Introduction
Objectives
Results
Erwinia amylovora-induced changes in host
Several authors have reported the accumulation of different PR transcripts after Erwinia amylovora attack (Venisse et al., 2002; Bonasera et al., 2006; Norelli et al., 2009). SA is synthesized in plants either via isochorismate synthase (Wildermuth et al., 2001) or through the shikimate-phenylpropanoid pathway. However, Erwinia was shown to delay the expression of phenylpropanoid genes (Venisse et al., 2002) to overcome plant defenses.
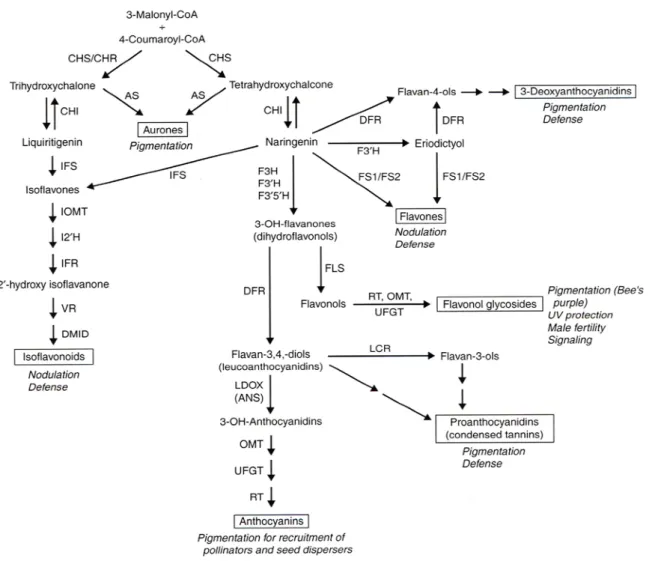
It is assumed that the phenylpropanoid pathway leads to the synthesis of defense-related compounds such as lignin and flavonoid phytoalexins as well as SA (Dixon et al., 2002) The importance of the key enzyme of this pathway, the. From three pools of 5 in vitro grown plants each (leaves and stems) the total RNA was isolated according to (Chang et al., 1993). The expression levels of the gene for PR1 as a potential SA marker (Uknes et al. 1993) were monitored in apple plants.
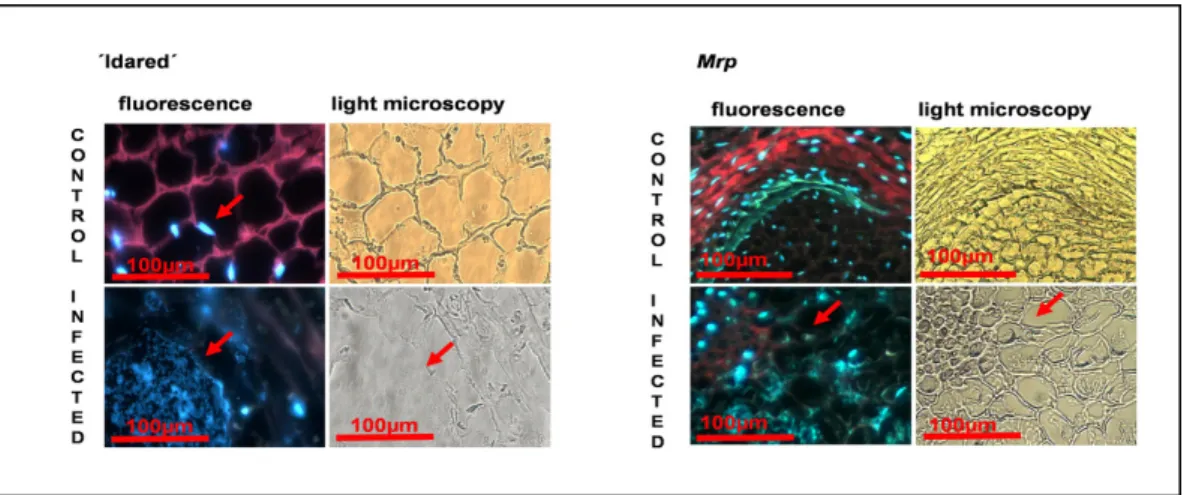
Genes related to drought stress, such as aquaporins and dehydrins, were affected in apple trees of the variety ´Gale Gala´ infected with fire blight (Norelli et al., 2009). However, high levels of SA can negatively regulate SA synthesis (Ogawa et al., 2007), which could explain the apparent. Nevertheless, higher SA levels in Mrp plants may provide an advantage against potential bacterial invasion compared to the susceptible 'Idared' (Yang et al., 2004).
Levels of SA increased with Erwinia infection in the susceptible plants indicating the activation of defense cascade (Verberne et al., 2000). The higher levels of SA molecules in Erwinia-infected apple plants coincide with the increased transcription levels of the gene for PR-1 protein considered as SA marker (Uknes et al., 1993). Similar behavior of this gene in fire blight-infected apple trees of 'Gale Gala' was reported by Norelli et al. 2009) in disagreement with Bonasera et al.
Consistent with the observations of others (Venisse et al., 2002), Erwinia induced suppression of most of the phenylpropanoid pathway genes studied at 1-2 dpi in both apple species. Suppression of phenylpropanoid production is thought to maintain cell wall permeability, which is a necessary condition for nutrient enrichment of the apoplastic environment for bacteria (Truman et al., 2006). This fact coincides with the increased number of hydroxycinnamate derivatives detected (Pontais et al., 2008) in blight-infected apples and may support PAL-directed SA synthesis in blight-infected apple.
An exception was elevated F3GT downstream activity in infected 'Idared' that could lead to higher levels of anthocyanins (anthocyanidin 3-O-glucoside) and proanthocyanidins (Xie et al., 2004). In conclusion, Mrp resistance may (at least partially) rely on relatively high levels of signal molecules (SA) (Yang et al., 2004) and/or some enzymes that produce antioxidant defenses such as flavonols (Venisse et al., 2002).
Fire blight-affected early genes in apple identified
Our analyzes revealed that of the 88 gene representatives identified in Malus domestica Borkh susceptible. In 1998 alone, apple yield losses in the northwestern USA due to Erwinia amylovora were estimated to be over $68 million (Bonn and van der Zwet, 2000). In wilt diseases, such as fire blight, that invade the vascular system of plants, large polysaccharide molecules released by the pathogen into the xylem may be sufficient to cause a mechanical blockage of the vascular bundles and thus initiate wilting.
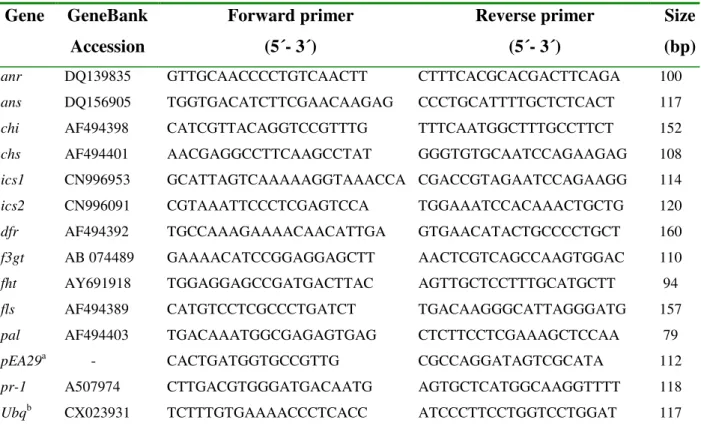
In vitro apple shoot cultures of 'Idared' and Mrp were micropropagated on MS medium (Murashige and Skoog w/w) sorbitol with 6-benzylaminopurine (BAP) and indole-3-butyric acid (IBA) (both 1 mg.l-1). Slides were stirred in blocking solution for 15 min in the dark and washed 5 times with millipore water. A total of 88 non-redundant genes were detected as differentially expressed (at p<0.01) in apple leaves after Erwinia attack.
A heat plot was generated from the microarray experiment (Fig. 5) quantifying differences in the expressions of fire-responsive genes in the two apple genotypes. For clarity, two types of figure configuration are given: The list of non-redundant clones with regulation patterns in two apple genotypes is given in (Tab. 1). Idared', genes induced in both species, genes repressed in both species, and bacterial-responsive genes significantly repressed in Mrp-resistant but not in 'Idared' (Tab. 1).
In addition to these, further defense-related genes such as those for endochitinases, protease (miraculin) or heavy metal stress-related genes (Al-induced proteins, metallothionein) were induced in resistant MRP, but little or not affected in susceptible 'Idared'. A set of genes involved in primary metabolism, protein turnover and signaling was significantly repressed in Mrp resistant but not in 'Idared'. Expression analysis of selected genes in the 3-day period after infection with Erwinia amylovora.
Different nature of bacterial colonization was reflected in the activated defense responses in the two cultivars. In this work, transcript profiles of uninfected and fire blight-infected leaves were compared in the leaves of susceptible 'Idared' and resistant Mrp apple. Gau A, Koutb M, Piotrowski M, Kloppstech K (2004) Accumulation of pathogenesis-related proteins in the apoplast of a susceptible apple cultivar (Malus domestica cv. Elstar) after infection with Venturia inaequalis and constitutive expression of PR genes in the resistant cultivar.
Oh CS, Beer SV (2005) Jeneetiksii molakiyuulaa Erwinia amylovora guddina dhukkuba ibiddaa keessatti hirmaatu. Venisse JS, Gullner G, Brisset MN (2001 ) Ragaa hirmaannaa dhiibbaa oksijiinii jalqabbii infekshinii peerii Erwinia amylovora keessatti.
Miraculin implicated in apple fire blight defence
Conclusion
The work presented was aimed at identifying components of apple defense against the phytopathogenic bacteria Erwinia amylovora blight. The analyzes revealed that the resistant Mrp likely represents a nutritionally poorer environment with respect to carbohydrate content compared to the sensitive 'Idared'. However, pinitol (and to a lesser extent maltose) content increased in the infected 'Idared' plants, while these changes were not apparent in the resistant species.
The increase in the content of polyols may be a reaction to changed water conditions (osmotic) in the affected plant tissue. In contrast to sugar levels, total salicylic acid was significantly higher in the resistant apple species, possibly providing an advantage against potential bacterial invasion. In these plants, most of the investigated phenylpropanoid-related genes including the gene for PAL and the two isochorismate synthases were significantly repressed.
However, increased PAL enzyme activity in infected 'Idared' plants suggests PAL-directed SA synthesis in blight-infected apple. In addition to the isohorism synthase gene and PAL enzyme activity, the F3GT enzyme responsible for anthocyanin synthesis showed distinct behavior in the two apple species reflecting a different defense strategy against fire blight. A total of 4,000 ESTs were obtained from suppressor subtraction of infected and non-infected plants of the two apple species.
Genes for the major apple allergen Mal d1, cytosolic aldolase, a ripening-induced protein, and formate dehydrogenase were induced in 'Idared' but unaffected or upregulated in resistant Mdr. In contrast, defense-related genes encoding for class III endo-chitinases (PR-3 gene cluster), the putative trypsin lineage miraculin MalMir 1 as well as several ESTs that may be related to heavy metal detoxification in plants (e.g. metallothionein 1a or aluminum homogenously resulted in reduced form). forced or intact in 'Idared'. Our further analyzes revealed that the putative Miraculin MalMir 1 gene of apple is located within the chromosome region responsible for a certain change in the resistance of apple offspring, and itself exerts response to the infection process.
The map position of the Malmir 1 gene overlaps with the small QTL for fire blight resistance previously identified on chromosome 3. Taken together, both studied apple genotypes are equipped with defense mechanisms that differ not only qualitatively (expression of certain bacterial genes, species-specific), but also qualitatively of salicylic acid, levels of certain transcripts or cinbohydrate). Although the lists of components of these mechanisms are not very complete and their activity and role are also not fully understood, they are contributing to the final outcome of the interactions between Erwinia and certain apple plants.
Curriculum vitae
Publication activity
Appendix