A systems biology approach to transcription factor binding site prediction.
Texto
Imagem
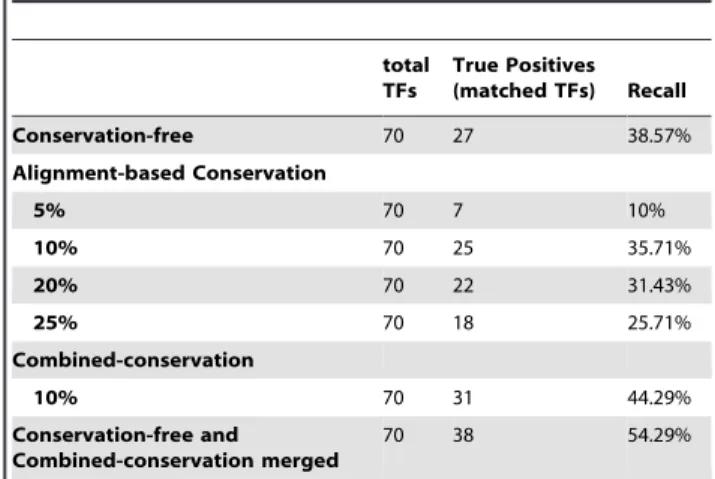


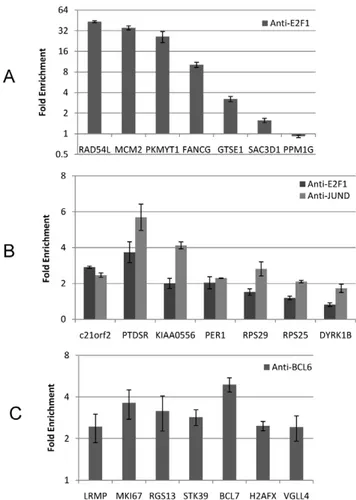
Documentos relacionados
When we compared the ME-matrix gene conservation across enterobacter and non-enterobacter species, we observed that many are highly conserved, as one would expect due to their
We propose that HCF-1 modulates longevity and stress response by binding to DAF-16 and preventing the transcription factor from accessing its target gene promoters, thereby
Finally, we used alignments produced by our program to study binding site conservation in genome-wide binding data of key transcription factors in the Drosophila blastoderm, with
Our HMM based algorithm identified regulated genes with promoters containing multiple EBNA-1 binding in both short- and long-term EBNA-1 expressing cells (Table S3) and the validity
Previous results using a SELEX (Systematic Evolution of Ligands by Exponential Enrichment)-based approach that selected DNA primer-template duplexes binding with high affinity to
Moreover, the predicted KLF18 proteins exhibit conserved features in the zinc finger regions as compared to known KLF proteins (Figure 2 and see Figure S1 for the alignment
By analyzing a large collection of human paralogous TF pairs, we show for the first time that the paralogous pairs whose DNA binding site motifs are similar tend to have
Since Sp1 is a well-known and ubiquitous protein and has been reported to bind practically everywhere in the human genome [5], the same LRCs trained on Sp1 were used to score test