Classification and structure-based inference of transcriptional regulatory proteins
Texto
Imagem
Documentos relacionados
Number of families, genera and species in cerrado physionomies in the Pé-de-Gigante Reserve, Santa Rita do Passa Quatro, São Paulo State, Brazil (21°36-44’S e 47°34-41’W).
According to the achieved results, out of the five domains of OMBOK structure including infrastructure, business, technology, customer relations and operation management, the
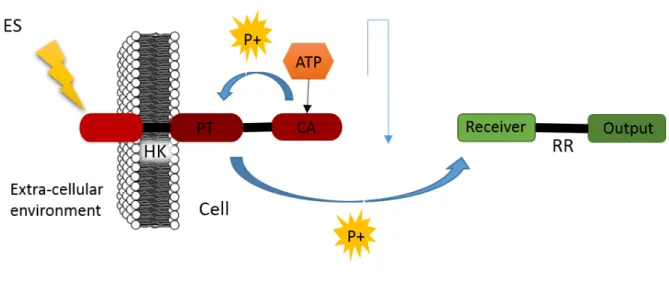
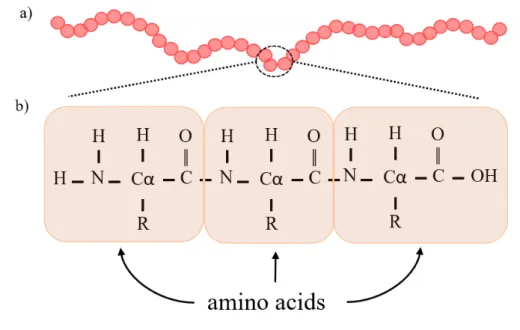
Proteins with a more complex structure with multiple domains (catalytic, extracellular, transmembrane etc.), even if classified very similar according to sequence similarity
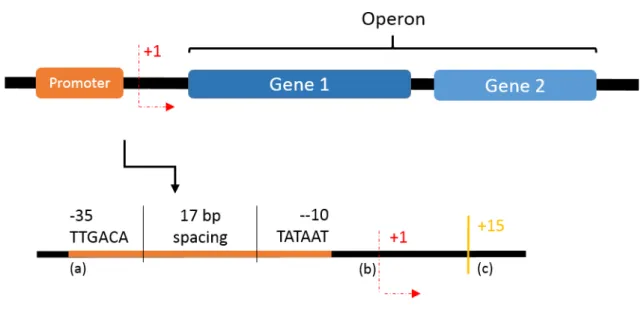
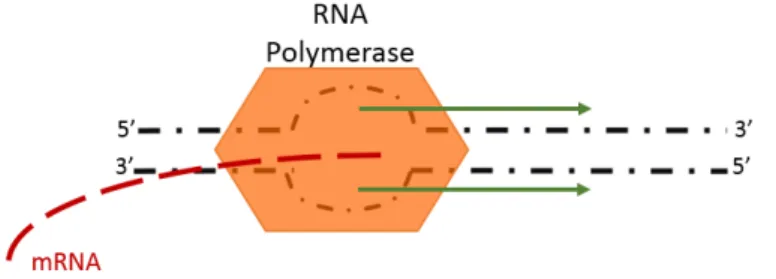
The evolutionary history of protein domains, including the origin of protein domains, the identification of domain loss, transfer, duplication and combination with other domains to
The work by [43] presents a 1-D model for the periphery of a 2-D cell based on the idea that proteins (with BAR domains) interact with membrane curvature to localize and direct
The structure of the remelting zone of the steel C90 steel be- fore conventional tempering consitute cells, dendritic cells, sur- rounded with the cementite, inside of
According to their similarity, 62 items were elaborated and grouped into six areas or domains, namely: Domain 1 - Performance of Practical Activities; Domain 2 - Professio-
Figure 3 – Distribution of the items according to the food practices domain, according to the irst version of EAPDI,. related to the other domains in the 5 th version
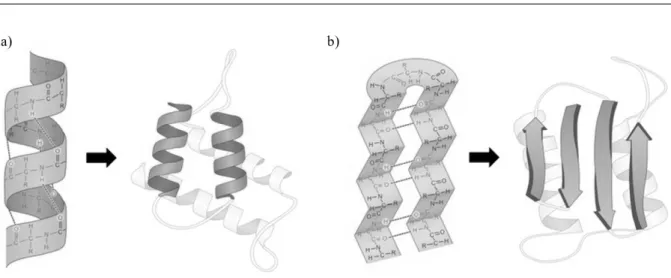
![Table 1.2: List of common protein motifs and the secondary structures that form them. Adapted from [2]](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123dok_br/17555836.816997/28.892.108.733.190.358/table-list-common-protein-motifs-secondary-structures-adapted.webp)