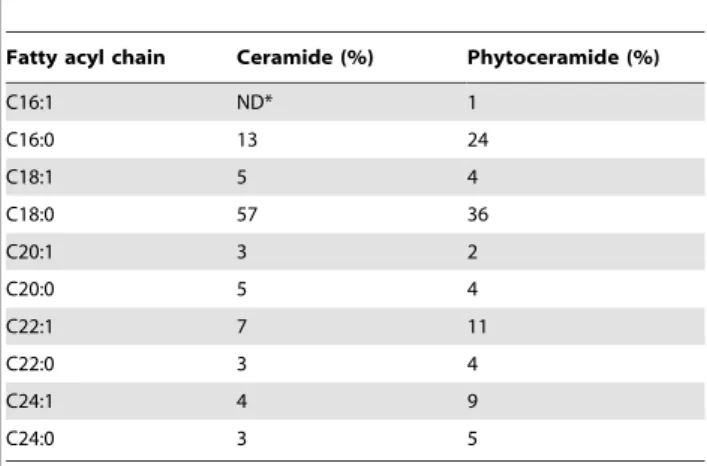
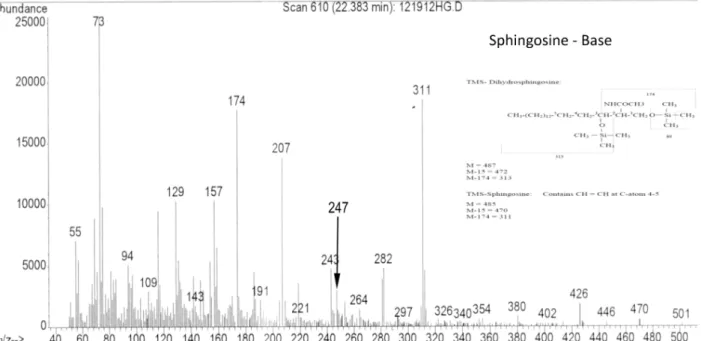
Phytoceramide in vertebrate tissues: one step chromatography separation for molecular characterization of ceramide species.
Texto
Imagem

Documentos relacionados
To evaluate BNZ biodistribution, a bioanalytical method was developed to determine its quantification in mouse tissues, including spleen, brain, heart, colon, liver, lung, and
vegrandis crude venom, hemorrhagic, and neurotoxic fractions were evaluated on mouse primary renal cells and a continuous cell line of Vero cells maintained in vitro.. Cells
Finally, similar to what was observed from the whole brain tissue, we demonstrated that alcohol exposure in BV2 cells, a mouse brain microglia cell line, increased both CIRP mRNA
Table S1 shows the band heights, standard deviations, and number of measurements for two different tissue cell lineages in suspension and the five normal mouse brain tissue pieces
Here, we describe the generation of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSc) from head-derived primary culture of mouse embryonic cells using small chemical inhibitors of the MEK
The naïve mouse embryon- ic stem cells (mESCs) derived from early embryo are significantly different from primed human ESCs (hESCs) and mouse epiblast stem cells (EpiSCs) in
Adherent cell cultures characterized in this study were isolated from different tissues: bone marrow, adipose tissue, brain, liver, and pancreas.. The results confirm the existence
Cell viability results (%) by Trypan blue assay, in human dental pulp cells (hDPCs), human dental follicle cells (hDFCs), human osteoblast- like cells (Saos-2) and mouse