r e v b r a s r e u m a t o l . 2016;56(6):469–470
w w w . r e u m a t o l o g i a . c o m . b r
REVISTA
BRASILEIRA
DE
REUMATOLOGIA
Editorial
Direct
oral
anticoagulants
in
antiphospholipid
syndrome
Anticoagulantes
orais
diretos
na
síndrome
antifosfolípide
Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is an acquired throm-bophiliacharacterizedbythrombosisand/orfetalloss asso-ciatedornotwiththepresenceofthrombocytopeniainthe presenceofcirculatingantiphospholipidantibodies (anticar-diolipin,lupusanticoagulantand/oranti-beta2-glycoprotein I). Chronic current treatment of this disease includes the useofvitaminK antagonistoralanticoagulants.There isa good response to treatment with oral anticoagulants; this therapyaimsatpreventingnewthromboticevents;however, re-thrombosisratesof16%coveringatimespanof10years were described.1 In this review, the authors found a high
rateofre-thrombosisintriple-positive(anticardiolipin,lupus anticoagulantandanti-beta2-glycoproteinI)patients(44%in 10 years). However, these medications are associated with variousdruginteractions and aregreatly influencedbythe dietaryvitaminK intake.2 Itisimportantthat adjustments
andmaintenancecontrolsarecarriedout,basedon prothrom-bintime(throughcontroloftheinternationalnormalization ratio –INR) regularly performedthroughout the lifeofthe patient,whichreduceshis/hertherapeuticadherence. More-over,insomecases,thelupusanticoagulantcanchangethe prothrombintimeandcompromisethepatient’smonitoring. Another disadvantageisthe decrease inC and Sproteins, whicharenaturalanticoagulants,withapossibleincreased riskofthrombosisintheacutephaseofanticoagulation.3
Hence,anewclassoforalanticoagulantdrugs(directoral anticoagulants)emerged,withtheadvantageofnotrequiring alaboratorycontrol,withtheaddedbenefitofbeingverylittle influencedfromfoodandothermedications.Examplesofsuch drugsare dabigatran, which is adirectthrombin inhibitor, andrivaroxaban,apixaban,and edoxaban,whicharefactor Xainhibitors.SuchdrugsareapprovedbytheFDAforusein venousthromboembolicevents andincasesofatrial fibril-lationinthe generalpopulation. Therearefewreportsand studiesontheuseofthesemedicationsinpatientswithAPS.
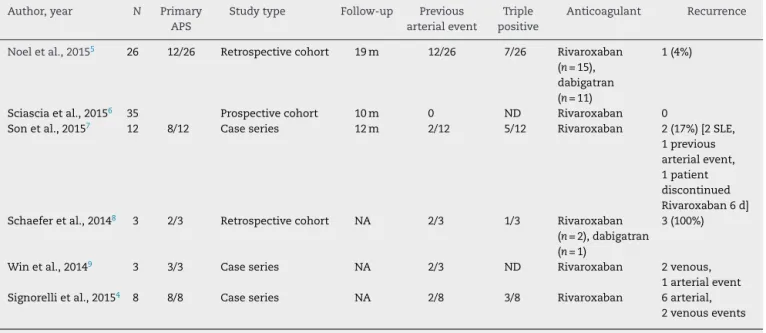
Table1summarizesthestudieswithdabigatranor
rivaroxa-baninAPS.
Intheliterature,about85casesofpatientswithAPSwho have taken the new oralanticoagulants were found. Most ofthesepapersare casereportsor seriesofcases,besides two retrospective studies and one prospective study. The medianfollow-uptimerangedfrom10to19monthsandthe most widely used medication was rivaroxaban. The recur-rencerangedfrom0to17%,includingseveralarterialevents, whenonlystudiesthatreportedthenumberofrecurrences inrelationtothenumber ofpatientsatrisk whowere fol-lowedforaperiodoftimewereevaluated.Thevastmajority ofpatientsincludedinallstudieshadsufferedprevious arte-rialeventsormultiplerecurrencesinthepresenceofvitamin K antagonists, or discontinued the use of the anticoagu-lant,or,ultimately,weretriple-positiveforantiphospholipid antibodies.4–9
Twoprospectiverandomizedstudies,oneofItalianorigin (TRAPS)andanotherEnglish(RAPS),3currentlyinafollow-up
phaseofpatientswithAPS,withagrouptreatedwithwarfarin versusrivaroxaban,werepublished.Thesestudieswillprovide theanswerstothisquestion.
470
rev bras reumatol.2016;56(6):469–470Table1–Summaryofcaseseries,prospectiveandretrospectivestudiesontheuseofneworalanticoagulantsinpatients withantiphospholipidsyndrome.
Author,year N Primary APS
Studytype Follow-up Previous arterialevent
Triple positive
Anticoagulant Recurrence
Noeletal.,20155 26 12/26 Retrospectivecohort 19m 12/26 7/26 Rivaroxaban
(n=15), dabigatran (n=11)
1(4%)
Sciasciaetal.,20156 35 Prospectivecohort 10m 0 ND Rivaroxaban 0
Sonetal.,20157 12 8/12 Caseseries 12m 2/12 5/12 Rivaroxaban 2(17%)[2SLE,
1previous arterialevent, 1patient discontinued Rivaroxaban6d] Schaeferetal.,20148 3 2/3 Retrospectivecohort NA 2/3 1/3 Rivaroxaban
(n=2),dabigatran (n=1)
3(100%)
Winetal.,20149 3 3/3 Caseseries NA 2/3 ND Rivaroxaban 2venous,
1arterialevent
Signorellietal.,20154 8 8/8 Caseseries NA 2/8 3/8 Rivaroxaban 6arterial,
2venousevents
NA,notapplicable;ND,notdetermined;SLE,systemiclupuserythematosus.
Funding
CarvalhoJF received grants from Federico Foundation and CNPq(300665/2009-1);LevyRAreceivedagrantfromFederico Foundation;LevyRAand AndradeDC aremembers ofAPS Action.
Conflicts
of
interest
Theauthorsdeclarenoconflictsofinterest.
r
e
f
e
r
e
n
c
e
s
1. PengoV,Ruiz-IrastorzaG,DenasG,AndreoliL,KhamashtaM,
TincaniA.Highintensityanticoagulationinthepreventionof
therecurrenceofarterialthrombosisinantiphospholipid
syndrome:‘PROS’and‘CONS’.AutoimmunRev.
2012;11:577–80.
2. SilvaFF,CarvalhoJF.Intensityofanticoagulationinthe
treatmentofthrombosisintheantiphospholipidsyndrome:a
meta-analysis.RevBrasReumatol.2015;55:159–66.
3. CohenH,DoréCJ,ClawsonS,HuntBJ,IsenbergD,Khamashta
M,etal.Rivaroxabaninantiphospholipidsyndrome(RAPS)
protocol:aprospective,randomizedcontrolledphaseII/III
clinicaltrialofrivaroxabanversuswarfarininpatientswith
thromboticantiphospholipidsyndrome,withorwithoutSLE.
Lupus.2015;24:1087–94.
4. SignorelliF,NogueiraF,DominguesV,MarizHA,LevyRA.
Thromboticeventsinpatientswithantiphospholipid
syndrometreatedwithrivaroxaban:aseriesofeightcases.
ClinRheumatol.2015;35:801–5.
5. NoelN,DutastaF,Costedoat-ChalumeauN,BienvenuB,
MarietteX,GeffrayL,etal.Safetyandefficacyoforaldirect
inhibitorsofthrombinandfactorXainantiphospholipid
syndrome.AutoimmunRev.2015;14:680–5.
6.SciasciaS,BreenK,HuntBJ.Rivaroxabanuseinpatientswith
antiphospholipidsyndromeandpreviousvenous
thromboembolism.BloodCoagulFibrinol.2015;26:476–7.
7.SonM,WypasekE,Celinska-LowenhoffM,UndasA.Theuse
ofrivaroxabaninpatientswithantiphospholipidsyndrome:a
seriesof12cases.ThrombRes.2015;135:1035–6.
8.SchaeferJK,McBaneRD,BlackDF,WilliamsLN,ModerKG,
WysokinskiWE.Failureofdabigatranandrivaroxabanto
preventthromboembolisminantiphospholipidsyndrome:a
caseseriesofthreepatients.ThrombHaemost.
2014;112:947–50.
9.WinK,RodgersGM.Neworalanticoagulantsmaynotbe
effectivetopreventvenousthromboembolisminpatients
withantiphospholipidsyndrome.AmJHematol.
2014;89:1017.
10.ErkanD,AguiarCL,AndradeD,CohenH,CuadradoMJ,
DanowskiA,etal.14thinternationalcongresson
antiphospholipidantibodies:taskforcereporton
antiphospholipidsyndrometreatmenttrends.Autoimmun
Rev.2014;13:685–96.
JozélioFreiredeCarvalhoa,∗,
DanieleCastroOliveiradeAndradeb,RogerA.Levyc
aUniversidadeFederaldaBahia,InstitutodeCiênciasdaSaúde,
Salvador,BA,Brasil bUniversidadedeSãoPaulo,FaculdadedeMedicina,
DivisãodeReumatologia,SãoPaulo,SP,Brazil cUniversidadedoEstadodoRiodeJaneiro,Divisãode
Reumatologia,RiodeJaneiro,RJ,Brazil
∗Correspondingauthor.
E-mail:jotafc@gmail.com(J.F.Carvalho). 2255-5021/©2016ElsevierEditoraLtda.Thisisanopen accessarticleundertheCCBY-NC-NDlicense(http://
creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).