RevBrasAnestesiol.2018;68(1):96---99
REVISTA
BRASILEIRA
DE
ANESTESIOLOGIA
PublicaçãoOficialdaSociedadeBrasileiradeAnestesiologiawww.sba.com.br
CLINICAL
INFORMATION
Bezold-Jarisch
reflex
in
a
patient
undergoing
endoscopic
sympathectomy
for
management
of
refractory
angina
pectoris:
a
case
report
Wendell
Jackson
de
Macêdo
Caldas
a,∗,
Maíra
Ferreira
Barbosa
a,b,
Cremilda
Pinheiro
Dias
aaHospitalUniversitárioGetúlioVargas,CETIntegradodoInstitutodeAnestesiologiadoAmazonas,Manaus,AM,Brazil bSociedadeBrasileiradeAnestesiologia,RiodeJaneiro,RJ,Brazil
Received15January2015;accepted4March2015
Availableonline16September2016
KEYWORDS
Bezold-Jarischreflex; Endoscopic
transthoracic sympathectomy; Ischemic cardiomyopathy
Abstract
Backgroundandobjectives: Ischemiccardiomyopathyischaracterizedbyimbalancebetween supplyanddemandofmyocardialoxygen.Endoscopictransthoracicsympathectomyisa ther-apeuticoptionindicatedinrefractorycases.However,thepatient’spositionontheoperating tablemayfavorischemiccoronaryeventstriggeringtheBezold-Jarischreflex.
Casereport: Afemalepatient,47yearsold,withrefractoryischemiccardiomyopathy,admitted tothe operating room for endoscopictransthoracic sympathectomy, developedthe Bezold-Jarischreflexwithseverebradycardiaandhypotensionafterplacementinsemi-sittingposition totheprocedure.
Conclusion:Bradyarrhythmia, hypotension, and asystoleare complicationspotentially asso-ciatedwithpatient placementinasemi-sittingposition,particularlyincaseswithprevious ischemicheartdisease.
©2015SociedadeBrasileiradeAnestesiologia.PublishedbyElsevierEditoraLtda.Thisisan openaccessarticleundertheCCBY-NC-NDlicense( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
PALAVRAS-CHAVE
Reflexode Bezold-Jarisch; Simpatectomia transtorácica endoscópica;
ReflexodeBezold-Jarischempacientesubmetidaàsimpatectomiaendoscópica paratratamentodeanginapectorisrefratária:relatodecaso
Resumo
Justificativaeobjetivos: Acardiomiopatiaisquêmicacaracteriza-sepelodesbalanc¸o entrea ofertaeoconsumo deoxigênio pelomiocárdio.A simpatectomiatranstorácicaendoscópica
∗Correspondingauthor.
E-mail:wendellcaldas@yahoo.com.br(W.J.Caldas).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjane.2015.03.006
Bezold-Jarischreflex:casereport 97
Cardiomiopatia isquêmica
éuma opc¸ão terapêuticaindicadanoscasosrefratários. Contudo,aposic¸ãodopaciente na mesacirúrgicapodefavorecereventoscoronarianosisquêmicosedeflagraroreflexode Bezold-Jarisch.
Relatodecaso: Pacientedosexofeminino,47anos, portadoradecardiomiopatia isquêmica refratária,admitidanasaladecirurgiaparasimpatectomiatranstorácicaendoscópica, defla-grou o reflexode Bezold-Jarisch e desenvolveu bradicardia e hipotensão graves logo após colocac¸ãoemposic¸ãosemissentadaparaoprocedimento.
Conclusão:Bradiarritmia,hipotensãoeassistoliasãocomplicac¸õespotencialmenteassociadas àcolocac¸ãodopacienteemposic¸ãosemissentada,especialmentenoscasosemqueháprévio comprometimentoisquêmicodocorac¸ão.
©2015SociedadeBrasileiradeAnestesiologia.PublicadoporElsevierEditoraLtda.Este ´eum artigo OpenAccess sobumalicenc¸aCCBY-NC-ND( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
Introduction
Ischemic cardiomyopathy (IC) is a disorder resulting from theimbalance betweensupply anddemand ofmyocardial oxygen, whose most common cause is atherosclerosis of theepicardialcoronaryarteries.Itisthe leadingcauseof deathworldwide1 and heart failurein Brazil.2 Endoscopic
transthoracicsympathectomy(ETS)hasemergedasasafe
andeffectivetherapytominimizeanginapectoris,reduce
myocardial oxygen consumption, and improve the quality
of life ofthese patients, especiallyin refractorycases.3,4
In this procedure, the patient is placed in a semi-sitting
position,whichmayprecipitateinsomesituationsischemic
coronaryeventsandpredispose theoccurrenceof
Bezold-Jarisch reflex (BJR).5,6 Because it is a reflex, its onsetis
immediateand may trigger severe bradyarrhythmia, with
hypotensionandasystole.
Case
report
Femalepatient,47yearsold,withsymptomaticand
progres-sive ischemic cardiomyopathy (IC),refractory tocoronary
revascularization procedures, contraindicated for heart
transplantation,admittedtotheoperatingroomfor
endo-scopictransthoracicsympathectomy(ETS).
Intheprevious twoyears,thepatientdevelopedacute
myocardialinfarctionwithtriple-vesseldiseaseand
under-wenttwocoronaryarterybypasssurgerieswithoutsuccess.
Over the past eight months, she remained confined to a
hospitalbed for treatmentof anginapectorisand intense
andpersistentdyspnea,aggravatedbytheslightesteffort.
Shehaddepressedmoodandaggressivebehaviorattributed
toprolongedhospitalization.Physicalexaminationrevealed
hypophoneticheartsounds,breathsoundsdecreasedinlung
bases, and presence of peripheral edema, without other
significantchanges.
Among thepreoperative laboratory tests,wehighlight:
hemoglobin=11.5g.dL−1; hematocrit=36%; INR=1.46;
creatine phosphokinase (CPK)=311IU.L−1, CK-MB
isoen-zyme=42U.L−1, and troponin-1=0.006ng.mL−1. Chest
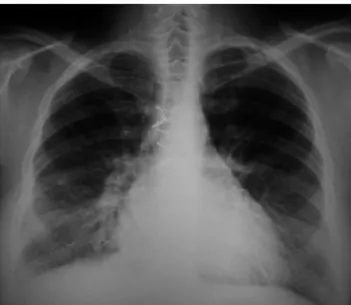
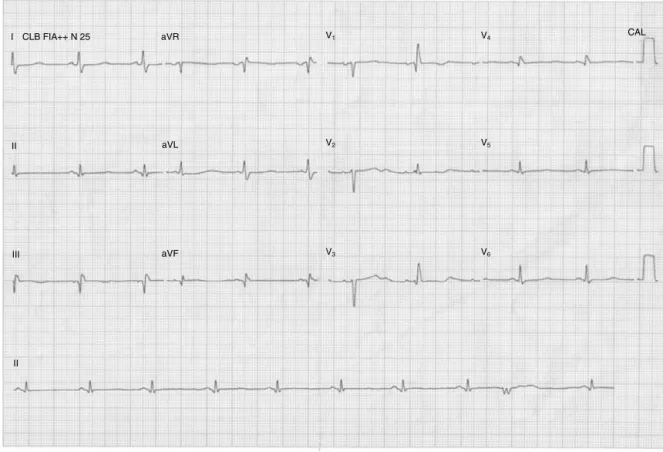
X-ray (Fig. 1) and electrocardiogram (Fig. 2) were
per-formed.Echocardiogram showedischemiccardiomyopathy
Figure1 PAchestX-rayshowingsymmetricalreticular
opac-itiesinlowerlung fieldsthatmay correspond tointerlobular
septa thickening due to heart disease; cardiomegaly;
ster-notomywires,andmediastinalclips.
withsevere systolic dysfunction (leftventricular ejection
fraction=34%).The patientwasclassifiedasclassII(NYHA
Functional Classification), group III (Goldman Risk Index),
andclassIV(ASAphysicalstatus).
Inthe operatingroom,monitoring wasperformed with
ECG,pulseoximetry,invasivebloodpressure,capnography;
central venous access was achieved through the internal
jugularvein.Aspremedication,weusedintravenous
mida-zolam3mg.Anestheticinductionwasperformedwithtarget
controlled infusion of remifentanil started at 6ng.mL−1,
rocuronium0.6mg.kg−1, and etomidate 0.3mg.kg−1, plus
lidocaine 1mg.kg−1 and dobutamine 5mcg.kg−1.min−1;
uneventfully.Single-lung ventilation wasachieved usinga
double-lumenendobronchialtubeandmaintenanceof
anes-thesiaperformedwithsevofluraneandremifentanil.
Thepatientwouldbeplacedinasemi-sittingpositionfor
theprocedure.Immediatelyaftertheheadelevation,with
98 W.J.Caldasetal.
aVR CLB FIA++ N 25
I V1 V4 CAL
V5
V6
V2
V3
aVL
aVF III
II II
Figure2 Electrocardiogram12-lead showing inactive area intheinferiorwall, isolated ventricularextrasystole, anddiffuse
changesofventricularrepolarization.
brain(higher)andheart,shedevelopedseverebradycardia
andhypotension,whichspontaneouslystoppedimmediately
afterreturningthepatienttotheneutralpositioninrelation totheverticalplane.
Thefluidsituation,bypulsepressurevariation,andthe
doses of current drugs have been checked and adjusted;
norepinephrinewasaddedstarting at 0.2mcg.kg−1.min−1.
Then, another attempt to place the patient in a
semi-sittingpositionwasmade, butwithout successduetothe
developmentofthecardiovasculareventsreported.Onthat
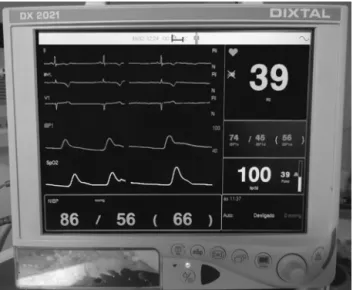
occasion,themonitoringpatternwasrecordedbeforeand
afterpositioning(Figs.3and4).
Theprocedurecontinuedwiththepatientinthesupine
positionandchestlateralizationtofacilitatethe
manage-mentofendoscopicinstruments,butwithoutanygapinthe
verticalplane. The leftsympathetic chain wasdissected,
andcompleteblockingofthenerveimpulsesatthelevelof
T1andT2wasachievedusingclips;therewasno
interven-tionintherightleftsympatheticchaintominimizepossible
hypotension.The patientwastransferred totheintensive
careunit(ICU)withoutvasoactivedrugsanddischargedfive
daysaftertheprocedure,reportingsignificantimprovement
ofsymptoms30daysaftersurgery.
Discussion
Ischemicheartdisease(IHD)isapredominantly
atheroscle-roticdiseaseduetotheimbalancebetweenoxygendelivery
(DO2)andconsumption(VO2)bythemyocardium.Ischemic
heart disease is the leading cause of death worldwide,
Figure3 Monitoringpatternbeforethepositioning.
accountingfor12.8%ofdeaths,1andthemostcommoncause
ofheartfailureinBrazil.2
Endoscopictransthoracicsympathectomy (ETS) maybe
a minimally invasive, effective, and safe therapy to
improve the quality of life of these patients, especially
in casesof coronaryartery bypassgrafting (CABG)failure
or percutaneous coronaryintervention(PCI). Studieshave
shown decreased angina pectoris3 and myocardial oxygen
Bezold-Jarischreflex:casereport 99
Figure4 Monitoringpatternafterplacingthepatientin
semi-sittingposition,whichshowsbradycardiaandhypotension.
levels of norepinephrine, and occurrence of ventricular
extrasystoles4aftertheprocedure.
InETS, thepatientshouldbeplacedsupine,ina
semi-sittingposition,withthechestelevatedatabout 45◦,and
twosmallcushionsundertheshouldersandtheback.These
maneuvers intend to deviate armpits from the operating
table,facilitatethemanipulationoftheendoscopic
instru-ments,pushtheshouldersforward,andpreventstretching
thebrachialplexus.
Inthisposition,theaccumulationofbloodincapacitance
vesselsleadstodecreasedeffectivecirculatingvolumeand
reducedatrialfillingpressure.Consequently,strokevolume
andcardiac outputdecrease,thus compromising coronary
perfusion and oxygen delivery to the myocardium (DO2).
Moreover, there may be a reflex increase in sympathetic
tone, with increased heart rate and oxygen consumption
bytheheart(VO2),whichpredisposestoischemiccoronary
events.
This decrease in venous returnassociated with
sympa-thetichyperactivitymaybethemechanismresponsiblefor
theBezold-Jarischreflex(reflexsympathetichyperactivity)
onset,whichstartsbysubendocardialsensoryreceptorsin
theinferoposteriorregionoftheheartduringischemiaand
culminatesinthevagalefferentaction,determining
reduc-tionofoxygenconsumptionbyreducingheartrate.
SomestudieshavereportedassociationbetweentheBJR
andsittingpositionforshoulderarthroscopy.5,6Inourcase,
positioning the patient in a semi-sitting position for ETS
triggered, twice, severe bradycardia and hypotension of
sudden onset and spontaneous regression after returning
to horizontal position. This demonstrates that the
regis-teredcardiocirculatorycollapse wasintimatelyrelated to
thepositioning.
Theacuteimbalancebetweenmyocardialoxygen
deliv-ery and consumption due to venous return reductionand
reflexsympathetichyperactivitymayhaveexacerbatedthe
priorischemic impairment ofthe lowercardiac wall seen
onpreoperative electrocardiogramand, thus, triggered a
BJRreflexthrough thestimulation of subendocardial
sen-soryreceptors sensitive toischemia, locatedin the heart
inferoposteriorregion.
Conclusion
Bradyarrhythmia, severe hypotension, and asystole that
are established with the Bezold-Jarisch reflex onset are
complications potentially associated with placing the
patientinasemi-sittingpositionforsurgery,particularlyin
caseswithpreviousischemicheartimpairment.
Conflicts
of
interest
Theauthorsdeclarenoconflictsofinterest.
References
1.NEWS.MED.BR,2011.OMSdivulgaasdezprincipaiscausasde mortenomundo.Availablefrom:http://www.news.med.br/p/ saude/222530/oms-divulga-as-dez-principais-causas-de-morte-no-mundo.htm[accessed21.10.14].
2.Bocchi EA, Marcondes-Braga FG, Bacal F, et al. Sociedade Brasileira deCardiologia.Atualizac¸ãoda DiretrizBrasileira de InsuficiênciaCardíacaCrônica---2012.ArqBrasCardiol.2012;98 Suppl.1:1---33.
3.BirkettDA,ApthorpGH,ChamberlainDA,etal.Bilateralupper thoracicsympathectomyinanginapectoris:resultsin52cases. BrMedJ.1965;2:187---90.
4.StriteskyM,DobiasM,DemesR,etal.Endoscopicthoracic sym-pathectomy---itseffectinthetreatmentofrefractoryangina pectoris.InteractCardiovascThoracSurg.2006;5:464---8. 5.D’AlessioJG,WellerRS,RosenblumM.Activationofthe
Bezold-Jarischreflexinthesittingpositionforshoulderarthroscopyusing interscaleneblock.AnesthAnalg.1995;80:1158---62.