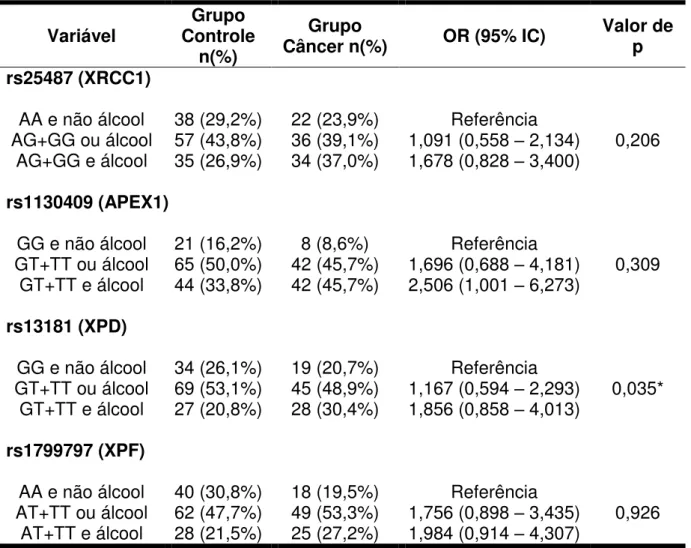
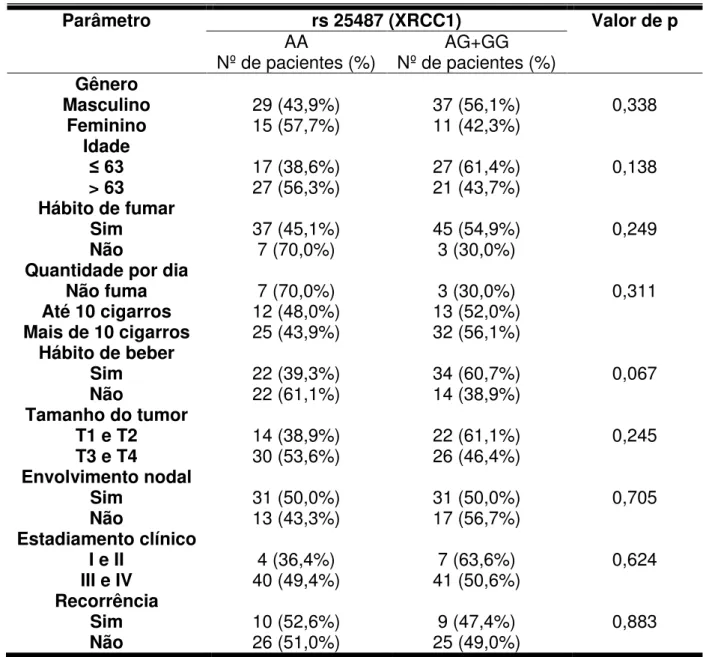
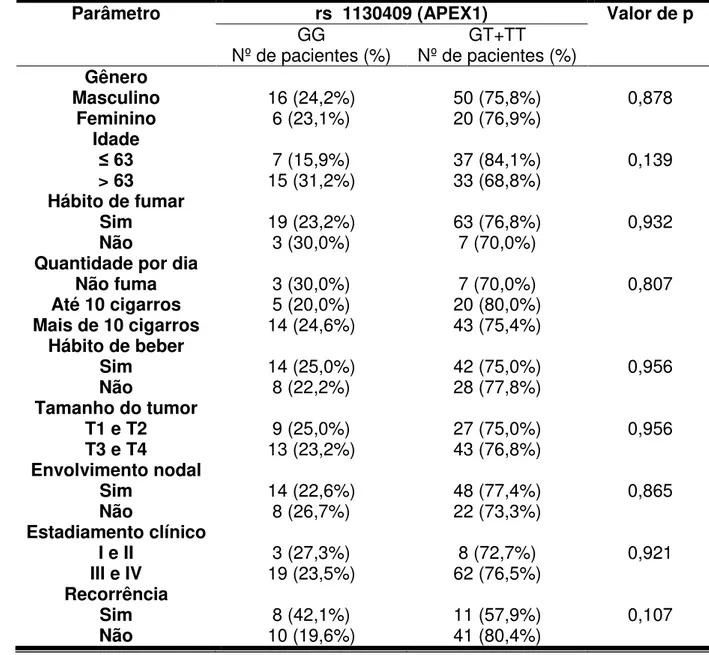
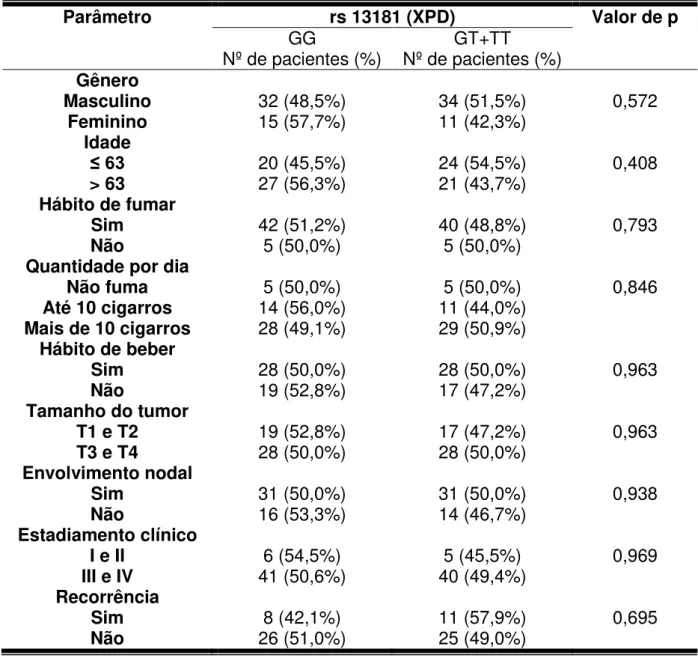
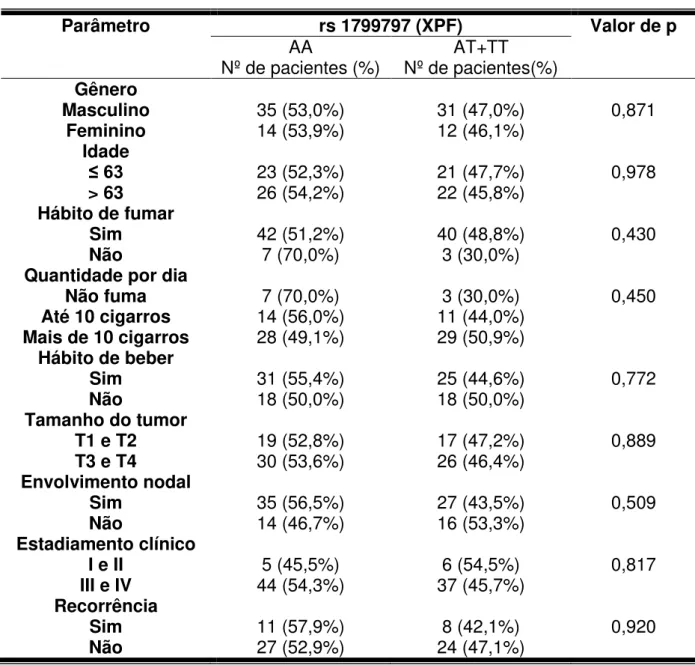
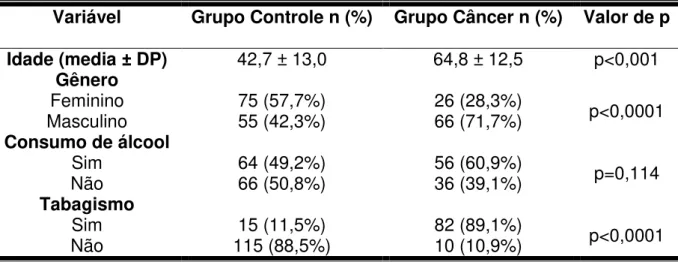
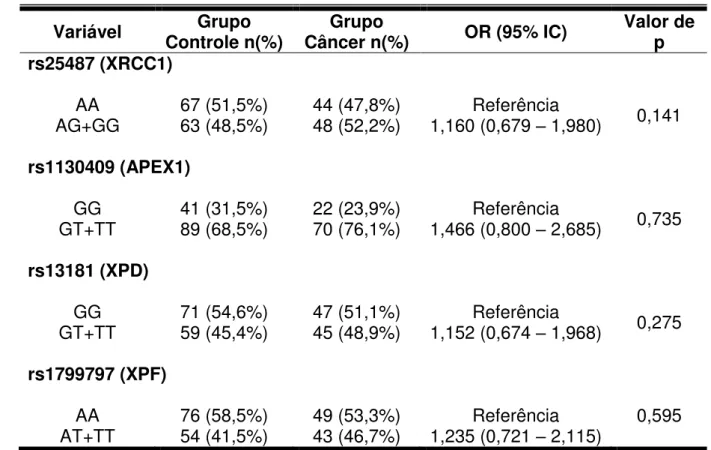
Avaliação de polimorfismos funcionais nos genes de reparo XRCC1, APEX1, XPD e XPF em carcinomas de células escamosas orais
Texto
Imagem

Outline
Documentos relacionados
Human papillomavirus (HPV) in head and neck cancer: an association of HPV 16 with squamous cell carcinoma of Waldeyer’s tonsillar ring. Alvarez Alvarez I, Sanchez Lazo P,
P53, and Rb proteins are independent from the presence of human papillomavirus genes in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral
The role of high-risk human papillomavirus infection in oral and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma in non-smoking and non-drinking patients: a clinicopathological and
Proteomics analysis of tissue samples from patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the penis and positive to human
Increased prevalence of squamous intraepithelial lesions in systemic lupus erythematosus: association with human papillomavirus infection.. High risk of human papillomavirus type
Evaluation of the Presence of Human Papillomavirus (HPV) and Epstein- Barr Virus (EBV) and the Expression of the Proteins p53, p16, E-cadherin, COX-2, MYC and MLH1 in Oral
The role of high-risk human papillomavirus infection in oral and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma in non-smoking and non-drinking patients: a clinicopathological and
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) has become an important risk factor for human papillomavirus (HPV) infection and the development of HPV associated lesions in the female