CORRECTION
Correction: Glucocorticoids Inhibit Basal and
Hormone-Induced Serotonin Synthesis in
Pancreatic Beta Cells
Moina Hasni Ebou, Amrit Singh-Estivalet, Jean-Marie Launay, Jacques Callebert,
François Tronche, Pascal Ferré, Jean-François Gautier, Ghislaine Guillemain,
Bernadette Bréant, Bertrand Blondeau, Jean-Pierre Riveline
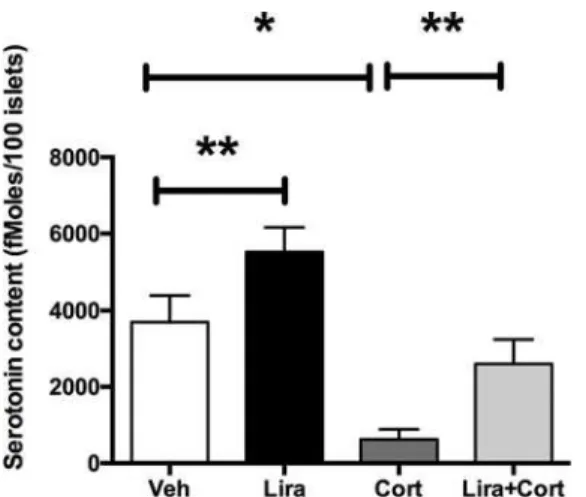
Fig 4
and its caption appear incorrectly in the published article. Please see the correct
Fig 4
and
its caption here.
Reference
1. Hasni Ebou M, Singh-Estivalet A, Launay J-M, Callebert J, Tronche F, Ferré P, et al. (2016) Glucocorti-coids Inhibit Basal and Hormone-Induced Serotonin Synthesis in Pancreatic Beta Cells. PLoS ONE 11 (2): e0149343. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0149343PMID:26901633
Fig 4. GCs inhibit liraglutide-induced increase of serotonin contents in vivo.Serotonin contents measured on isolated islets of mice treated with vehicle only (Veh, white bar), liraglutide (Lira, black bar), corticosterone (Cort, dark grey) or both liraglutide and corticosterone (Lira+Cort, light gray) for 4 weeks. Results are expressed as means±SD for n = 5 mice in each group.*p<0.05**and p<0.01 when comparing the different groups using a ANOVA test.
doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0155174.g001
PLOS ONE | DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0155174 May 4, 2016 1 / 1
a11111
OPEN ACCESS
Citation:Ebou MH, Singh-Estivalet A, Launay J-M, Callebert J, Tronche F, Ferré P, et al. (2016) Correction: Glucocorticoids Inhibit Basal and Hormone-Induced Serotonin Synthesis in Pancreatic Beta Cells. PLoS ONE 11(5): e0155174. doi:10.1371/ journal.pone.0155174
Published:May 4, 2016
Copyright:© 2016 Ebou et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the