Serological Tests Do Not Predict Residual Fibrosis in Hepatitis C Cirrhotics with a Sustained Virological Response to Interferon.
Texto
Imagem

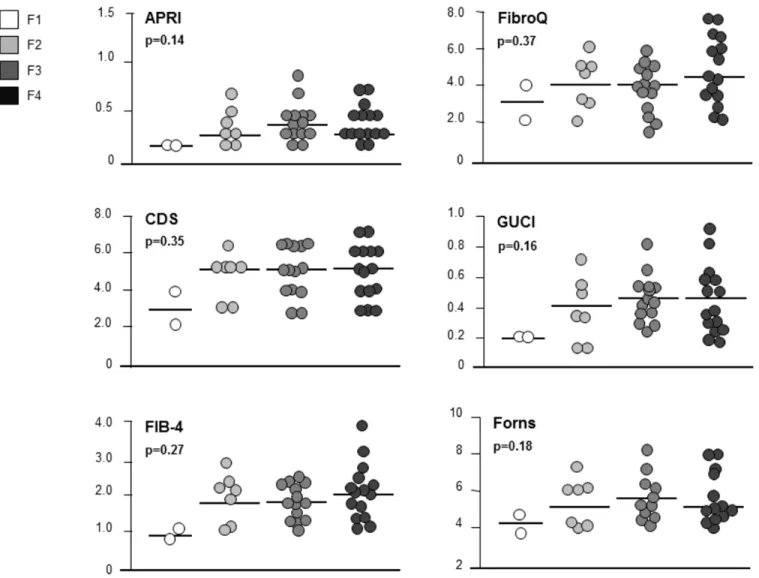
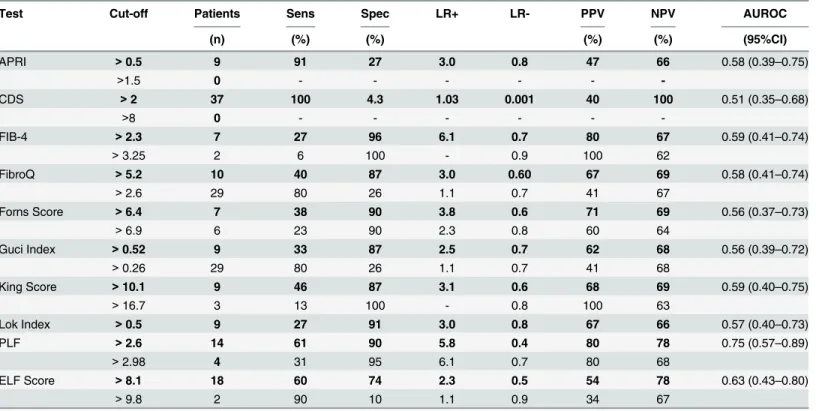
Documentos relacionados
CHRONIC HEPATITIS C VIRUS INFECTIONS IN BRAZILIAN PATIENTS: ASSOCIATION WITH GENOTYPES, CLINICAL PARAMETERS AND RESPONSE TO LONG TERM ALPHA
The present study aimed to evaluate the association between pretreatment plasma levels of chemokines and soluble tumor necrosis factor recep- tors (sTNF-R) and the virological
The aim of this study was to describe rates of hepatitis C recurrence and sustained virological response (SVR) to interferon-based treatment after OLT and its relationship to
A reduced response to interferon therapy has been described in individuals with chronic hepatitis C and serological markers of a resolved HBV infection (HBsAg
Background and aim: The durability of the sustained virologic response (SVR) in patients with chronic hepatitis C after treatment and the ideal follow-up time for
Objective: To compare the sustained virological response (SVR) rates following treatment with biosimilar standard IFN plus ribavirin (RBV) versus Peg-IFN plus RBV in patients with
Conclusion - In the evaluated patients the presence of liver steatosis did not inluence the sustained virological response of patients with chronic hepatitis C treated with
Conclusion - Heterozigozity for H63D and/or C282Y HFE gene mutation predicts absence of sustained virological response to combination treatment with interferon and ribavirin