Description of the purpose, tasks and main results The purpose of the research is to investigate the relationship between the level of compliance with the best practices of corporate governance and the firm market value of Russian public companies. The result of this study is as follows: there is a positive relationship between the level of compliance with the best corporate governance practices and the market value of the company measured as Tobin's Q. The study is devoted to investigating the relationship between the level of compliance with corporate governance practices and the sustainable market value of Russian public companies.
The aim of the study is therefore to investigate the relationship between the level of compliance with best corporate governance practices and the market value of Russian listed companies. Based on the research objective, it is possible to formulate the research question: “Is there any relationship between the degree of compliance with best corporate governance practices and the market value of Russian listed companies?”. Conducting the empirical analysis aimed at identifying the relationship between the level of compliance with best corporate governance practices and business value.
In addition, the chapter presents the literature review of the most important sources that study the relationship between different mechanisms of corporate governance and the company's market value. 8 As a result of the panel data regression analysis, a strong positive relationship was revealed between the level of compliance with the best corporate governance practices and the value of the company.
Best corporate governance practices and company value
Corporate governance
- Agency problem and corporate governance mechanisms
- Corporate governance in Russia
- Main principles of the Code of Corporate Governance
The board of directors (or supervisory board) is a collegiate body that performs the general management of the company and acts according to the authorizations provided by law and the statute (On joint-stock companies, 1995). Members of the collective executive body may not hold more than 25% of the seats in the board of directors. 13 that the role and importance of the board of directors and, above all, of the independent directors have greatly increased.
Another study focuses on the identification of main trends and priorities in board work. As stated in the Act on limited liability companies, decisions on remuneration for the board of directors are made by the general meeting. This chapter is the broadest in the code, which emphasizes the board's role in corporate governance.
Rights and responsibilities of the board will be specified in internal documents of the company. System of remuneration for the board members, executive bodies and other key managers of the company.
Corporate governance and company value: literature review
Academics often consider the board of directors as the most important mechanism of corporate governance responsible for monitoring. Let us consider the question by applying the agency theory, which states that the board's core task is to monitor top management, as there may be potential conflicts between managers and owners. 24 diversified and highly leveraged companies the correlation between board size and Tobin's Q is positive, in the opposite case the relationship is negative.
The study among the sample of Russian companies (Berezinets, Ilina, Cherkasskaya, 2013) shows that there is a non-linear relationship between the size of the board and Tobin's Q, and reaches the same finding as in (Coles, Daniel, Naveen , 2008). The authors interpret the results in the following way: the market considers small boards to be very efficient from the perspective of monitoring job performance, while companies with large boards are efficient from the perspective of resource dependence theory, since how more members make up the board, the more access it has to external resources. Therefore, the relationship between board size and firm value for Russian companies is U-shaped.
The study “Corporate Governance, Board Diversity, and Firm Value” examines whether board diversity is associated with improved company value for Fortune 1000 publicly traded firms (Carter, Simkins, Simpson, 2003). By the term diversity, researchers understand the gender, cultural and racial composition of the board. In this case the gender diversity of the board can provide the company with a competitive advantage.
Compared to male board members, women are more responsible in terms of participation in board meetings; they often become members of committees and fulfill the monitoring function (Adams, Ferreira, 2009). The independence of the board is determined by the individual characteristics of the company, such as size, age and the number of business segments in which the company operates. The article (Rosenstein, Wyatt, 1990) notes that if the company with a significant number of independent directors on the board if another independent director is added, its value will increase.
Because management remuneration data are usually not disclosed, far fewer research articles are devoted to this mechanism of investigating corporate governance than articles related to the board of directors. Opponents of the practice of rewarding CEOs argue that the board of directors determines CEO compensation in such a way that it is not always aimed at maximizing shareholder value, as it is influenced by the CEO (Core, Holthausen, Larcker, 1999). In summary, there are a decent number of articles examining various mechanisms of corporate governance and their impact on firm performance and value, but the board of directors is particularly widely covered.
Corporate governance index construction
Openness of information is one of the main characteristics of superior corporate governance that helps to solve the information asymmetry problem. To this end, researchers create corporate governance indices that characterize the quality of corporate governance in general. Since the level of compliance with the Code is measured by the index of corporate governance, it is necessary to pay special attention to the articles where different indices of corporate governance are constructed and to study the existing methods of their construction.
The authors of one of the most cited papers devoted to the corporate governance index construction (Gompers, Ishii, Metrick, 2003) use 24 governance rules divided into five thematic groups and assign points according to the following rule: for each firm they add one to point for each provision that weakens shareholder rights. Consequently, companies with a higher corporate governance index are referred to as having the "weakest shareholder rights". The paper (Black, Love, Rachinsky, 2006) considers six corporate governance indices from five different providers: two major investment banks, one rating agency and two Russian non-profit organizations.
The study (Klapper, Love, 2003) refers to the report of Credit Lyonnais Securities Asia (CLSA), where the index of corporate governance ranking for 495 companies in 25 countries was calculated. The authors estimated the percentage of positively answered questions for each category and calculated the governance index as the average of the six categories with the social awareness category excluded. As stated in the paper, social awareness is not relevant to corporate governance.
The authors construct a Korean Corporate Governance Index (KCGI) based on the survey by the Korean Stock Exchange using 38 elements. Corporate governance characteristics are provided by Governance Metrics International (GMI) and subcategorized into the following groups: board accountability, financial disclosure and internal control, shareholder rights, compensation, market for control and corporate behavior. In other words, the authors give one point for each characteristic a company has in place and zero otherwise.
As a result of the PCA application, the authors set the index equal to the first principal component, which explains 16.4% of the total variance. The 31 approach was also used by Larcker, who claims that PCA-based corporate governance index has less measurement error than indices with equal or subjectively assigned weights of components (Larcker, Richardson, Tuna, 2007). Empirical investigation of the relationship between the level of adherence to best corporate governance practices and firm value.
Empirical study of the relationship between the level of compliance with best
Hypothesis statement and methodology
- Model description
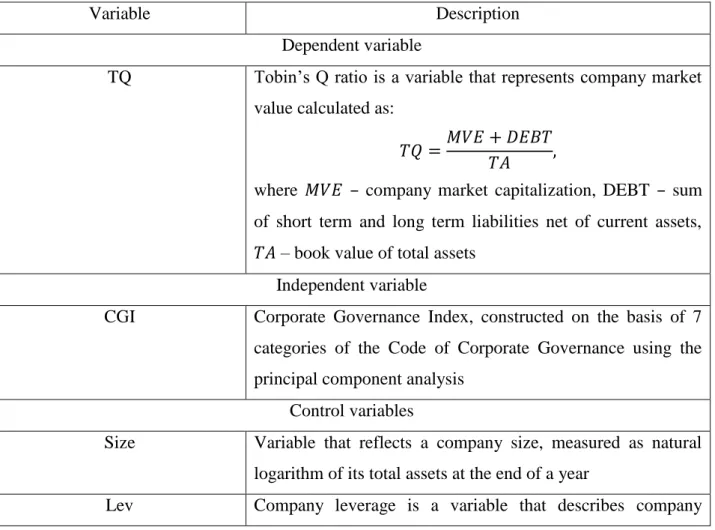
- Variables description
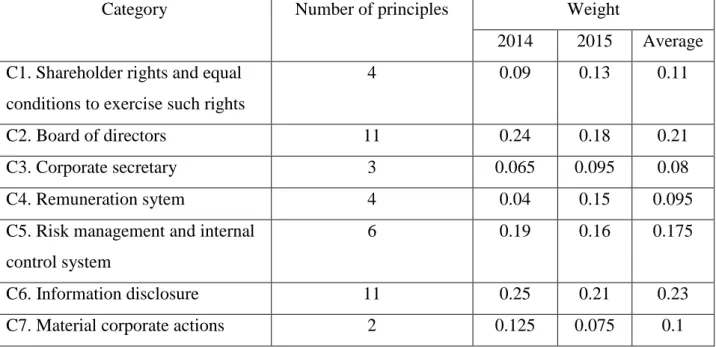
- Corporate Governance Index (CGI) construction
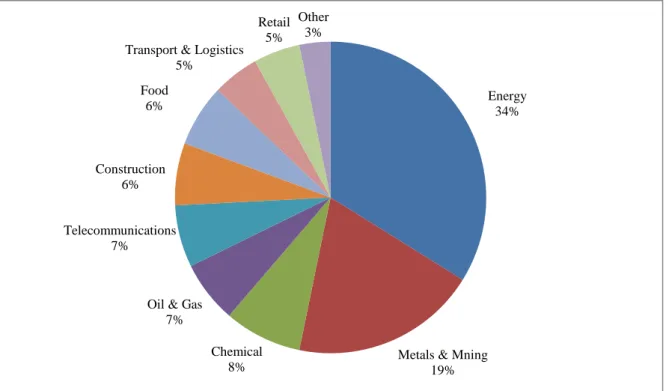
- Sample description
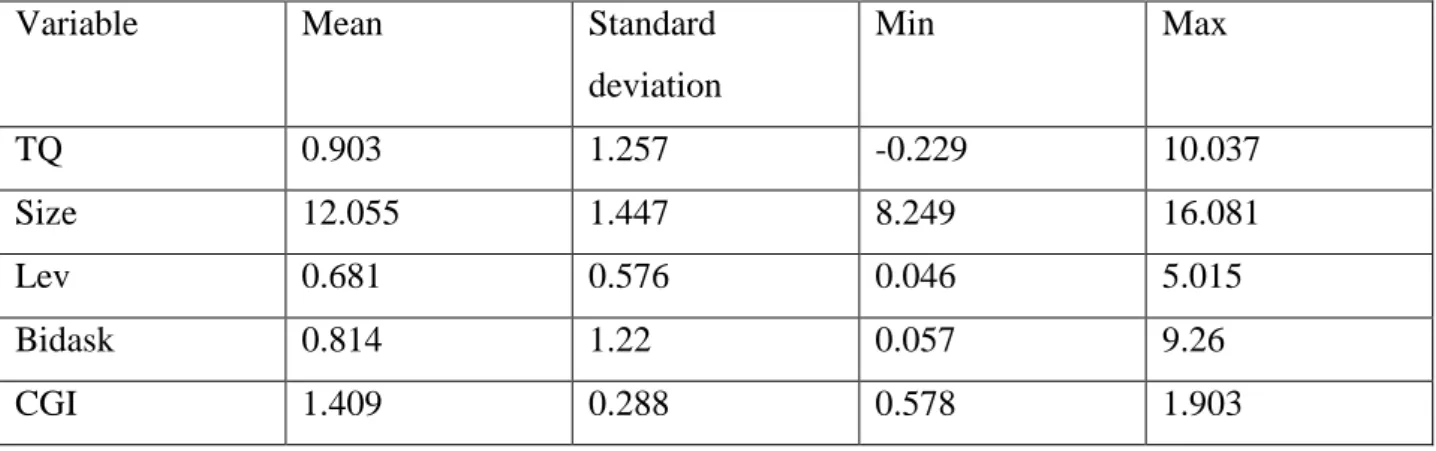
- Descriptive statistics
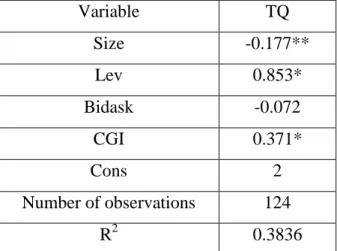
- Results of regression analysis
67.7% of companies specify the payments, benefits and privileges available to board and executive body members and other key managers in the company's internal regulations. According to the Code, the board of directors must determine the principles and approaches of risk management and internal control of the company. According to the data collected, 67.7% of companies adopted an internal regulation that defines the company's information policy in accordance with the Code.
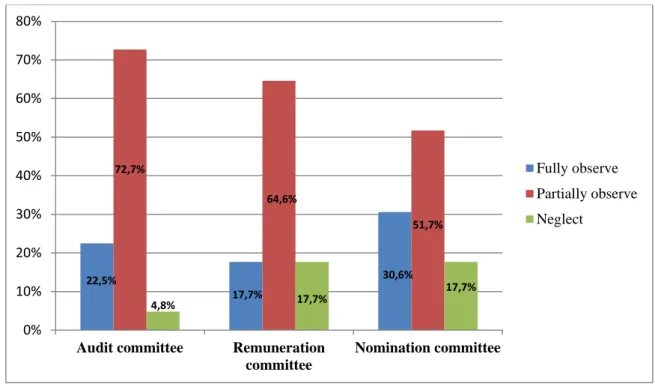
In addition, compliance with the Code will contribute to the increased confidence that shareholders and investors place in the company. Shareholders must be given equal and fair opportunities to receive a share of the company's profits in the form of dividends. The Board should form committees to preview key matters related to the company's operations.
His responsibilities must be defined in the company's procedures and comply with the recommendations of the Code of Management of Public Joint Stock Companies. Members of the board and executive bodies and other key managers must be rewarded in accordance with company rules. Payments, benefits and privileges available to members of the board and executive bodies and other key executives must be specified in the company's internal regulations.
The company must not pay any cash compensation to the Board members other than their fixed annual compensation. The company must establish an effective risk management and internal control system to reasonably guarantee the fulfillment of the company's objectives. The Board has defined the Company's risk management and internal control principles and approaches.
The company should establish an independent internal audit unit that functionally reports to the board. The company should approve an internal regulation defining its information policy as recommended by the Corporate Governance Code. Control over correct publication and compliance with the information policy should be exercised by the company's board of directors.
The company must disclose annual and interannual (half-yearly) consolidated or individual financial statements prepared in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). The company should disclose information on its capital structure in accordance with the recommendations of the Code of Management of Public Joint Stock Companies.