Use of microsatellites for evaluation of genetic diversity in cherry tomato
Texto
Imagem

Documentos relacionados
keywords Digital images analysis, feature extraction, image segmentation, classifica- tion, content-based image retrieval, similar images, image histogram, edge detection
Therefore, this temporal model of perceived control refers to cognitions that have not been addressed by the attribution model – particularly those associated with
Table 2 shows a summary of the genetic diversity observed in five livestock species in Brazil, obtained using microsatellite markers at the Animal Genetics Laboratory (AGL)
In the evaluation of breeding sires with higher genetic values in the various environments using Spearman’s correlation, values between 0 and 0.98 were observed,
The present study was aimed at using microsatellite markers to characterize the genetic diversity and population structure of Anglo- Nubian goats in four municipalities
Sin embargo, la presencia de pocos alelos en el lote (2 y 3 alelos por locus), los alelos de baja frecuencia, observados en los parentales y en las larvas, y el alelo raro,
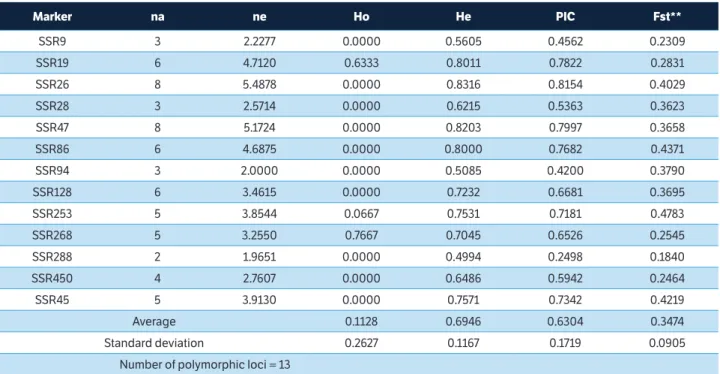
Given the high polymorphism level of microsatellites when compared to other markers, SSRs have been used to study population structure, for genetic diversity analysis, genetic
The main conclusions of the study were: the content of genetic information detected in Brazil nut by AFLP markers was high, and can be used for genetic analysis to obtain