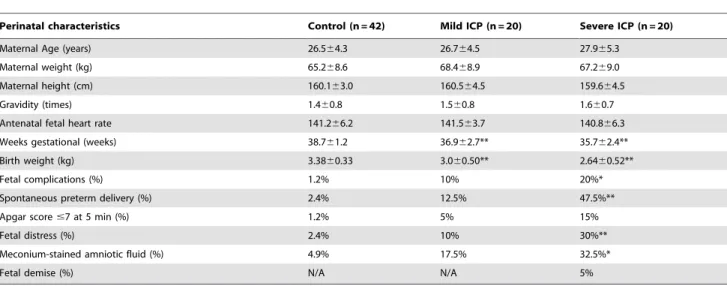
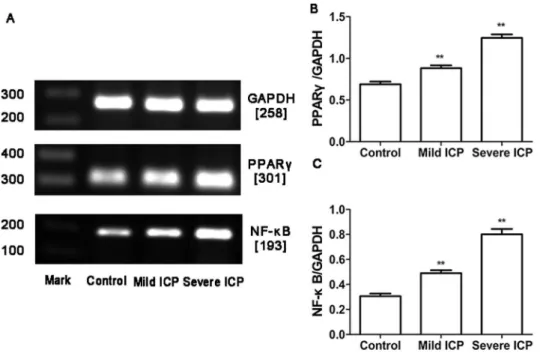
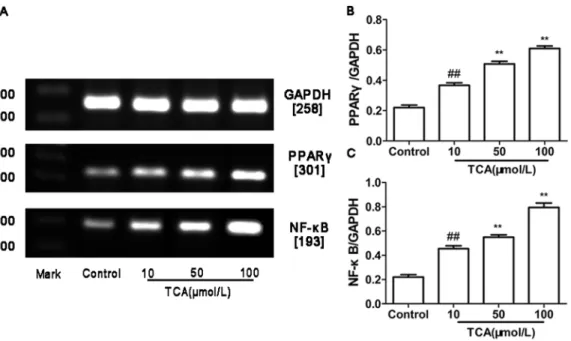
Roles of PPARγ/NF-κB signaling pathway in the pathogenesis of intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy.
Texto
Imagem

Documentos relacionados
The in vitro results showed that nicotine up-regulated the expression of α 5-nAChR protein and inhibited cis- platin-induced apoptosis by regulating α 5-nAChR/AKT signaling pathway
The serum levels of C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukins (IL)-6 and IL-10, nuclear transcription factor- k B (NF- k B) and E-selectin (E-Sel) were determined in 120 individuals,
Given the known regulation of CD69 by NF- B, we hypothe- sized that while the canonical NF- B pathway could control the early expression of CD69 as an activation marker,
imaging showed that chitosan activated the PPAR activity in the brain and the KEGG pathway analysis showed that chitosan significantly regulated the expression of genes involved
In the present study, BPE treatment strongly suppressed C/EBP b mRNA and protein expression and markedly reduced the expression levels of C/EBP a and PPAR c compared with those
Minimal expression and activity of PPAR c was detected in mock-infected and infected PPAR c VillinCre+ mice compared to littermate control PPAR c VillinCre- and wild-type (C57BL/6)
To check the role of TRIM8 in negative regulation of PIAS3 mediated NF- k B pathway, we co-transfected TRIM8 and p65 with PIAS3 in HEK293 cells and monitored NF- k B activity..
Expression of NIK wild-type reactivated non-canonical NF- N B signaling manifesting in nuclear translocation of p52 ( Fig. 4c and d) , demonstrating that the presence of functional