1 Ext ract ed fr om Resear ch Pr oj ect ; 2 Nur se, PhD in Nur sing, Facult y; 3 Nur se, Doct oral st udent , Facult y, e- m ail: m ar li.j er ico@fam er p.br ; 4 Nur se, Facult y. Medical School of São José do Rio Pr et o, Br azil
D isponible e n ca st e lla no/ D isponíve l e m língua por t ugue sa SciELO Br a sil w w w .scie lo.br / r la e
SURGERY CANCELLI NG AT A TEACHI NG HOSPI TAL: I MPLI CATI ONS FOR COST MANAGEMENT
1Már cia Galan Per r oca2 Mar li de Car v alho Jer icó3 Solange Diná Facundin4
Per r oca MG, Jer icó MC, Facundin SD. Sur ger y cancelling at a t eaching hospit al: im plicat ions for cost m anagem ent . Rev Lat in o- am En fer m agem 2 0 0 7 set em br o- ou t u br o; 1 5 ( 5 ) : 1 0 1 8 - 2 4 .
This study discusses the problem of surgery cancellation on the econom ic-financial perspective. I t was carried out in the Surgical Center Unit of a school hospital with the objective to identify and analyze the direct costs (hum an resources, m edications and m aterials) and the opportunity costs that result from the cancellation of elective surgeries. Dat a were collect ed during t hree consecut ive m ont hs t hrough inst it ut ional docum ent s and a form elaborat ed by t he researchers. Only 58 ( 23.3% ) of t he 249 cancelled scheduled surgeries represent ed cost s for t he inst it ut ion. The cancellations direct total cost was R$ 1.713.66 (average cost per patient R$ 29.54); distributed as follows: expenses with consum ption m aterials R$ 333.05; sterilization process R$201.22; m edications R$149.77 and hum an resources R$1,029.62. The hum an resources costs represented the greatest percentile in relation to the total cost (60.40% ). I t was observed t hat m ost of t he cancellat ions could be part ially avoided. Planning on m anagem ent ; redesigning work processes, training the staff and m aking early clinical evaluation can be strategies to m inim ize this occurrence.
DESCRI PTORS: hospit als t eaching/ organizat ion and adm inist rat ion; nursing; hospit al cost s; direct service cost s
CANCELAMI ENTO DE CI RUGÍ AS EN UN HOSPI TAL- ESCUELA: I MPLI CACI ONES PARA LA
GESTI ÓN DE COSTOS
Este artículo discute la problem ática del cancelam iento de cirugías bajo una perspectiva económ ico-financiera. Fue llevado a cabo en la Unidad del Centro Quirúrgico de un hospital- escuela con obj eto de identificar y analizar los costos directos (recursos hum anos, recursos m ateriales y m edicam entos) e indirectos ocasionados por el cancelam iento de cirugías no urgentes. Los datos fueron recogidos durante tres m eses consecutivos m ediante docum entos institucionales y un cuest ionario elaborado por las invest igadoras. Solam ent e 58 ( 23,3% ) de las 249 operaciones previst as y que fueron canceladas resultaron en costos para la institución. El costo directo total de los cancelam ientos fue R$ 1.713,66 ( costo m edio por paciente de R$ 29,54) , repartidos así: gastos con m ateriales de consum o R$ 333,05 y proceso de esterilización R$ 201,22, m edicam entos R$ 149,77 y recursos hum anos R$ 1.029,62. El costo de los recursos hum anos repesentó el m ayor porcentaje en relación al costo total (60,1 % ). Se constató que la m ayor parte de los cancelam ientos podría haber sido evit ada. Planificación adm inist rat iva, rediseño de los procesos de t rabaj o, m edidas educat ivas del personal y evaluaçión clínica previa constituyen estrategias recom endadas para reducción de los casos de cancelam iento.
DESCRIPTORES: hospitales escuela/ organización y administración; enfermería; costos hospitalares; costos directos de servicios
CAN CELAMEN TO CI RÚRGI CO EM UM HOSPI TAL ESCOLA: I MPLI CAÇÕES SOBRE O
GERENCI AMENTO DE CUSTOS
Este estudo discute a problem ática do cancelam ento de cirurgias sob a perspectiva econôm ico-financeira. Foi realizado na Unidade de Centro Cirúrgico de um hospital de ensino, com o objetivo de identificar e analisar os custos diretos (recursos hum anos, m edicam entos e m ateriais) e custo de oportunidade gerados pelo cancelam ento de cirurgias eletivas. Os dados foram coletados durantes três m eses consecutivos, utilizando-se docum entos institucionais e form ulário elaborado pelas pesquisadoras. Apenas 58 ( 23,3% ) das 249 cirurgias program adas canceladas representaram custos para a instituição. O custo direto total dos cancelam entos foi de R$ 1.713,66 (custo m édio por paciente de R$ 29,54), assim distribuídos: despesas com m ateriais de consum o R$ 333,05; processo de esterilização R$ 201,22; m edicam entos R$ 149,77 e recursos hum anos R$ 1.029,62. O cust o com recursos hum anos represent ou o m aior percent ual em relação ao cust o t ot al ( 60,1% ) . Observou- se que a m aior part e dos cancelam ent os eram pot encialm ent e evit áveis. Planej am ento adm inistrativo, redesenho dos processos de trabalho, m edidas educativas de pessoal e avaliação clínica prévia const it ue em est rat égias recom endadas para m inim ização da ocorrência.
DESCRI TORES: hospit ais de ensino/ organização e adm inist ração; enferm agem ; cust os hospit alares; cust os diret os
I NTRODUCTI ON
T
h e c a n c e l l i n g o f s c h e d u l e d s u r g i c a l p r oced u r es h as b een st u d ied n ot on ly in Br azil( 1 - 2 ),but also in ot her count r ies like Aust r alia( 3), I r eland( 4),
M e x i c o( 5 ), t h e U n i t e d S t a t e s( 6 ) a n d t h e U n i t e d
Kin g d om( 7 ) . Lik e Br azilian r esear ch , t h ese st u d ies
h av e in dicat ed h igh f r equ en cy of can cellin g, du e t o
organizat ional problem s in healt h inst it ut ions, including
lack of beds( 3 - 4 , 7 ), sch edu lin g er r or s, com m u n icat ion
er r or s( 3 , 5 ) and ot her adm inist r at iv e pr oblem s.
Alt h ou g h sev er al au t h or s ack n ow led g e t h at
t he im pact of surgery cancelling raises t he operat ional
an d f in an cial cost s of t h e Su r g ical Cen t er Un it an d
reduces t he efficiency of t he service, few st udies have
a n a l y ze d t h e t h e m e f r o m t h e e co n o m i c- f i n a n ci a l
asp ect , esp ecially in t er m s of d ir ect cost s ( h u m an
r e so u r ce s, m e d i ca t i o n a n d m a t e r i a l ) a n d co st o f
o p p o r t u n i t y. As t h e su r g i ca l m o v e m e n t h a s b e e n
appoint ed as an int er venient fact or in pr oduct ivit y and
hospit al qualit y rat es( 8), t he m axim um use of sur gical
capacit y is one of t he m ain m easures for t he efficiency
of f i n an ci al r esou r ce u se. A st u d y p er f or m ed at a
t eaching hospit al( 9) dem onst r at ed t hat sur gical pat ient s
represent 24% of t ot al hospit alizat ions and cont r ibut e
t o 43% of r ev enues.
Sur ger y cancelling is an er r or r esult ing fr om
non com pliance wit h t he unit ’s adm inist rat ive planning
r e q u i r e m e n t s. I t co r r e sp o n d s t o o n e o f t h e f o u r
com ponent s of qualit y cost , classified in cost s of int ernal
and ext ernal errors, cost s of prevent ion and analysis.
To ach iev e excellen ce, t h e h ospit al m u st con t in u ally
be com m it t ed t o t he problem solving capacit y, qualit y
and low cost s of m edical pr ocedur es. Ther efor e, t he
elim inat ion of wast e is needed, as well as t he abilit y t o
im pr ov e t h e h ospit al pr ocess ( diagn osis, t r eat m en t ,
h o s p i t a l i z a t i o n , m a n a g e m e n t s u p p o r t ) t h r o u g h
adequat e aut om at ion, m ore inform at ion and decrease
of t he pat ient ’s hospit al st ay( 10).
Wa st e ca n b e co n si d e r e d a s a n y a n d a l l
r esour ces used, bey ond t he necessar y, t o execut e a
pr odu ct or ser v ice ( con su m pt ion m at er ial, su pplies,
hum an effor t , ener gy, t echnology, am ong ot her s) . I t
is ext r a expendit ur e added t o t he pr oduct or ser vice’s
r egular cost s w it hout any kind of im pr ovem ent t o t he
clien t( 1 1 ). Wh en w or k pr ocesses ar e in adequ at e, t h e
cost of pr oduct s or ser v ices incr eases. Consequent ly,
t he inst it ut ions incur financial losses due t o r ew or k ,
absor bin g t h e t im e t h at w ou ld be u sed f or an ot h er
act iv it y.
Th e r e p e r c u s s i o n s o f s u r g e r y c a n c e l l i n g
negat ively affect not only t he client , w ho experiences
a br ok en bond of t r ust in r elat ion t o t he inst it ut ion,
but also t he nur sing t eam ( w or k oper at ion, t im e and
m a t e r i a l r e so u r ce co n su m p t i o n , d i m i n i sh e d ca r e
qualit y) and t he hospit al it self( 1). The cancelling of t he
sur gical pr ocedur e incr eases oper at ional and financial
cost s, causing losses t o t he inst it ut ion. The financial
loss is cau sed b y t h e d ef icien t p r ocess an d can b e
ev id en ced b y t h e r eser v at ion of t h e su r g er y r oom
and loss of oppor t unit y t o schedule anot her pat ient ,
under used sur ger y r oom s, longer hospit alizat ions ( and
r isk of hospit al infect ion) and, consequent ly, incr ease
in t he bed pr ice/ day and dim inished bed av ailabilit y.
Ot h e r so u r ce s o f l o ss a r e t h e w a st e o f st e r i l i ze d
m at er i al , r ew o r k o f t h e p er so n n el i n v o l v ed i n t h e
pr epar at ion of t he sur gery r oom and in t he st er ilizat ion
p r ocess( 2 ).
The cost of oppor t unit y can be defined as t he
v alue of a r esour ce in it s best alt er nat iv e use( 12). I t
r ep r esen t s t h e v alu e t h at is n ot g ain ed d u e t o t h e
d e c i s i o n o f i n v e s t i n g t h e r e s o u r c e i n a n o t h e r
a l t e r n a t i v e , t o t h e d e t r i m e n t o f o t h e r s. D i f f e r e n t
p a r a m e t e r s h a v e b e e n u s e d t o a d d r e s s c o s t o f
o p p o r t u n i t y, su ch a s t h e m e a su r e m e n t o f p r o f i t ,
incom e, am ong ot her s. Since each decision inv olv es
a d if f er en t cost of op p or t u n it y, t h e con cep t can b e
a s s o c i a t e d w i t h d i f f e r e n t a t t r i b u t e s( 1 3 ). Th e
im plem ent at ion of t he concept guides t he m anager ’s
decision in t he use of a cer t ain r esour ce dur ing t he
w h ole decision pr ocess, i. e. in t h e ph ase pr ecedin g
t h e d e c i s i o n , a s a n e l e m e n t f o r e v a l u a t i n g t h e
per for m ance of t he m anager r esponsible for t he act ion
and also t o evaluat e t he result s of t he decision, aft er
i t s i m p l e m e n t a t i o n( 1 4 ). Th e f o c u s o n e c o n o m i c
m easu r em en t b y cost of op p or t u n it y is a r elev an t
in st r u m en t of f eedback f or plan n in g an d con t r ol( 1 5 ).
Thus, t his st udy aim s t o suppor t nur sing in t he decision
m aking pr ocess based on qualit y and oppor t unit y cost
in f or m at ion .
OBJECTI VES
- I dent ify and analy ze t he dist r ibut ion of dir ect cost s
r e l a t e d t o h u m a n r e so u r ce s, co n su m e d su p p l i e s
( c o n s u m p t i o n a n d r e p r o c e s s e d m a t e r i a l s ) a n d
m edicat ions, gener at ed by t he cancelling of elect iv e
su r g er ies at t h e Su r g ical Cen t er Un it of a t each in g
- Ver ify t he dir ect cost r elat ed t o t he t im e spent by
dif f er en t pr of ession al cat egor ies.
- I dent ify t he cost of oppor t unit y at t he sur gical cent er.
METHODOLOGY
This is an ex plor at or y and descr ipt ive st udy,
ca r r i e d o u t a t t h e Su r g i ca l Ce n t e r o f a Te a ch i n g
Hospit al of ex t r a capacit y in a cit y in t he int er ior of
São Pau lo, Br azil. Th is h osp it al is a r ef er r al cen t er
an d deliv er s h ospit al an d ou t pat ien t car e in sev er al
m ed i ca l sp eci a l t i es, t o t a l i n g a n a v er a g e o f 2 , 5 0 0
h osp it alizat ion s/ m o. an d 1 , 6 0 0 lar g e, m ed iu m an d
sm all- size sur ger ies/ m o. The sur gical pr ogr am cov er s
t he per iod fr om 7am t o 7pm , daily, fr om Monday t o
Fr i d a y a n d o n Sa t u r d a y m o r n i n g s. Ni g h t p er i o d s,
w eekends and holidays ar e r eser ved for em er gencies.
Th e st u d y p o p u l a t i o n i s co m p o se d o f a l l e l e ct i v e
sur ger ies in t he per iod fr om Sept em ber t o Novem ber
2 0 0 4 a t t h e s t u d y h o s p i t a l , c a n c e l l e d a f t e r t h e
pr epar at ion of t he sur ger y r oom ( SR) and dur ing t he
sur ger y it self. This cr it er ion w as used because t hese
t y p es of can cellin g im p ly cost s ( con sid er ed in t h is
st u d y ) .
The m ap w it h t he m ont hly sur gical schedule
w a s u s e d t o v e r i f y t h e o c c u r r e n c e o f s u r g e r y
cancelling. For t he ident ificat ion of causes, a st ruct ured
for m w as elabor at ed, cont aining 4 gr oups of dat a: 1
-D em o g r a p h i c Ch a r a ct er i st i cs ( a g e, g en d er, h ea l t h
in su r an ce, su r g er y r oom an d t im e of su r g er y ) ; 2
-Cir cu m st an ce in w h ich t h e su r ger ies w er e can celled
( befor e and aft er t he pr epar at ion of t he sur ger y r oom
and dur ing t he sur gical pr ocedur e) ; 3 - Pr ofessional
Cat eg or ies in v olv ed in t h e ar r an g em en t of t h e SR,
t im e spent and act ivit ies developed; 4 - Mat er ial and
equipm ent used in t he ar r angem ent of t he SR w hich
w ere not included in t he debt bill of t he Surgical Cent er
Un it ( SCU) , su ch as clot h i n g ( sh eet s, g ow n s) an d
in st r u m en t s.
D a t a c o l l e c t i o n s t a r t e d a f t e r f o r m a l
au t h or izat ion w as obt ain ed f r om t h e in st it u t ion an d
fr om t he head nur se at t he SCU, and aft er or ient at ion
o f t h e n u r s e s w h o w o r k e d i n t h e m o r n i n g a n d
aft er noon shift s about how t o fill out t he inst r um ent
t o b e u s e d . A p p r o v a l b y t h e Re s e a r c h Et h i c s
Com m it t ee w as not necessar y because t his r esear ch
d i d n o t i n v o l v e h u m a n b e i n g s . Th e r e s e a r c h e r s
c o l l e c t e d t h e f o r m s e v e r y d a y a n d d a t a w e r e
com p lem en t ed .
An elect r on ic w or k sh eet w as elab or at ed in
Micr osof t Ex cel f or d at a t r eat m en t . Th is con t ain ed
infor m at ion on t he client ’s ident ificat ion, healt h plan,
h o sp i t a l i za t i o n u n i t , su r g er y, d a t e a n d r ea so n f o r
ca n ce l l i n g . Th e sh e e t w a s d i v i d e d i n f o u r p a r t s:
m at er ials, fees, m edicat ion and hum an r esour ces. The
cost id en t if icat ion w as b ased on t h e BRASI NDI CE,
fact or y pr ice fr om Apr il 2005 and AMB t able ( Br azilian
Med ical Associat ion ) . Dat a r eg ar d in g salar ies w er e
p r o v i d ed b y t h e Per so n n el Dep ar t m en t . To su r v ey
cost s r elat ed t o t he t im e spent on hum an r esour ces,
t h e m i n i m u m r e m u n e r a t i o n o f t h e p r o f e s s i o n a l
cat eg or ies in v olv ed an d social ch ar g es ( FGTS, PI S,
v acat ion an d 1 3t h salar y at t h e pr opor t ion of 1 / 1 2 )
w er e t ak en in t o accou n t . Th e t ax es t ot aled 2 1 . 6 7 %
of added cost . To est im at e t h e cost of oppor t u n it y,
t he sur ger ies w er e classified accor ding t o anest het ic
size and t he SR and Post Anest hesia Car e Unit ( PACU)
fees fr om t he AMB t able w er e used.
RESULTS
I n t o t a l , 2 4 9 s c h e d u l e d s u r g e r i e s w e r e
cancelled at t he Surgical Cent er unit during t he st udy
per iod. Fr om t hese, 191 ( 76.7% ) occur r ed befor e t he
p r ep ar at ion an d ar r an g em en t of t h e su r g er y r oom ,
54 ( 21.7% ) aft er it s pr epar at ion and only four of t hem
( 1 . 6 % ) d u r i n g t h e a n e st h e t i c- su r g i ca l p r o ce d u r e .
Ca n c e l l a t i o n s b e f o r e t h e S R p r e p a r a t i o n w e r e
e x c l u d e d f r o m t h e a n a l y s i s s i n c e t h e y d i d n o t
r ep r esen t a d d i t i o n a l co st s. Th u s, t h e sa m p l e w a s
com posed of t he 58 ( 23. 3% ) r em aining sur ger ies.
Am ong t he pat ient s w ho had t heir sur ger ies
cancelled, 30 were m en and 28 wom en, wit h an average
age of 43.1 ± 24.2 years ( ranging from 6 m ont hs t o 80
years old) . Most pat ient s ( 82.7% ) used t he Single Healt h
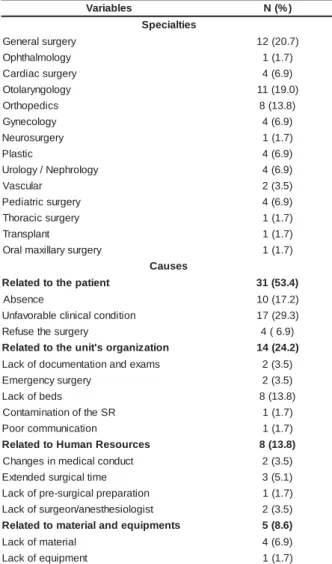
Syst em ( SUS) . As can be observed in Table 1, t he m ost
fr equent m edical specialt ies in t he cancelled sur gical
procedures wit h cost s for t he inst it ut ion were: general
surgery ( 20.7% ) , followed by ot olaryngological surgery
( 1 9 % ) an d or t h op ed ic su r g er y ( 1 3 . 8 % ) . Th e m ain
causes for cancelling were relat ed t o t he pat ient ( 53.4% ) ,
su ch a s u n f a v o r a b l e cl i n i ca l co n d i t i o n ( a r t e r i a l
hypert ension and respirat ory diseases, am ong ot hers)
- 29.3% and absence ( 17.2% ) . Problem s relat ed t o t he
unit ’s or ganizat ion ( 24. 2% ) also caused a significant
share of cancelling, m ainly because of t he lack of beds
a t t h e I n t e n si v e Ca r e Un i t ( 1 3 . 8 % ) . La ck o f
cont am inat ion of t he SR were responsible for a sm aller
par t of can cellat ion s, r espect iv ely, 3 . 5 % , 3 . 5 % an d
1.7% . I n only 8 of t he 58 surgeries t hat were cancelled
( 13.8% ) , t he m ain causes of cancelling were relat ed t o
t he allocat ion of hum an resources, such as, ext ended
surgical t im e ( 5.1% ) , changes in m edical conduct ( 3.5% )
and lack of surgical t eam professionals ( anest hesiologist
a n d su r g e o n ) - 3 . 5 % . Th e ca u se s r e l a t e d t o t h e
a l l o ca t i o n o f h u m a n r e so u r ce s a n d e q u i p m e n t
represent ed only 8.6% of t he t ot al causes of cancelling.
Table 1 - Medical Specialt ies and causes for cancelling
t he surgeries t hat ent ailed cost s for t he st udy inst it ut ion
( N= 58) . São José do Rio Pr et o, SP, 2004
Table 2 - Direct cost s of surgeries cancelled at t he st udy
inst it ut ion ( N= 58) . São José do Rio Pret o, SP, 2004
s e l b a i r a
V N(%)
s e i t l a i c e p S y r e g r u s l a r e n e
G 12(20.7)
y g o l o m l a h t h p
O 1(1.7)
y r e g r u s c a i d r a
C 4(6.9)
y g o l o g n y r a l o t
O 11(19.0)
s c i d e p o h t r
O 8(13.8)
y g o l o c e n y
G 4(6.9)
y r e g r u s o r u e
N 1(1.7)
c i t s a l
P 4(6.9)
y g o l o r h p e N / y g o l o r
U 4(6.9)
r a l u c s a
V 2(3.5)
y r e g r u s c i r t a i d e
P 4(6.9)
y r e g r u s c i c a r o h
T 1(1.7)
t n a l p s n a r
T 1(1.7)
y r e g r u s y r a ll i x a m l a r
O 1(1.7)
s e s u a C t n e i t a p e h t o t d e t a l e
R 31(53.4)
e c n e s b
A 10(17.2)
n o i t i d n o c l a c i n il c e l b a r o v a f n
U 17(29.3)
y r e g r u s e h t e s u f e
R 4(6.9)
n o i t a z i n a g r o s ' t i n u e h t o t d e t a l e
R 14(24.2)
s m a x e d n a n o i t a t n e m u c o d f o k c a
L 2(3.5)
y r e g r u s y c n e g r e m
E 2(3.5)
s d e b f o k c a
L 8(13.8)
R S e h t f o n o i t a n i m a t n o
C 1(1.7)
n o i t a c i n u m m o c r o o
P 1(1.7)
s e c r u o s e R n a m u H o t d e t a l e
R 8(13.8)
t c u d n o c l a c i d e m n i s e g n a h
C 2(3.5)
e m i t l a c i g r u s d e d n e t x
E 3(5.1)
n o i t a r a p e r p l a c i g r u s -e r p f o k c a
L 1(1.7)
t s i g o l o i s e h t s e n a / n o e g r u s f o k c a
L 2(3.5)
s t n e m p i u q e d n a l a i r e t a m o t d e t a l e
R 5(8.6)
l a i r e t a m f o k c a
L 4(6.9)
t n e m p i u q e f o k c a
L 1(1.7)
The dir ect cost s r elat ed t o hum an r esour ces
a n d s u p p l i e s ( m e d i c a t i o n , c o n s u m p t i o n a n d
r epr ocessed m at er ial) t ot aled R$ 1 , 7 1 3 . 6 6 ( av er age
cost per pat ient R$ 29.54) , w hile R$ 1,169.08 ( 68.2% )
w er e r elat ed t o can cellat ion s du r in g t h e pr epar at ion
of t he sur ger y r oom and R$ 544. 58 ( 31. 8% ) dur ing
t he sur gical pr ocedur e ( Table 2) .
l a c i g r u S e c n a t s m u c r i
c N HR Material Medication SPD Total(%)
g n i r u D n o it a r a p e r
p 54 R$922.22 R$55.89 R$31.30 R$159.67
8 0 . 9 6 1 . 1 $ R ) 2 . 8 6 ( g n i r u D e r u d e c o r
p 4 R$107.40 R$277.16 R$118.47 R$41.55
8 5 . 4 4 5 $ R ) 8 . 1 3 ( ) % ( l a t o
T 58R$1,029.62 ) % 1 . 0 6 ( 5 0 . 3 3 3 $ R ) % 4 . 9 1 ( 7 7 . 9 4 1 $ R ) % 7 . 8 2 2 . 1 0 2 $ R ) % 8 . 1 1
( R$1,713.66
HR: Hum an r esour ces; SPD: St er ile Pr ocessing Depar t m ent
Nu r sin g ( n u r sin g t ech n ician s an d aids) w as
t h e ca t e g o r y t h a t t o t a l e d t h e h i g h e st n u m b e r o f
m in u t es w or k ed ( 2 , 2 5 5 ) cor r espon din g t o 4 6 . 7 % of
t he w or k load dur ing t he pr epar at ion of t he SR and
54. 9% dur ing t he anest het ic- sur gical pr ocedur e. The
t i m e o f t h i s ca t e g o r y w a s d i st r i b u t e d a m o n g t h e
f u n c t i o n s o f t h e s c o u t n u r s e , h e l p t o t h e
anest hesiologist and sur gical inst r um ent at ion. At t he
st u d y i n st i t u t i o n , t h e n u r si n g p r o f e ssi o n a l h a s a
m a n a g e m e n t f u n c t i o n a n d i s r e s p o n s i b l e f o r
su p e r v i si n g t h e su r g e r y r o o m s. Be ca u se i t i s a n
i n d i r e c t c o s t , t h i s p r o f e s s i o n a l ’ s t i m e w a s n o t
consider ed. The findings show ed t hat t he scout nur se
spends m or e t im e w or king bot h in t he pr epar at ion of
t h e SR ( 3 0 . 5 % ) an d d u r in g t h e su r g ical p r oced u r e
( 24.1% ) . The highest cost for t he inst it ut ion is r elat ed
t o t he sur geon ( R$ 446.40) and t he anest hesiologist
( R$ 286.75) ( Table 3) .
Table 3 - Professional Cat egories/ funct ions t hat worked
in t he cancelled surgeries which incurred cost s for t he
st udy inst it ut ion. São José do Rio Pret o, SP, 2004
s a i r o g e t a C / s i a n o i s s i f o r p s e õ ç n u f O S a d o r a p e r
P ProDceudraimnteento H C ) n i m ( % o t s u C ) $ R ( H C ) n i m ( % o t s u C ) $ R ( m e g a m r e f n
E 2.255 46,7 209,72 365 54,9 33,95 e t n a l u c r i
C 1.475 30,5 137,18 160 24,1 14,88 r o d a t n e m u r t s n
I 250 5,2 23,25 100 15 9,30 a i s e t s e n a à o i l í x u
A 530 11 49,29 105 15,8 9,77 a t s i g o l o i s e t s e n
A 825 17,1 255,75 100 15 31,00
o ã i g r u r i
C 1.325 27,4 410,75 115 17,3 35,65 e t n e t s i s s a o ã i g r u r i
C 425 8,80 34,00 85 12,8 6,80
l a t o
T 4.830 100 920,12 665 100 107,4
HL - Hour Load
Due t o t he high num ber of it em s am ong t he
d i f f er en t m a t er i a l s, i n t h i s st u d y, t h e t h r ee m o st
r epr esent at iv e it em s of each m at er ial w er e select ed.
Th e m ost u sed con su m p t ion m at er ials t h at cau sed
h i g h e r s p e n d i n g f o r t h e i n s t i t u t i o n d u r i n g S R
p r e p a r a t i o n w e r e m e d u l l a r y p u n c t u r e n e e d l e s ,
elect rode; during t he sur gical procedur e, t he m at er ials
w e r e m e d u l l a r y p u n c t u r e n e e d l e s , s u r g i c a l
c o m p r e s s e s a n d m a l l e a b l e p e r i p h e r a l v e n o u s
p u n ct u r e ca t h e t e r s. I n t e r m s o f m e d i ca t i o n , t h e
m a t e r i a l s w e r e : a n e st h e t i c e y e d r o p s, l i d o ca i n e ,
i so b a r i c b u p i v a ca i n e a n d o x y g en ( SR p r ep a r a t i o n
p h ase) an d p r op of ol, lid ocain e an d su x am et h on iu m
( dur ing t he sur gical pr ocedur e) .
Th e m a t e r i a l r e p r o c e s s e d b y t h e St e r i l e
Pr ocessin g Depar t m en t ( SPD) u sed in t h e can celled
su r ger ies w as classif ied in in st r u m en t s an d su r ger y
clot h in g. Th e t ot al cost of in st r u m en t al r epr ocessin g
w as R$ 5 9 . 3 2 ( t h e m ost ex p en siv e it em s w er e t h e
s m a l l s u r g e r y b o x , s e p t o p l a s t y b o x a n d
g l o sse ct o m y ) . Su r g e r y cl o t h i n g r e p r o ce ssi n g co st
a m o u n t e d t o R$ 1 4 1 . 9 0 f o r t h e i n s t i t u t i o n ; t h e
g en er a l l a p a r o t o m y p a ck a g e i n cu r r ed i n a h i g h er
cost . To su r v ey SR an d PACU cost s, t h e can celled
su r g e r i e s w e r e cl a ssi f i e d a cco r d i n g t o a n e st h e t i c
size, w h ich v ar ies f r om 0 t o 7 . Th e m ost f r eq u en t
su r g er i es w er e o f si ze 2 . Ho w ev er, su r g er i es t h at
in cu r r ed a h ig h er cost of op p or t u n it y w er e of size
5 , r esp o n si b l e f o r 2 2 . 1 % ( R$ 2 , 3 8 8 . 0 8 ) , f o l l o w ed
by size 2 w it h 1 9 % ( R$ 2 , 0 5 0 . 8 0 ) an d sm aller size
( s i z e 0 ) w i t h 0 . 7 % ( R$ 7 8 . 9 6 ) . T h e c o s t o f
op p or t u n it y at t h e Su r g ical Cen t er Un it t ot aled R$
1 0 , 7 8 2 . 4 0 .
DI SCUSSI ON
Fift y- eight of all surgeries t hat w ere cancelled
ent ailed cost s. The m ain causes w er e r elat ed t o t he
pat ient ( 53.4% ) , such as unfavorable clinical condit ion
( hyper t ension and r espir at or y diseases am ong ot her s)
- 29.3% and absence ( 17.2% ) . St udies per for m ed in
Mex ico( 5 ) an d Au st r alia( 3 ) also sh ow ed alt er at ion s in
pat ient s’ clinical condit ions as sour ces of cost s, w it h
4 0 % a n d 1 7 . 1 % r esp ect i v el y. Pr e- su r g er y cl i n i ca l
assessm ent is appoint ed as an im por t ant fact or t o be
considered for reducing t he rat es of cancelled surgical
pr ocedu r es( 6 , 1 6 ).
Reg ar d i n g t h e p at i en t ’ s ab sen ce f r o m t h e
scheduled surgery, research in t eaching hospit als have
in d icat ed v alu es of 4 1 % ( cat ar act su r g er y )( 1 7 ) an d
54. 3% ( sev er al specialt ies)( 1), higher t han w hat w as
f o u n d i n t h i s st u d y ( 1 7 . 2 % ) . Th e r easo n s f o r t h e
p a t i e n t ’ s a b s e n c e h a v e b e e n a s s o c i a t e d t o t h e
inst it ut ional condit ion ( unaw ar eness and alt er at ion of
t he dat e of sur ger y, hospit alizat ion difficult y, lack of
vacancy and lack of pr e- sur gical exam ) ; t o t he clinical
con d it ion , social con d it ion ( occu p at ion al p r ob lem s)
and also per sonal condit ion( 1).
Su r g e r y ca n ce l l i n g d u e t o o r g a n i za t i o n a l
pr oblem s at t he unit ( 24.2% ) is m ainly r elat ed t o t he
lack of beds at t he I nt ensiv e Car e Unit and also for
h o sp i t a l i za t i o n ( 1 3 . 8 % ) . I n a st u d y p er f o r m ed i n
I reland( 4), t he lack of beds r epr esent ed 31% of sur ger y
ca n ce l l a t i o n s, a g a i n st 1 8 . 1 % i n Au st r a l i a( 3 ). Th e
f in din gs of t h is r esear ch r ev ealed t h at can cellat ion s
d u e t o h u m a n r e so u r ce f a ct o r s r e p r e se n t e d o n l y
1 3 . 8 % of t he t ot al, in w hich ex t ended sur ger y t im e
pr edom inat ed ( 5 . 1 % ) . Values of 1 8 . 7 % for pr ev ious
su r g er ies t h at ex ceed ed est im at ed t im e h av e b een
r ep or t ed in lit er at u r e( 3 ), as w ell as t h e ob ser v at ion
t hat sur geons w ho fr equent ly under est im at e t he t im e
n e ce ssa r y f o r t h e su r g e r y h a v e a l so p r e se n t e d a
significant ly higher num ber of cancellat ions t han t hose
w ho do not .
Measu r es t o m in im ize can cellat ion s ar e an
im por t ant at t r ibut ion for t he head nur se at t he sur gical
cen t er. I t is est im at ed t h at ar ou n d 6 0 % of elect iv e
pr ocedu r e can cellat ion s is pot en t ially av oidable an d
cou l d b e p r ev en t ed b y u si n g q u al i t y i m p r ov em en t
t e ch n i q u e s. Th e ca n ce l l a t i o n s sh o u l d b e se e n a s
ad v er se ev en t s an d b e r ou t in ely m on it or ed in t h e
clinical sy st em s of hospit al incident s, since t hey ar e
t he m ain cause of inefficient t im e use at t he SR and
w ast e o f r eso u r ces( 3 ). Th ese au t h o r s co n si d er t h e
follow ing t ypes of cancellat ion as pot ent ially avoidable:
pr evious sur ger ies t hat exceeded t he est im at ed t im e,
sch edu lin g er r or s, adm in ist r at iv e cau ses, equ ipm en t
an d t r an sp or t at ion p r ob lem s, p oor com m u n icat ion ,
e r r o r s i n a d e q u a t e p a t i e n t p r e p a r a t i o n a n d n o n
-av ailab le su r g eon .
The Unit ed Kingdom ’s ex per ience( 7) in using
au d it in g as an in t er v en t ion p r ocess h as p r esen t ed
p r om i si n g r esu l t s. Th e f i r st au d i t f ou n d a su r g er y
cancellat ion r at e of 16.1% , w hile t he r easons r elat ed
t o t he hospit al ( m ainly lack of beds) r epr esent ed 42%
of t ot al cancellat ions, clinical reasons 34% ( especially
lack of anest het ic and sur gical condit ions) and pat ient
-r elat ed cancellat ions 21% ( absence) . The second audit
w as per for m ed 1 5 m on t h s aft er t h e m easu r es w er e
im plem ent ed ( im provem ent in bed dist ribut ion, clinical
assessm en t b ef or e sch ed u lin g an d im p r ov em en t in
com m u n i cat i on w i t h t h e p at i en t b y d i scu ssi n g t h e
sur gical dat e and his( er ) convenience and pr e- sur gical
or ien t at ion ) . Th e can cellat ion r at e w as r ed u ced b y
T h e r e s u l t s o f t h i s s t u d y s h o w e d t h a t
su r g er y can cellin g p r esen t ed a t ot al d ir ect cost of
R$ 1 , 7 1 3 . 6 6 , a sm all am ou n t if w e con sider t h e size
o f t h e st u d y i n st i t u t i o n . I t al so r ev eal ed t h at t h e
co st o f h u m a n r eso u r ces r ep r esen t ed t h e h i g h est
p er cen t ag e o f t o t al co st ( 6 0 . 1 % ) . Th e d i r ect co st
g e n e r a t e d b y t h e ca n ce l l i n g o f e l e ct i v e su r g e r i e s
i n d i c a t e d t h a t e r r o r s o c c u r r e d i n t h e i n t e r n a l
en v ir on m en t of t h e Su r g ical Cen t er Un it an d t h at ,
c o n s e q u e n t l y , t h e a d m i n i s t r a t i v e p l a n n i n g
r e q u i r e m e n t s w e r e n o t m e t . I t i s a l o ss f o r t h e
h o s p i t a l , s i n c e i n t e r n a l e r r o r s d o n o t r e s u l t i n
p r oced u r es t h at w ill ev en t u ally g en er at e r ev en u es.
S i n c e m o s t o f t h e c a n c e l l a t i o n s w e r e
p o t e n t i a l l y a v o i d a b l e , t h e s e f i n d i n g s e v i d e n c e
con cr et e possibilit ies of r edu cin g t h e lev el of su r gical
can cellat ion s by an aly zin g cau ses t h at gen er at e t h e
p r ob lem . We ar g u e t h at ch an g in g on ly on e f act or,
t h e m a i n r ea so n f o r t h e ca n cel l i n g , p r o b a b l y w i l l
n ot ex er t a p osit iv e ef f ect if ot h er f act or s ar e n ot
ch an ged sim u lt an eou sly( 3 ). For t h e h ospit al t o r edu ce
t h e r at e of can cellat ion s, each pr oblem n eeds t o be
s o l v e d i n t h e p r o c e s s , s t a r t i n g w i t h s u r g e r y
s c h e d u l i n g , e f f e c t i v e d i s t r i b u t i o n S CU a n d
n ot if icat ion t o t h e pat ien t . I n t h e qu alit y appr oach ,
t h e cost s m u st b e com p osed m ain ly b y p r ev en t iv e
c o s t s ( e m p h a s i z i n g t h e e d u c a t i o n o f s e v e r a l
c a t e g o r i e s w i t h r e s p e c t t o u n n e c e s s a r y
e x p e n d i t u r e s) t o t h e d e t r i m e n t o f e v a l u a t i o n o r
cor r ect ion cost s( 1 8 ).
Th e e co n o m i c a m o u n t t h a t co m p o se s t h e
cost of oppor t unit y of t he cancelled sur ger ies under
st udy w as R$ 10, 782. 40. The differ ence bet w een t he
SR u sage capacit y an d it s ef f ect iv e u se det er m in es
t h e e c o n o m i c v a l u e t h a t c o u l d b e o b t a i n e d a n d
r epr esen t s t h e r elat iv e econ om ic loss in r elat ion t o
t he oppor t unit y cost of not using t he sur ger y r oom .
Th i s co st i s r e l a t e d t o m a n a g e m e n t i n e f f i ci e n cy,
because it is an econom ic consum pt ion and ident ifies
an in efficacy, sin ce in com e t h at w ou ld con t r ibu t e t o
t h e r esu lt if t h e su r g er y h ad b een p er f or m ed w as
n ot g en er at ed .
Consider ing t hat econom ic pr ofit is obt ained
b y t h e i n c o m e m i n u s a l l c o s t s i n v o l v e d i n i t s
ach iev em en t , t h e m easu r em en t of t h e r esu lt s, f or
t h e sak e of m an ag em en t p er f or m an ce assessm en t ,
should t ak e int o account t he cost of oppor t unit y( 1 4 ).
How ever, it is obser v ed t hat it is difficult t o per ceive
t his cost in t he st udy inst it ut ion for t w o r easons. The
fir st is r elat ed t o a high dem and for sur ger ies, w it h a
c o n s e q u e n t w a i t i n g l i s t . On t h e o n e h a n d , t h i s
pr ev ent s t he inefficient pr ocess fr om being r eflect ed
in t he idle capacit y of t he SR and PACU and, on t he
ot her side, it hinder s t he j udgm ent of w hat is a r ight
or w r on g d ecision d u e t o t h e ex p ect ed r esu lt . Th e
seco n d i s r el a t ed t o t h e co m m o n h a b i t o f l et t i n g
p a t i en t s w i t h n o n - sch ed u l ed su r g er i es, f a st f o r a
p ot en t ial su r g er y.
Thus, t he inst it ut ional st r uct ur e t r ansfer s t he
inefficiency of t he pr ocess t o t he pat ient ( usually an
SUS user ) , w ho ends up car r ying t he r elat ive cost s of
t h e s u r g e r y c a n c e l l a t i o n ( w a i t i n g t i m e , f a s t i n g ,
em ot ional cost s) . Pat ient s w it h ot her healt h insurances
t h an t h e Sin gle Healt h Sy st em ( SUS) , h ow ev er, ar e
n ot w illin g t o deal w it h poor ly elabor at ed pr ocesses
or inefficient m anager s. These char act er ist ics of t he
in st it u t ion , su ch as h ig h d em an d f or su r g er ies an d
k e e p i n g n o n - s c h e d u l e d p a t i e n t s f a s t i n g c a n g o
u n n ot iced an d u n cor r ect ed f or a lon g t im e becau se
t h ey h av e been accept ed as a n at u r al par t of daily
w o r k .
Th e im plem en t at ion of t h e oppor t u n it y cost
concept in m easur ing t he cost of a good is t he m et hod
t h a t b e s t r e f l e c t s a m a n a g e r ’ s e f f i c a c y i n t h e
m anagem ent of t he r esour ces used( 15). The focus on
e co n o m i c m e a su r e m e n t b y o p p o r t u n i t y co st i s a
r el ev a n t i n st r u m en t o f f eed b a ck f o r p l a n n i n g a n d
cont r ol( 16). Measur em ent is t he fir st st age t hat leads
t o cont r ol an d, ev en t ually, t o t he im pr ov em ent of a
pr ocess( 1 9 ).
CONCLUSI ON
Th i s st u d y h i g h l i g h t ed t h e m i cr o eco n o m i c
aspect s of su r ger y can cellin g, in clu din g dir ect cost s
and cost of oppor t unit y, and allow ed for a sit uat ional
diagnosis of t he Sur gical Cent er Unit . Based on t his
i n f o r m a t i o n , n u r s e s c a n u s e s t r a t e g i e s i n t h e i r
m a n a g e m e n t w o r k t o m i n i m i z e t h i s o c c u r r e n c e .
Adm inist r at iv e planning, r edesigned w or k pr ocesses,
educat iv e m easur es and pr ev ious clinical assessm ent
ar e r ecom m en d ed st r at eg ies.
Alt h ou g h t h e r esu lt s r ef lect t h e ex p er ien ce
of a public t eaching hospit al and, t her efor e, m ay not
be r epr esent at ive of ot her hospit als, t he aut hor s hope
t h a t t h e s e f i n d i n g s c a n h e l p h o s p i t a l s i n t h e
developm ent of st r at egies t o r educe t he cancelling of
s c h e d u l e d s u r g e r i e s a n d i t s i m p a c t o n c o s t
REFERENCES
1 . Pa sch o a l MLH. Ta x a d e su sp en sã o d e ci r u r g i a em u m
hospit al univer sit ár io e os m ot ivos de absent eísm o do pacient e
à cir ur gia pr ogr am ada. [ disser t ação] . São Paulo ( SP) : Escola
d e En f er m ag em / USP; 2 0 0 2 .
2 . Cav alcan t i JB, Pag liu ca LMF, Alm eid a PC. Can celam en t o
de cir ur gias pr ogr am adas em um hospit al- escola: um est udo
ex plor at ór io. Rev Lat ino- am Enfer m agem 2000 j ulho- agost o;
8 ( 4 ) : 5 9 - 6 5 .
3 . Sch of ield WN, Ru b in GL, Piza M, Lai YY, Sin d h u sak e D,
Fear n sid e MR, Klin eb er g PL. Can cellat oin of op er at ion s on
t h e day of in t en ded su r ger y at a m aj or Au st r alian r ef er r al
h osp it al. Med J Au st 2 0 0 5 Ju n e 2 0 ; 1 8 2 ( 1 2 ) : 6 1 2 - 5 .
4 . Robb WB, O‘Su lliv an MJ, Br an n igan AE, Bou ch ier - Hay es
D J. A r e e l e c t i v e s u r g i c a l o p e r a t i o n s c a n c e l l e d d u e t o
i n cr e a si n g m e d i ca l a d m i ssi o n s? I r J Me d Sci 2 0 0 4 Ju l y
-Sep t em b er ; 1 7 3 ( 3 ) : 1 2 9 - 3 2 .
5 . Ag u ir r e- Cor d ov a JF, Ch av ez- Vazq u ez G, Hu it r on - Ag u illar
GA, Cor t es- Jim en ez N. Wh y is su r g er y can celled ? Cau ses,
im p licat ion s, an d b ib liog r ap h ic an t eced en t s. Gac Med Mex
2 0 0 3 No v em b er - D ecem b er ; 1 3 9 ( 6 ) : 5 4 5 - 5 1 .
6. Tait AR, Voepel- Lew is T, Munr o HM, Gut st ein HB, Rey nolds
PI . Cancellat ion of pediat r ic sur ger y: econom ic and em ot ional
im plicat ions for pat ient s and t heir fam ily. J Clin Anest h 1997
May ; 9 ( 3 ) : 2 1 3 - 9 .
7. Abdellaoui A, Addison A. A st udy of cancelled oper at ions
in an or t h opaedics depar t m en t . Clin Gov Bu ll 2 0 0 5 Mar ch ;
5 ( 6 ) : 6 - 9 .
8 . Gat t o MAF, Jou clas VMG. Ot im izan d o o u so d a SO. Rev
SOBECC 1 9 9 8 j an ei r o - m ar ço ; 3 ( 1 ) : 2 3 - 8 .
9 . S i l v a S H d a . Co n t r o l e d a q u a l i d a d e a s s i s t e n c i a l :
im plem ent ação de um m odelo. [ t ese] . São Paulo ( SP) : Escola
d e En f er m ag em / USP; 1 9 9 4 .
1 0 . Rob les A Ju n ior. Cu st os d a q u alid ad e: u m a est r at ég ia
par a a com pet ição global. São Paulo ( SP) : At las; 1994.
11. Souza D de LE. CCQ - Fazendo acont ecer. Belo Hor izont e:
Ch r ist ian o Ot t on i/ Escola d e En g en h ar ia/ UFMG; 1 9 9 6 .
1 2 . Per eir a GBS, Bar aú n a MLPS de. Cu st o de opor t u n idade
s o b o e n f o q u e d o m o d e l o g e s t ã o e c o n ô m i c a . I n : 9 º
Con gr esso Br asileir o de Cu st os; 2 0 0 2 . Ou t u br o 1 3 - 1 5 ; São
Pau l o, São Pau l o. [ ci t ad o 2 0 0 4 set em b r o 2 1 ] . Di sp on ív el
e m : U RL : h t t p : / / w w w . a b c c u s t o s . o r g . b r / t e x t o /
v i e w p u b l i c?I D _ TEXTO= 1 4 4 3 .
13. Silva AS, Reis EA dos, Leão LCG. Cust o de oport unidade.
I n : 4 º Con g r esso Br asileir o d e Cu st os; 1 9 9 7 . Nov em b r
o-Dezem br o 28- 01; Belo Hor izont e, Minas Ger ais. [ cit ado 2004
s e t e m b r o 2 1 ] . D i s p o n ív e l e m : URL: h t t p : / /
w w w . abccu st os. or g. br / t ex t o/ v iew pu blic?I D_ TEXTO= 2 0 5 .
1 4 . N a s c i m e n t o A M , S o u z a M A d e . C u s t o s d e
op or t u n id ad e: ev olu ção e m en su r ação. I n : 1 0 º Con g r esso
Br a si l e i r o d e Cu st o s; 2 0 0 3 . Ou t u b r o 1 5 - 1 7 ; Gu a r a p a r i ,
Es p ír i t o Sa n t o . [ c i t a d o 2 0 0 4 s e t e m b r o 2 1 ] . D i s p o n ív e l
e m : U RL : h t t p : / / w w w . a b c c u s t o s . o r g . b r / t e x t o /
v i e w p u b l i c ?I D _ TEX TO = 1 7 2 9 .
15. Cat elli A. Cust os de opor t unidade na gest ão da cadeia de
valor. I n: 9º Congr esso Brasileir o de Cust os; 2002. Out ubr o
1 3 - 1 5 ; São Pau lo, São Pau lo. [ cit ad o 2 0 0 4 set em b r o 2 1 ] .
D i sp o n ív el em : URL: h t t p : / / w w w . a b ccu st o s. o r g . b r / t ex t o /
v i e w p u b l i c?I D _ TEXTO= 1 4 2 1 .
16. Ar iet a CEL, Taiar A, Kar a-José N. Ut ilização e causas de
su sp en são d e in t er v en ções cir ú r g icas ocu lar es em Cen t r o
Ci r ú r g i co am b u l at o r i al u n i v er si t ár i o . Rev Asso c Med Br as
1 9 9 5 ; 4 1 ( 3 ) : 2 3 3 - 5 .
1 7 . Lir a RPC, Nascim en t o MA, Tem p or in i ER, Kar a- José N,
Ar iet a CEL. Suspensão de cir ur gias de cat ar at a e suas causas.
Rev Saú d e Pú b lica 2 0 0 1 ; 3 5 ( 5 ) : 4 8 7 - 9 .
1 8 . Pi n h o RCS, Pesso a MNM, Pet er MGA, Co ch r an e TMC,
Pet er FA. Cust os da qualidade na at iv idade de audit or ia. I n:
1 0 º Con gr esso Br asileir o de Cu st os; 2 0 0 3 . Ou t u br o 1 5 - 1 7 ;
Gu a r a p a r i , Esp ír i t o Sa n t o . [ ci t a d o 2 0 0 4 se t e m b r o 2 1 ] .
D i sp o n ív el em : URL: h t t p : / / w w w . a b ccu st o s. o r g . b r / t ex t o /
v i e w p u b l i c?I D _ TEXTO= 1 6 8 3 .
19. Maia JRC, Nascim ent o M do, Kielw agen KE, Cost a FA. A
g est ão d os cu st os d a q u alid ad e ot im izan d o o p r ocesso d e
gar ant ia da qualidade. I n: 8º Congr esso Br asileir o de Cust os;
2003. Out ubr o 3- 5; São Leopoldo, Rio Gr ande do Sul. [ cit ado
2 0 0 4 s e t e m b r o 2 1 ] . D i s p o n ív e l e m : U RL: h t t p : / /
w w w . ab ccu st os. or g . b r / t ex t o/ v iew p u b lic?I D_ TEXTO= 2 1 0 9 .