The projection of the angular velocity on the rotating frame of the body is (doubly) periodic, with a quarter period. 5 Note that the function is homogeneous of degree 0 if viewed as a function of the (principal) moments of inertia (for fixed energy and momentum), or as a function of hand2. 12 The quarter periodT in the first line of the formula (for α) can be replaced by.
We consider a complicated case of the orbit of the orthogonal group, the orbit consisting of nilpotent matrices. In contrast to the nilpotent trajectories, the construction of the trajectories generated by the diagonalizable matrices is simple. The core of the nilponent matrix is not isotropic, but has isotropic subspaces.
The iteration process of the factorization and contraction produces a pair of the block-triangular matrices.
Solution
The structure of the resonance set of a polynomial of degrees is described in terms of partitions of number n. The main algorithms, described in the preprint, are organized as a library of the computer algebra system Maple. In casean= 0 one of the roots is zero, therefore the resultant can be written in the form.
The detailed structure of the resonance set (2) can be described using so-called ith generalized subdiscriminantsGD(i)p:q(fn), which are non-trivial factors of ith subresultants of a pair of polynomialsfn(px)andfn( qx). The functions p(n) and pl(n) return the number of all partitions and the number of all partitions of natural integer length, respectively. CONTINUATION: allows to obtain the parameterization of the entire manifold Vi+1 obtained in the previous step.
Example: FDA according to the KdV equation•. We illustrate the approach described above using an example of the KdV equation. The output is the left side of the FDA to (6), written in the conventional form as. The classical Newton-Puiseux algorithm constructs the roots of the polynomial f in the field Ω using the method of Newton dashed lines.
Then for each r > 0 the pair (yj,r, αj,r) can be found considering the Newton broken line of the polynomial. The field kj is a finite extension of the field and generated over all the elementsyj,i (actually by a finite number of them). Similar to the case of zero-characteristic the degree of the minimal polynomial of the elementij.
After this, the following elements of yj,ic can be found in a simple way using a version of Hensl's lemma. We studied the growth and fluctuation of the normalized amplitude function in sequences of Young's diagrams. A study of the growth of maximal and typical normalized dimensions of strict Young's diagrams.
On the other hand, the search for the generating function of discrete Chebyshev polynomials seems to be a more complicated task.
Khvedelidze and Torosyan
Eigenvalue decomposition for X − states
Applying the Peres-Horodecki separability criterion
2Hermicity and semi-positivity of the density matrix are assumed to be taken into account. The main problem in studying evolution is finding the most likely paths. The behavior of the model depends – as is typical for quantum mechanics – on the choice of time intervals between measurements∆ti.
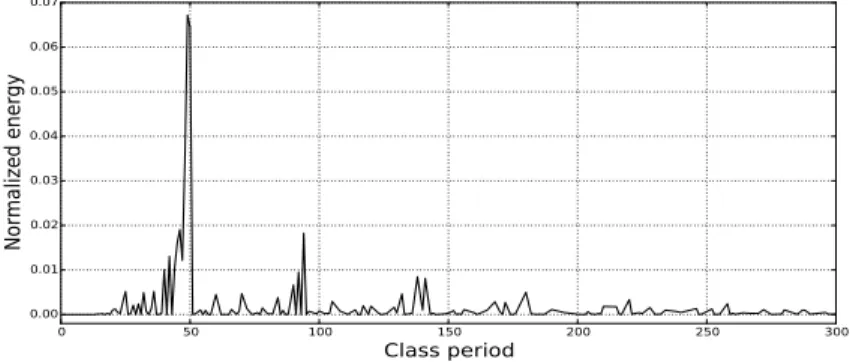
Of course, this definition is only approximate, because the unitary operator associated with the permutation contains many frequencies: they are the inverses of the lengths'1. K of disjoint cycles forming the permutation and the period of the permutation is equal to ordp = lcm K). Furthermore, the permutations of the dominant conjugation classes usually contain a small number of different frequencies and the definition becomes “almost exact”.
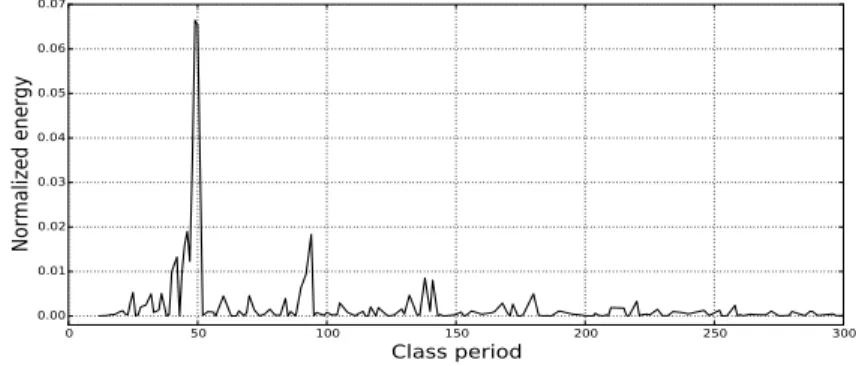
Figure 1 shows the "energy spectrum" of the dominant classes in group S50 in the range of periods [1,300]. The study of the model mentioned here using analytical methods seems to be problematic. 1Both the idea of the irreducibility of quantum randomness and Monte Carlo methods were actively promoted by John von Neumann.
So it is very easy to calculate the composition of relations as a relation of the corresponding matrices. Lagutinski's work on the theory of integration of differential equations was interrupted by his tragic death in 1915; Here they are considered from the perspective of modern computer algebra. Singer's theorem paves the way for the application of this method to the integration of differential equations in quadrature.
Coloring of a singular triangulation is a division of the set of its open simplices into classes (colors). Let X be a simple complex and let be a collection of affine homeomorphisms between some of the faces of X.
Introduction
An experience of provably programming a computer algebra library using a purely functional language with dependent types (Agda) is discussed.
Example with termination proof
Several examples are given that illustrate particular points when implementing the approach to constructive mathematics. The type check determines that it terminates because in the second line the left argument term 'm' of __+_ on the right side is syntactically less than the argument (suc m) on the left side. For more complex functions, the programmer is often supposed to aid type checking by introducing the counter expression.
The algorithm prime for determining the primality of nis is defined by searching all1 < m < n using m. If no prime number is found before, and it becomes cnt = 0, then n ≡ b is the necessary prime number . But it performs strangely at runtime: (nextPrime 31) hangs for a very long time.
So: one bound is easy to prove but expensive to compute at runtime, the other bound is fast to compute but hard to prove. Otherwise, search again from 1+pup to (bound p). This program 1) is checked, including interrupt, 2) has a fast comparison in the search loop. But what is the way out in the case where an "expensive" binding like the one above is proven, and no better binding is known at all.
In Search-II, set forbound2 to an infeasible number - one that will never be reached in practice in the above loop (I take this solution from Ulf Norell's message). In fact, this infeasible bound trick partially replaces Markov's principle in constructive mathematics. This principle [2] allows a contradiction proof for a termination proof and it cannot be implemented in Agda without using.
Refuting the two prejudices
Several books have been devoted to the theory of Painle's equations [1], [2]. Painle's equations can be generated via linear Heun equations [3, 4, 5]. In this way our package can cover all Heun equations and Painleve equations presented in the NIST project [6]. We present the structure of our package and give results of special calculations. We show that a suitable generalization of the oriented area function is a perfect Morse function in the space of three-dimensional configurations of an equilateral polygonal connection with an odd number of edges.
A hypothetical Turing machine using an innit tape containing initial values as input and a number as a time interval can compute the state of the system given timed real numbers. Based on the works of Sitnikov and Alexeyev, we can deduce that a particular case of the three-body problem is so combinatorially rich that no Turing machine can find the solution in polynomial time. Tasks with verifiable answers are those tasks for which a student's answer can be automatically checked based on its statements.
This means that a teacher only needs to provide a statement for an assignment, and does not need to provide an answer, usually does not need to solve an assignment, but the assignment can still be checked automatically. Comparative experience with the use of different computer tools in the international competition "Bebras Construct-Test-Explore" and the Olympiad on discrete mathematics and theoretical informatics is presented in the report. One of the reasons lies in the existence of so-called apparent singularities, which correspond to suitable parameters, but for which a monodromy matrix is trivial.
Among Fuchsian singularities, one can distinguish apparent singularities near which the general solution y(z) is a holomorphic function. We show in examples that if we have an equation without apparent singularities, the equation for the derivative of a solution has apparent singularities. At the ordinary point in a differential equation, Cauchy data can be set up, and afterwards all other derivatives of a solution can be calculated via the differential equation.
However, in the case of apparent singularity, the derivative of order equal to or higher than the order of the equation may be arbitrary. Any linear differential equation with polynomial coecients containing apparent singularities can be obtained as a.
Any linear dierential equation with polynomial coecients containing apparent singularities can be obtained as an
Any linear dierential equation with polynomial coecients containing apparent singularities can be transformed to
On the other hand, if a cubic form has sufficiently small rank, then the corresponding hypersurface is invariant under a nonidentity birational involution of the complex projective space. Let us focus on cubic hypersurfaces that are invariant under a nonidentity birational involution of complex projective space. A hypersurface given by formf is smooth if its gradient∇f is nonzero outside the origin; otherwise it is singular.
The general cubic form in four variables is not equivalent to any form of type y20y3+g(y1, y2, y3). Let us assume that the general cubic formf in four variables is equivalent to a form of typey02y3+g(y1, y2, y3). The matrix H is equal to the sum of the diagonal matrix diag(6x0, . . ,6xn) and the matrix with values 6αiαj`.
The corresponding cubic hypersurface is invariant under a nonidentity birational involution of the surrounding projective space. If there is a regular involution of an open set of the surface with a unique singular point, then the point is fixed under the involution. At a single point of the section the hyperplane h= 0 coincides with the tangent plane of the hyperplane f = 0.
According to the Alexander–Hirschowitz theorem [2], the rank of the general cubic form in four variables is equal to five. Institute of Information Transmission Problems of the Russian Academy of Sciences (Kharkevich Institute) Moscow, Russia. By developing C. Jacobi's approach, we present interpolants based on Hankel polynomials generated by the sequences {PN.
The problem of interpolating the given data set{yj}Nj=1 by the set{p(xj)}Nj=1. The extension of the results of sections 1 to 4 to the multivariate case is also a subject of future research.