MULTIELEMENT COMPOSITION OF SEDIMENT CORE FROM LAKE KITEŽ (KING GEORGE ISLAND, ANTARCTIC): RESPONSE TO GLOBAL CLIMATE. DEVELOPMENT OF THE NATURAL ECOSYSTEMS OF THE ZND-BAIKAL AREA OF NORTHERN ASIA AS A RESPONSE TO GLOBAL CLIMATE CHANGE IN THE LATE. GEODYNAMICAL MOVEMENT IN CONTINENTAL SEAS ON THE MARGIN OF THE BALTIC CRYSTAL SHIELD (LAKE LADOZA, WHITE SEA, GULF OF FINLAND).
In order to determine the geochemical characteristics of the meteor impact, they analyzed Late Pleistocene sediments from the deepest part of Lake Medvedev, located in the central highlands of the Karelian Isthmus. Late Glacial to Holocene environments in the present-day coldest region of the Northern Hemisphere, evident from the pollen record of Lake Billyakh, Verkhoyansk Mountains, NE Siberia. Diatoms as indicators of the development of lake ecosystems" (1985) and the book series "History of Lakes", for which she prepared many thematic articles and edited some volumes.
Natalia Davydova was an active member of the Russian Geographical Society, chairing its paleolimnological commission for many years. For the book series "The History of Lakes" Natalia Davydova was awarded honorary diplomas of the Russian Geographical Society.
Evolution of lake ecosystems of the Northern Eurasia in the Past
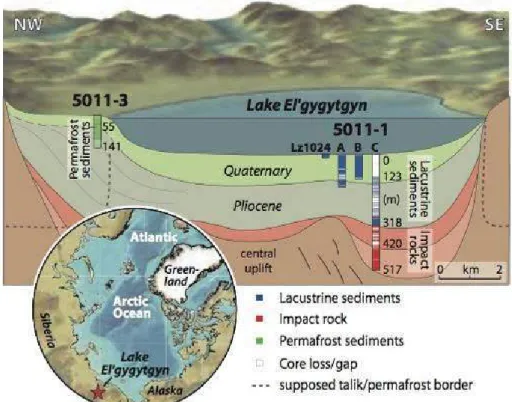
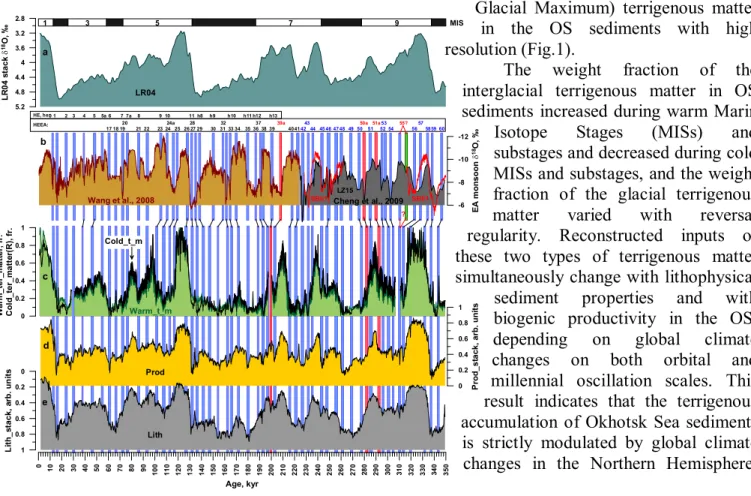
MILLION YEARS OF ARCTIC CLIMATE CHANGE FROM LAKE EL’GYGYTGYN, NE RUSSIA
Permafrost >100 m deep occurs throughout the bottom of the basin, but there is a continuous talik below the lake. The structure of the lake sediments reflects changes in climate, precipitation and vegetation changes on the lake catchment. In the middle part of the section (within the alluvium) there is a 1-m colored layer; vars are composed of silty sand, and may indicate a distal (shallow) part of proglacial lake.
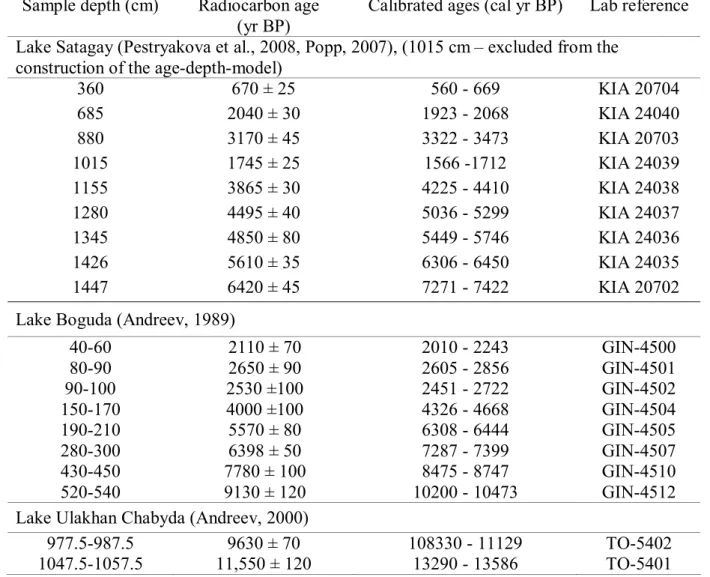
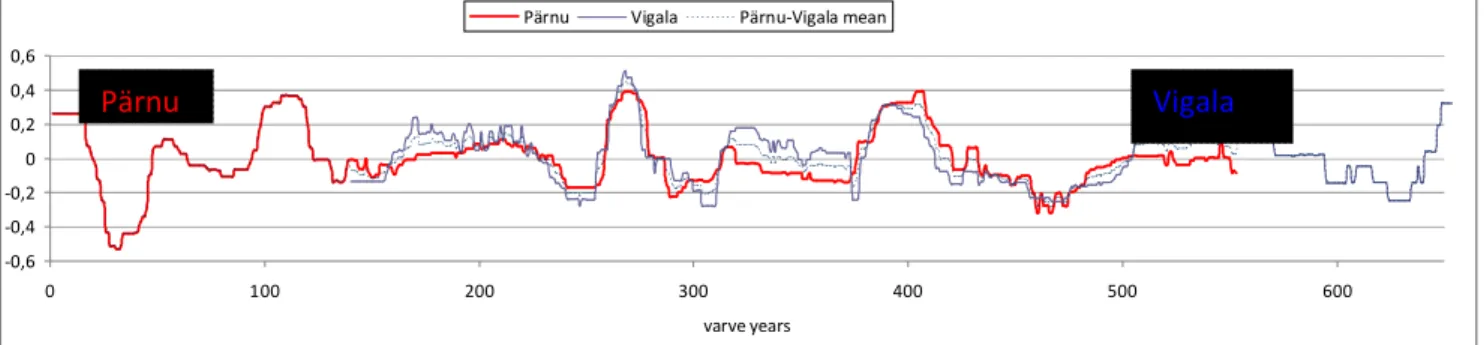
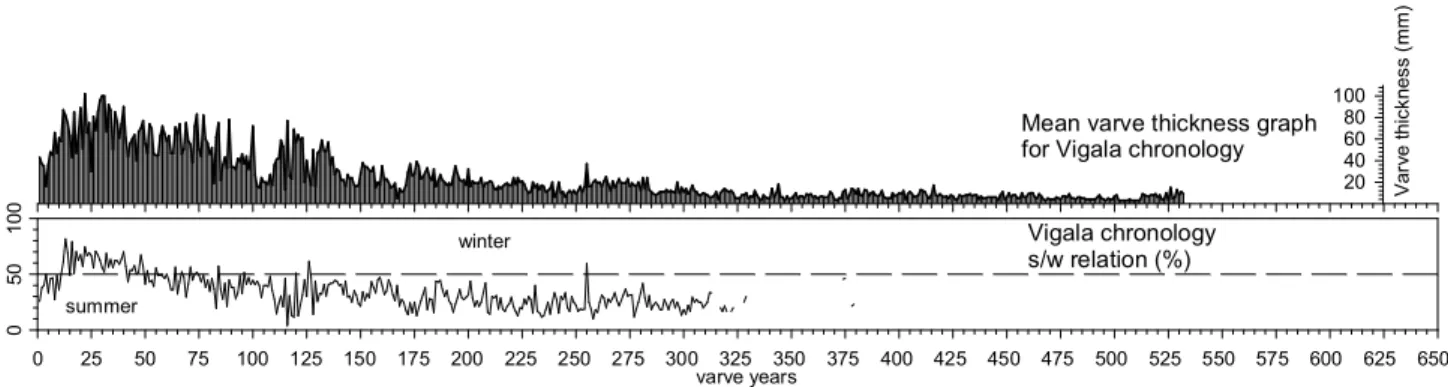
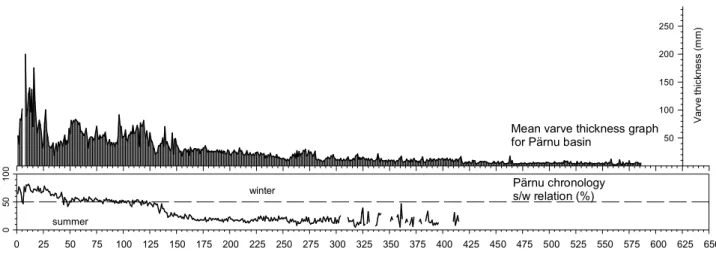
We previously showed that the layered sediments of the Shira salt lake (Khakassia) contain annual layers (varves) suitable for estimating the sedimentation rate in different parts of the core [1]. One of the most interesting is related to paleolimnological studies of Lake Kamyshovoe (Vishtynetskaya Hill, Kaliningrad Region of the RF). PALEOLIMNOLOGY EVIDENCE OF CHANGES IN THE LEVEL OF GREAT BASINS DURING THE HOLOCENE AGE - REVIEW OF SIGNS IN THE KARELIAN ISTMUUS AND.
(Pinus+Elm+Duk) . (Pinus+spruce+NAP) (Pinus+spruce+NAP)(Pinus+spruce+NAP)(Pinus+spruce+NAP). Pine+Spruce+Larch).
Paleontological, geological, geochemical and isotopic methods in paleolimnology
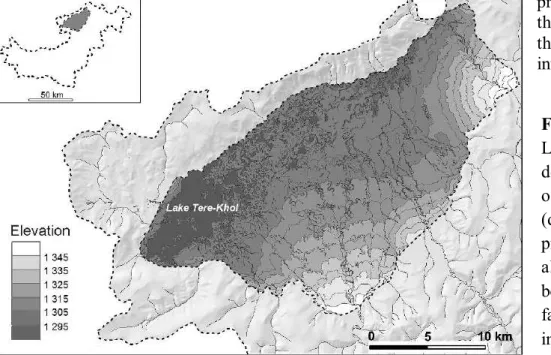
Map of Central Yakutia and area studies of the dynamics of the development of thermokarst lakes
The temporality of the thermokarst and its influence on the growth of trees varied depending on the climatic conditions of the period (fig.2). The analysis showed that the extent of the thermokarst boundaries changes in different periods resulting in the extinction of forest species growing adjacent to the thermokarst depression. The increase in average air temperatures during summer results in more sensitive melting of ground ice and, consequently, in the appearance of deeper thermokarst depression.
As a result of the ice wedge thawing, more will recede along the lake as a result tree stems slope towards the depression. According to our analysis, tree trunks originate under the influence of thermokarst depression and wind heels and form driftwood; further increase in the lake area leads to tree litter.
The reconstruction of thermokarst lake borders by the date of compression tree ring formation
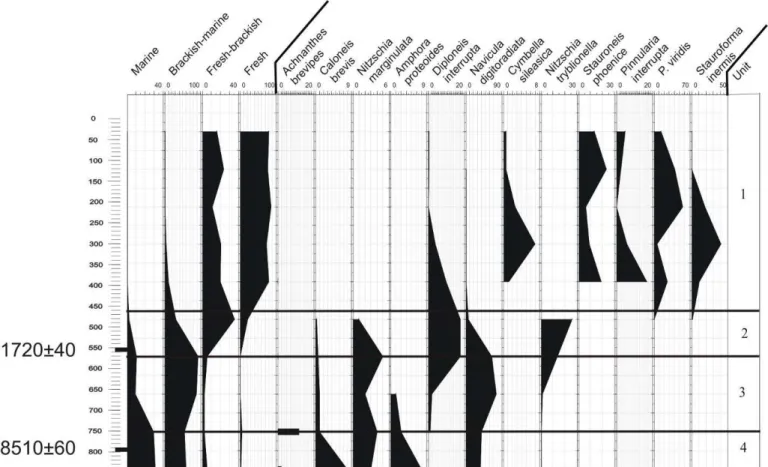
POST-GLACIAL AND HOLOCENE EVOLUTION STAGES OF THE WATER BODIES ON THE POMOR WHITE SEA COAST, BASED ON DIATOME ANALYSIS FROM BELOW. Stratigraphic subdivision of the sediments was first carried out in the field on the lithological basis and then by analysis of the composition of diatom complexes. The low degree of preservation of the valves and a high percentage of fragments indicate the redeposition of the sediments.
Marine species are either absent from the bottom sediments of the lakes, which lie at lower absolute marks (45-24.4 m) or occur as rare poorly preserved valves and fragments. The latter dominates together with Gyrosigma acuminatum in the sediments of the lakes located at higher absolute altitudes (49-46 m.a.s.l.), while Anomoeoneis sphaerophora and Navicula peregrine dominate in lakes with lower water mark m). The species of the genera Cymbella, Eunotia, Fragilaria, Staurosira are the most diverse incrusting forms.
The absence of relict diatom flora from some of the sedimentary horizons also suggests that periglacial conditions in the Late Glacial and Early Holocene periods persisted for a long period. Translocation of the White Sea coastline and glacioisostatic uplift in the Holocene (Kuzema area, North Karelia). Reconstruction of the relative position of the White Sea level in the Holocene on the Karelian coast, Engozero area, North Karelia.
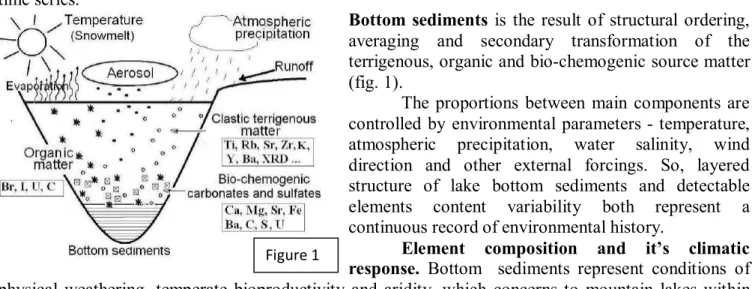
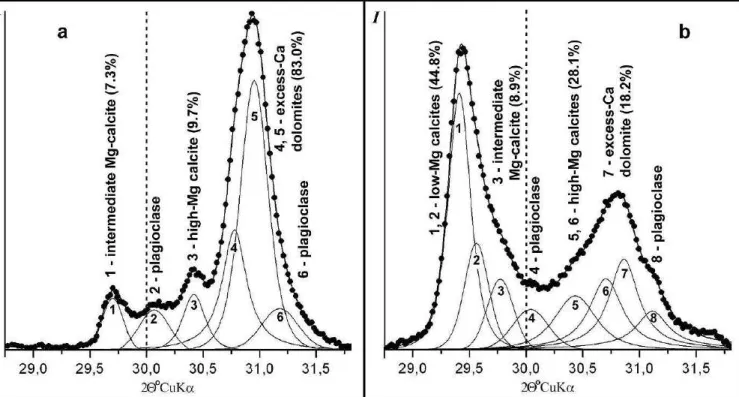
Diatoms from the bottom sediments of lakes on the coast of the White Sea, Sumsky Posad area, Karelia, Russia. The bottom sediments of these lakes are high-resolution paleoclimatic archives due to the fact that the small dimensions of the reservoirs predetermine their unique sensitivity to climate change. The endogenous carbonate mineral assemblage of Holocene lacustrine sediments consists of calcite, Mg-calcite with various Mg contents, Ca-excess dolomites, less commonly aragonite, monohydrocalcite, and rhodochrosite.
Holocene climate reconstruction based on a carbonate sedimentary record from the shallow saline Lake Verkhnee Beloe (west. Transbaikalia) // Russ. RECONSTRUCTION OF THE PALEOCLIMATE OF THE KARELIAN ISTHMUS IN THE LATE GLALACIAL AND HOLOCENE (EVIDENCE FROM LAKE ANALYSIS OF CHIRONOMIDS . MEDVEDEVSKOE). The dominant taxa of the upper zone are of the type Microtendipes pedellus, Dicrotendipes nervosus, Corynocera ambigua.
Paleolimnological reconstructions of environmental and climate changes in the Past
Introducing
Within the research project, which aims at a high-resolution reconstruction of environmental and climatic changes in the southeastern Baltic region since the Last Glacial Maximum, lake sediment sequences have been investigated in the Vishtynets Highlands applying a high-resolution sampling strategy high. Our paleogeographical investigations began in 2009 and include analyzes of sediment cores from peatlands and lakes.
Methods
Results
Holocene water levels and corresponding coastlines have been determined in the aforementioned microregions, including the Preboreal coasts. Additional factors were the discovery of desalinated water at the bottom of the water column section in Kandalaksha Bay. Based on the results of this research, the dynamics of Holocene sea level changes in the area of the Northern Siberian Islands were reconstructed.
In the lower part of the core sample, there are five levels with pronounced organic-rich layers. At the same time, no sudden changes in the water depth of the lake were found. On the issue of changes in the natural environment of the New Siberian Islands during the Late Pleistocene and Holocene.
In Collection of Scientific Articles: Stratigraphy and Paleogeography of the Late Cenozoic in the Arctic. The database currently contains 78 objects that have information on the age of the formation of Quaternary sediments in the area of the study (Figure 1). Sometimes only small relict pools surrounded by swamps remained at the site of the lake.
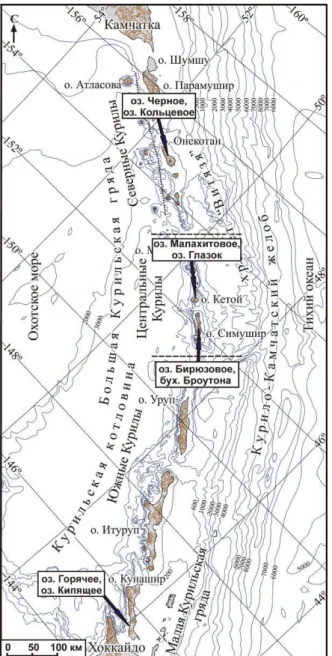
Features of the tsunami deposits are well detected in the layer accumulated during the passage of the same event. Main data on tsunami on the Pacific coast of the USSR Study of tsunami at the open ocean. Deposits of the largest lakes were found in the coastal cliff on the Okhotsk Sea side of the island south of Ivanovskiy Cape.
On the southeast of Kunashir Island, paleolake deposits were found in parts of the cliffs, the formation of which began in the early Holocene. The areas of positive magnetic susceptibility are located two-thirds of the way from the southeastern edge of the lake (Fig. 2). One of the well-known travertine deposits on the territory of Russia is the Izhora Plateau (Leningrad Province).
A list of participants
Il'ichev Pacific Oceanology Institute of the Far East Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Vladivostok, Russia. Institute of Limnology of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences, 664033, Ulan-Batorskaya st. Institute of Archeology and Ethnography of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Russia.
Names