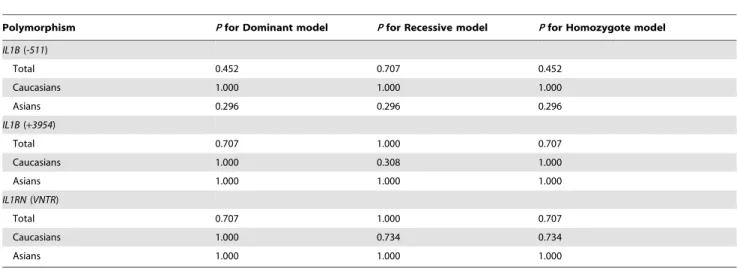
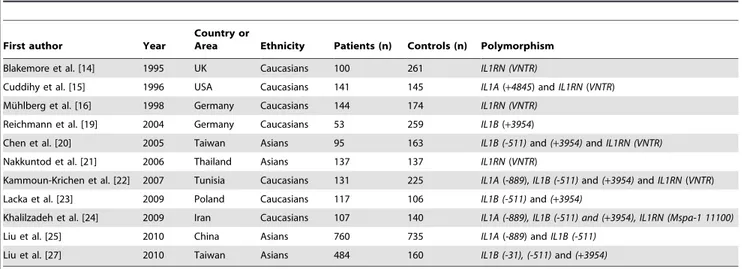
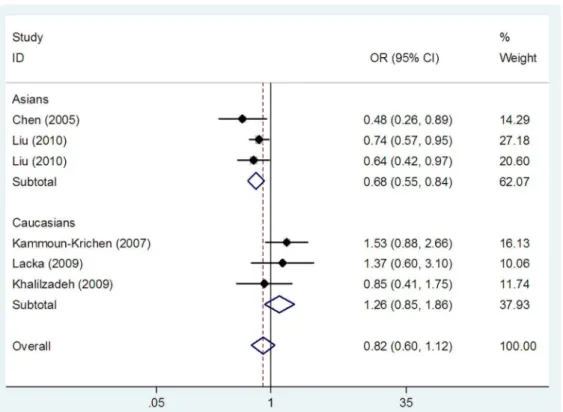
Association between the IL1B (-511), IL1B (+3954), IL1RN (VNTR) polymorphisms and Graves' disease risk: a meta-analysis of 11 case-control studies.
Texto
Imagem


Documentos relacionados
In order to better understand the genetic role of PDE4B for schizophrenia sus- ceptibility, we recapitulated the association of different PDE4B SNPs with schizophrenia risk
The inclusion criteria for the gene association studies in this meta-analysis were as follows: (1) independently published case-control studies explored the association between
Although the association in this study suggested a modest risk of 20% for both-819T and -592A alleles in leprosy susceptibility, these results support the role of these polymorphisms
Association of folate-pathway gene polymorphisms with the risk of prostate cancer: a population-based nested case-control study, systematic review, and meta- analysis.. Cancer
Conclusions/Significance: This meta-analysis indicates that ADPRT Val762Ala and APE1 Asp148Glu polymorphisms are not associated with increased breast cancer risk.. Citation: Wu B,
This meta- analysis explored the association between the CYP1A1 exon7 gene polymorphisms and lung cancer risk, and performed the subgroup analysis stratified by ethnicity,
Studies were included in the meta-analysis if they met the following criteria: (1) the study as- sessed the association between hepatocellular carcinoma risk and COX-2
Considering the relatively small sample size in each single study might have low power to detect the effect of the polymorphisms on cancer risk and the underlying heterogeneity