau 2004; Ghosh, Marra and Moon 2010). RNS!S0N100,.is the binary variable that equals "1" if all the members of the audit committee of firm i are independent as of the end of year t;.
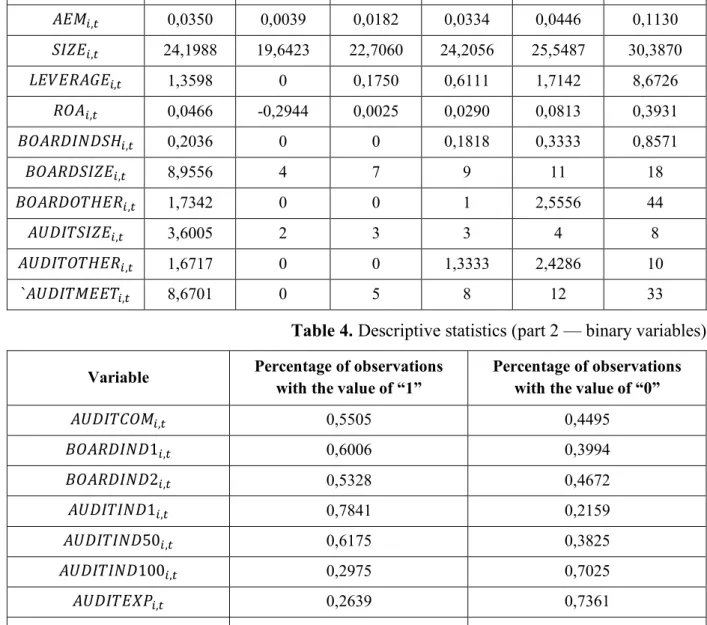
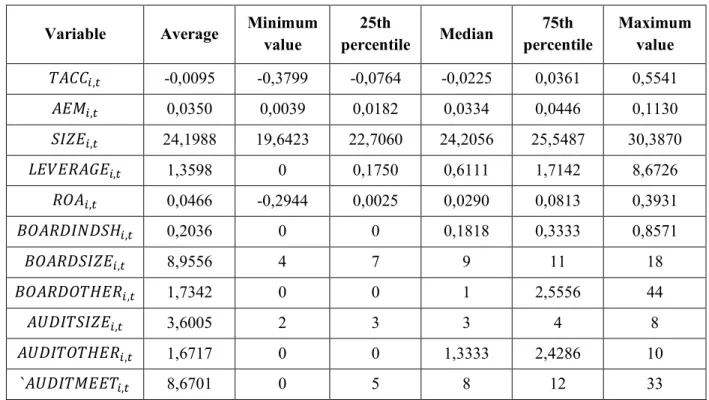
Descriptive statistics
The study of any phenomenon related to earnings management is highly dependent on the quality of discretionary income estimation. To test the robustness of the findings, the same analysis was conducted using not the widely used Jones model (which was used for the main analysis in this study), but its modification offered in (Dechow, Sloan, and Sweeney 1995) . The modified version of the Jones model was also applied in several previous articles analyzing the relationship between board and audit committee characteristics and the level of earnings management (e.g.
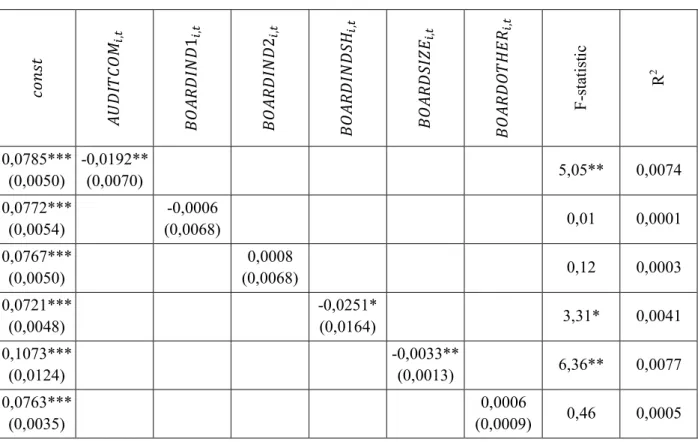
Regarding the corporate governance variables, the average proportion of independent directors on the boards of companies in the sample is slightly higher than 20%. At the same time, 60% of observations include at least one independent director (\;'XNS0N1,.). It is not true that the vast majority of analyzed companies already have an established audit committee.
As mentioned earlier, the absence of an audit committee in 45% of cases could be related to the fact that some companies at the third level of the Moscow Stock Exchange are not obliged to establish this committee. The average size of an audit committee ('RNS!ISVK,.) is 3; the largest committee in the sample has 8 members.
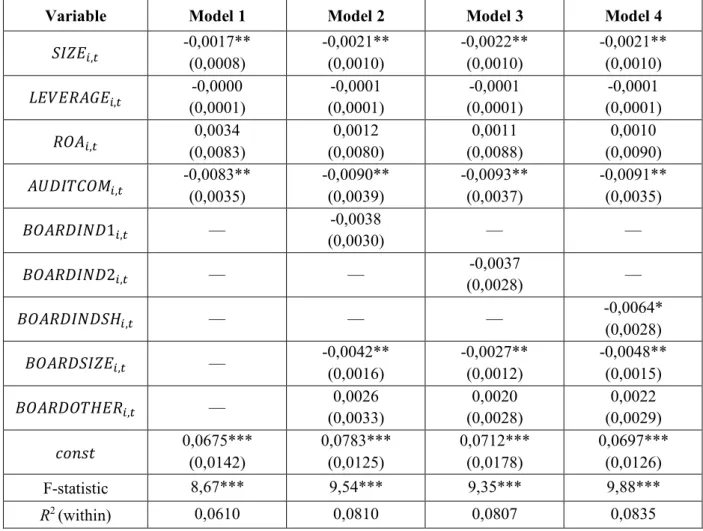
Empirical results
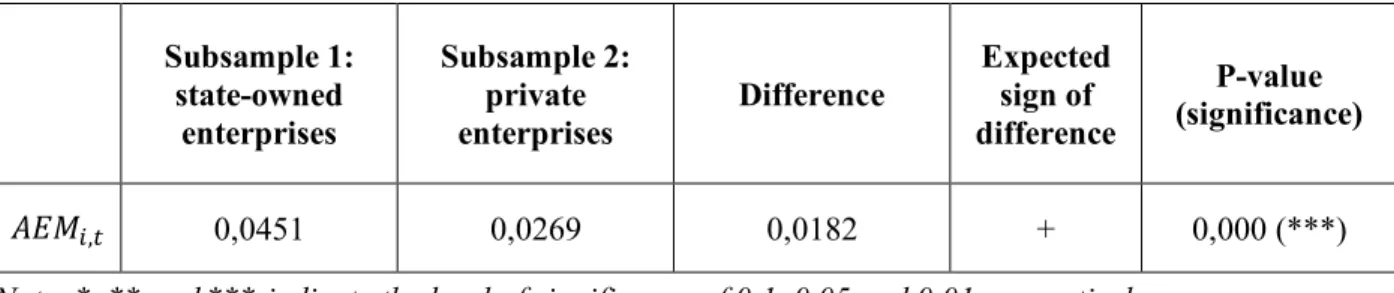
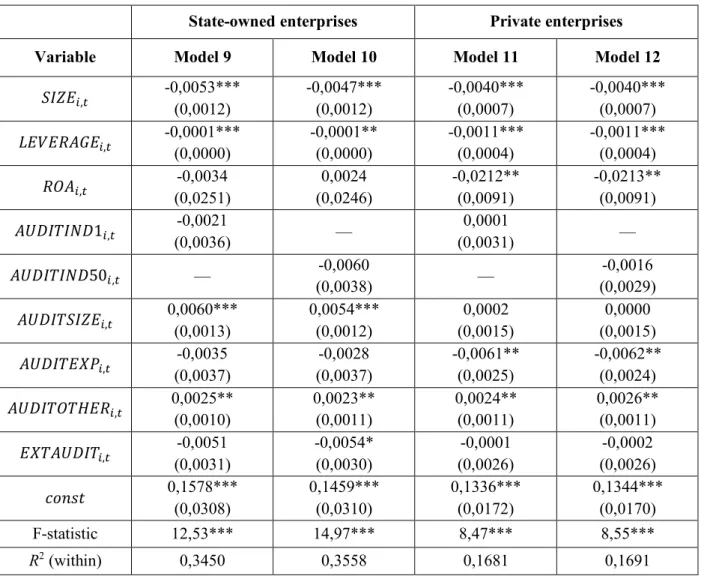
The estimation of the models is shown in Table 7; these models only include observations where the audit committee is present (models 5-7 are based on 408 observations). The correlation matrix for all variables used in the models for audit committee characteristics is shown in Exhibit 5. Model specifications 5-7 differ due to the three different approaches to measuring audit committee independence.
Another interesting result is the significant positive relationship between the level of earnings management and the size of the audit committee ('RNS!ISVK,.). Interestingly, the relationship between earnings management and audit committee size is different from the relationship between earnings management and board size (for which the relationship is negative). The first notable difference between state-owned and private companies concerns the size of the audit committee ('RNS!ISVK,.).
The association is positive: the larger the selection, the higher the level of earnings management (all other things being equal). Finally, the effect of the degree of busyness among audit committee members remains significant and positive in both subsamples.
Results discussion
Finally, the study found that there was a significant positive relationship between the number of other directorships held by audit committee members and the level of earnings management. For Russian companies, there is a negative relationship between the annual number of meetings of audit committee members and the level of earnings management. For Russian companies, there is a positive relationship between the number of other directorships of audit committee members and the level of earnings management.
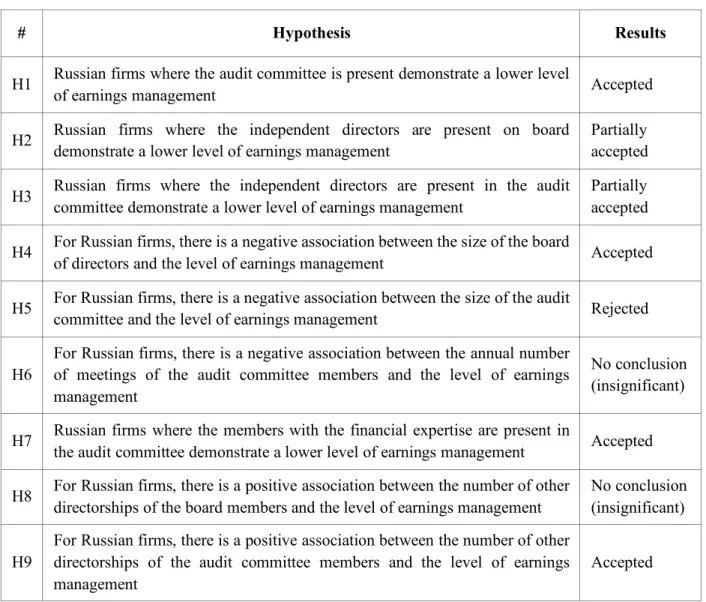
The purpose of this thesis was to investigate the influence of the characteristics of the board of directors and the audit committee on the extent of earnings management of Russian companies. The aim of the thesis was to determine the connection between the structure of the board of directors and the presence and composition of the audit committee and profit management. The first set of models tested possible associations between board attributes and the extent of earnings management of Russian firms.
The Russian firms where an audit committee is present also showed a lower level of earnings management. Some recent research in the area has recently focused on softer factors that may influence the relationship between earnings management and audit committee composition.
List of companies in the sample
Jones model
Modified Jones model
Correlation matrix: board of directors models
Correlation matrix: audit committee models
Variance inflation factors: board of directors models
Variance inflation factors: audit committee models