– Vol-7, Special Issue3-April, 2016, pp1117-1129
http://www.bipublication.com
Case Report
Identification and ranking barriers and drivers of e-commerce with the
approach of organizational agility and fuzzy logic
(Case study: public and private banks selected by city of Shiraz)
1
Abdolreza Naddaf, Salalah Sadeghi2* and 3Laleh Mohammadi
1Assistant Professor, Faculty of Management,
Shiraz University, Iran Dr.arnadaf@gmail.com
2Graduate Student, Faculty of Management,
Islamic Azad University, Fars Science and Research Branch, Iran
Sadeghi.solale@gmail.com
3Graduate Student, Faculty of Management,
Islamic Azad University, Fars Science and Research Branch, Iran
laleh2.mohammadi@gmail.co
ABSTRACT
The rapid and increasing expansion of e-commerce through web sites and portals has caused identification and measurement of critical factors of e-commerce to be considered an essential and necessary affair. The main objective of this research is to identify and rank the barriers and motives of e-commerce with organization agility and fuzzy logic approach (Case Study: public and private banks selected from Shiraz city). Hence, the conceptual model was created based on the research literature and theoretical framework to assess the barriers and motives of e-commerce and organization agility. Methodology is quantitative of descriptive - survey type.
The tool used in the research is questionnaire. For this purpose, 200 employees of public and private banks selected from Shiraz city have been selected in random sampling method by using Morgan Table. Then the questionnaire has been filled by them. 30 experts were also selected for paired comparisons questionnaire sample. The questionnaires' validity has been measured by using review of specialist professors' views. Questionnaires' reliability was evaluated by Cronbach's alpha criterion. Here Cronbach's alpha has become 0.93. Multiple Criteria Decision Making technique (MCDM) and Fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) and Expert choice software were used in this research meantime analyzing and evaluating factors of barriers and motives of e-commerce for evaluating and ranking them. Deterrent factors of e-commerce in bank and driving factors of e-commerce in bank and organization agility were identified. Then the importance degree of each of them was determined in order of priority.
Keywords: e-commerce, barriers, motive, agility, fuzzy logic.
1.INTRODUCTION
New Era that is known as the era of information and knowledge promises a new world with new ways of using information and knowledge (Babaei, 2002). E-commerce phenomenon is of very important subjects of Information and
e-banking. Impressive development of information and communication technology has changed the world and consequently the banking world (Kohzadi, 2002). One of the most important factors of companies' survival and progress in today's dynamic environment is their agility. Agility in banking domain is not only meant speed in implementation of current affairs, but also meant bank's flexibility and agility.Agility paradigm or the same paradigm of the 21st century was provided in order to adjust and adapt to business environment changes, as well as to empower employees to respond quickly to the needs of market and customer (Goldman & Nagel, 1993; Gunasekaran, 1998). Foundation and base of agile organization is integration of information system / technology, people (employees), commercial processes and equipment, coordinated and flexible inter-organization to respond quickly to events and changes in the environment.
In general, agile organization can lead to lower production costs, increasing market share, satisfy needs of customers, facilitate the rapid introduction of new products and the elimination of non-value added activities and improve organization competitiveness. So, agility is posed in the current era as a commercial paradigm of twenty-first century and as a successful and winner strategy (Lin & et al, 2006). Today, the importance of e-commerce is obvious for everyone.
This issue has been also emphasized in Iran.But it has not very satisfactory position in terms of the amount of benefit from this type of commerce in the global arena. Development of e-commerce is facing with several barriers and challenges in Iran (AkhavanSaffar, 2013). Iran is not in a proper situation in the field of the necessary infrastructures as it should be. However researches show that moving toward expansion and more and more appropriate use of Internet has begun in the country.
Lack of proper culture of coping with the phenomenon of e-commerce and false thought, as well as negative treatment of businessmen,
physical distribution units and customers with e-commerce is considered an important barrier to the growth of this phenomenon (Mahdavi and RezaeeDoust, 2007; Jafarnejad et al., 2009; Khani, 2007).Fuzzy logic is a new technology that replaces and / or to a great extent completes conventional methods for designing and modeling a system that requires advanced and fairly complex mathematics.
Fuzzy logic performs this by using expert's knowledge and with the aim to simplify or make more efficient the system design. This theory is able to mathematically formulate many of the concepts, variables and systems that are inaccurate and ambiguous (as in the real world is also often such this).
It provides the context for reasoning, inference, control and decision making in uncertain conditions (Taheri, 2008).Considering that the multi-criteria decision-making methods are usually associated with criteria that have different importance for decision makers, therefore, it is necessary that an information to be existed about the relative importance of the criteria. This importance will be achieved by determining the weight for each criterion.
Extraction of weights is considered as key measure to understand the priorities of decision-makers. The more weight, it can be said that the criterion is associated with more importance in the attainment of general interest (Mir Katouli and Kanaani, 2011). .
2. RESEARCH LITERATURE
To know more and more concepts of e-commerce and fuzzy logic, each of these concepts will be defined separately.
2.1 E-commerce: e-commerce has different definitions in various references because of being new and also because of extremely diverse usages and contexts of activity. No single definition of e-commerce has been provided so far. Perhaps there is a definition of e-commerce in the number of authors of articles related to this topic (Sokol, 1995). Some of them are referred:E-commerce is a kind of commerce that is based on electronic processing and transmission of data including text, voice and image. This commerce contains diverse activities such as electronic exchange of goods and services, instant delivery of digital issues, electronic funds transfer, electronic stock exchange, electronic waybills, commercial plans, joint design and engineering, direct marketing, and after-sales services (Sokol, 1995).
E-commerce is an equivalent term for purchase and sale of products, services and information by network infrastructures (Kalakota&Whinston, 1997).E-commerce means exchange of products and services in exchange for money and by using Internet abilities (Erl, 2000).
2.2 Agility: many definitions have been suggested for agility so far. But none of them is against each other and do not violate each other. These definitions generally show thought of speed and understanding of environmental changes in order to respond to them appropriately (Huang &Nof, 1999; Zain& et al, 2005).Agility according to some authors' statement asks organization to accelerate in integration of technology,
employees, and management with
communicational infrastructure.
So that it shows appropriate response to the changing needs of customers in a market environment that has constant and unpredicted changes. So, agility is the organization's ability to create the necessary information for management decision making in turbulent and chaotic environment (Agarwal& et al, 2007).Agility in
term is combined operations of several companies, each of which has its own particular skills and competencies, and has common operational collaboration together. This affair enables partner institutions (with a common profession) to adapt and respond to changes according to the needs of customer (McKenzie & Aitken, 2012).
2.3 Fuzzy logic: Professor LotfiAsgarZadeh introduced fuzzy sets for the first time in 1965 (L.A.Zadeh, 1965). These sets were base of a successful way for model of uncertainty and ambiguity (John &Coupland, 2007). Being fuzzy means being multivalued, and in contrary, being two valued is placed, in which there can be only two answers or states for each question and / or concept (right or wrong, black or white).In fact Aristotelian logic can be considered a special state of fuzzy thinking (Burrough& et al, 1992). This theory was expanded based on this hypothesis that the key components of human thoughts are not numerical (Zimmerman, 1982). Fuzzy logic is a new technology that replaces and / or to a great extent completes conventional methods for designing and modeling a system that requires advanced and fairly complex mathematics. Fuzzy logic performs this by using verbal values and conditions or in other word expert's knowledge and with the aim to simplify or make more efficient the system design.This theory is able to mathematically formulate many of the concepts, variables and systems that are inaccurate and ambiguous. It provides the context for reasoning, inference, control and decision making in uncertain conditions (Taheri, 2008).
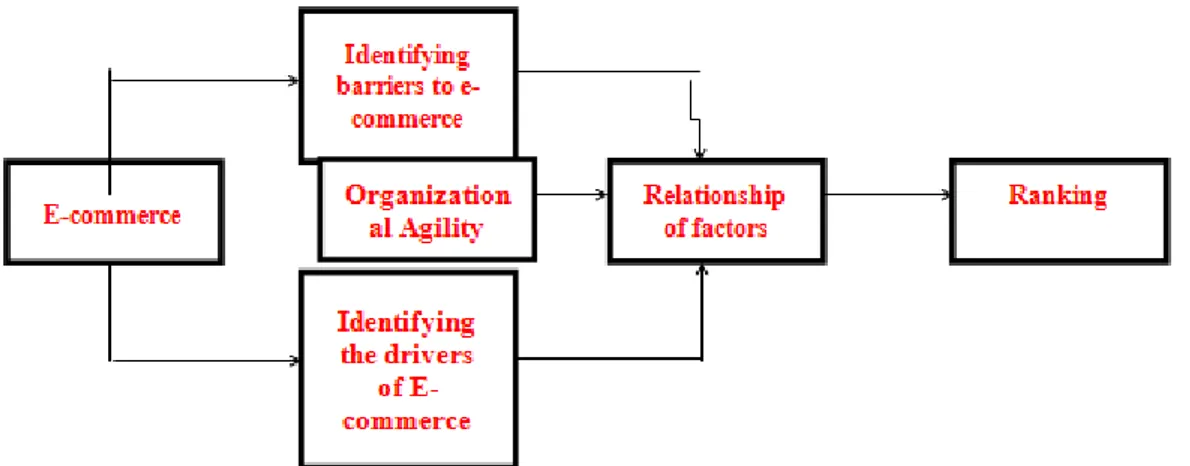
2.4 Conceptual model of research
In this study due to lack of a model appropriate to the cultural and social conditions of the country, was tried, with considering the researches, previous studies and existing models;
Figure 1: Conceptual model of research
2.5 Research questions: 2.5.1The main question
What are the most important barriers and drivers of e-commerce in Shiraz banks? 2.5.2. Secondary questions of research
What are the factors hindering of the e-commerce in the bank? What are the driving factors of the e-commerce in the bank? What are the indices of organizational agility in the bank?
What is the importance degree of each of the hindering and drivers factors in the bank?
3. METHODOLOGY:
This research in terms of goal is an applied research and in terms of data collection is descriptive - survey. Statistical population of this research includes experts, specialists and experts familiar with the issue of e-commerce and its related issues, especially electronic banking and stakeholders involved in its implementation in the city of ShirazBecause of the difficulty of identifying and defining correctly and also detect and estimate it to institutions such as "Ministry of Science, Research and Technology", "Organization of Management and planning", "High Council of informing" and "High Council of Informatics" to identify individuals with history of academic and administrative and above characteristics the staff of elected public and private banks in city of Shiraz, preliminary and initial list of people were prepared who have the above characteristics.Then preliminary list more complete and ultimately statistical population consists of 420 employees were selected from
staff of public and private banks.According to population of research in this study, random sampling method and the type of stratified has been used. The sample size was estimated by using Morgan table as 200 people and the simple random sampling method has been used to collect data. 30 experts were selected as respondents for selective sample of paired comparisons questionnaire.
3.1 Methods and tools for data collection: 3.1.1 Questionnaire: In this study related questions of barriers to e-commerce is driven from a standardized questionnaire "Barriers to E-commerce" written by Jafarnejad and colleagues (2009). Questions related to drivers of e-commerce and agility of the organization is compiled by researcher and it is hoped to be the basis for future research.Since the research methodology of this research had been fuzzy
MCDM techniques. The use of paired
of work and the easy availability of responses. Questions of questionnaire have been shown to the breakdown of research variables in Table 2.
3.1.2 Questionnaire validity and reliability: Questionnaires used in this study are standard questionnaires. Also in this study, the initial plan of questionnaire was prepared to enhance validity and reliability of before the distribution among the statistical population by 9 experts of topic was investigated, ranging from marketing professors, banking managers and e-commerce experts, that as a result cases was proposed to reform, the final
questionnaire was developed after the applying the reforms.
To determine the "reliability" of the research, designed questionnaire were tested in a pilot sample study of eleven-samples. By using Cronbach's alpha method reliability of research tools was calculated as 93% that it is at a high level. As a result, it can be claimed that above tools is reliable enough.Range of fuzzy and fuzzy verbal phrases used in this study has been shown in Table 1 that these words ultimately in matrix of paired comparisons have become to fuzzy numbers (Yuksel, 2010).
Table 1: Range of fuzzy and fuzzy verbal phrases
Verbal Expressions Fuzzy number
Prefer is completely equal (1,1,1)
Prefer is approximately (0.5,1,1.5)
Prefer is low (1,1.5,2)
Most preferred (1.5,2,2.5)
Prefer is too much (2,2.5,3)
Prefer is quite a lot (2.5,3,3.5)
3.1.3. Statistical population:
The study population of this research includes employees of governmental and private banks in city of Shiraz and sampling method in this research is random sampling method in this research because the entire population of this study is similar with each other and is homogeneous and uniform.
Table 2: questionnaire questions to the breakdown of questions
Motives for E-commerce (D)
D1: education and making culture
D11: spreading the culture of proper and effective application of E-commerce D12: practical training for customers on how to using E-commerce services D13: incentives necessary for Internet banking users
D2: availability
D21: qualitative and quantitative development of skilled manpower in the field of e-commerce D22: want to work with the site even with low speed of Internet connection
D23: the possibility of enjoying the Internet with low cost D3: Supporting the government and people
D31: the development of e-commerce
D32: ensuring security of site and networks banking
D33: focusing on the private sector in national implementation plans and projects related to e-commerce
D4: programs leading of bank
D41: good infrastructure to introduce economic benefits using e-commerce D42: creating the feel the need to in customer to e-commerce
Criterion Dimension - Questions (sub criteria for level 2 and sub criteria for level 3)
Barriers to E-commerce
(B)
B1: technical barriers and hardware
B11: difficulty in continuous updating of systems and software relating to trade
B12: insufficient investment in the field of application of e-commerce
B13: inadequate and Inappropriate access to means of communication in the field of
e-commerce development
B2: Financial and software problems
B21: the high cost of purchasing and installing the software and hardware necessary
B22: the high cost of resources necessary for the establishment and development of
e-commerce
B23: Lack of Iran's membership in the World Trade Organization
B3: Customs issues, trade and tax
B31: inadequate free competition and the lack of adequate equal opportunities in sectors of
the economy
B32: being governmental of a large part of economy of the country and the non-risking of
the private sector to enter the e-commerce arena
B33: inappropriate existence of macroeconomic policies and strategies and Modernity in
Iran and A strong emphasis on traditional economic development strategies
B4: legal problems, legal and Customs representative
B41: improper copyright law and security and encryption
B42: risk of exposing the secrets and personal information and inadequate support of
personal data
B43: lack of legal infrastructure necessary for e-commerce
B5: problems and barriers related to informational infrastructure
B51: slow speed of Internet in Iran
B52: poor electronic economic deployment such as electronic financial and credit
B53: insufficient promotion of knowledge of users and users of e-commerce
B6: humanitarian problems, educational, cultural
B61: being insufficient of electronic banking and payment standards for establishing
coordination among banks and financial institutions to electronic funds transfer
B62: The required insufficient manpower skills and being inadequate of infrastructures of
humanitarian capital such as skill...
B63: inefficient making culture in government and people
A1: Technologies used
A11: amount of use of Portal
A12: amount of use of databases
A13: amount of use of management information system (MIS)
Agility
)A(
A21: speed of service delivery to customers
A22: time duration of doing processes and activities between units
A23: receiving and sending speed and data processing and data extraction and reporting
A3: Competence
A31: brand and reputation and good image
A32: electronic services for 24 hours without interruption
A33: financial coverage (insurance financial) against any and all misuse and possible
mistakes
A4: Accountability
A41: assistance in the event of a problem in the use of services and compensation for
occurring defects
A42: the possibility of receiving support services (responding to customer problems) by
communicating online, via phone and email.
A43: quickly and effectively respond to customer complaints
A5: Flexibility
A51: flexibility to provide the type and number of services
A52: non-predictability, flexibility and risk management are factors that are received more
value to predictable, stable, ensuring the kind of future events
A53: moving from stable jobs to more flexible roles
4. ANALYSIS OF THE DATA:
Descriptive and inferential statistical methods have been used to analyze the data. Mean, median, frequency tables, frequency percentage and charts has been used in descriptive level.
4.1 Descriptive statistics: about 79% of the respondents were men and 21% of the respondents were women. In terms of age, most respondents were in the age range of 35 and older that constituted the 42.5% of the total participants. After that 26.5% in the age range of 26-30 years, 26% in the age range of 31-35 years and the remaining 5% were in the age range of 20-25 years.In terms of work experience, 6% of respondents had work experience of 5 years or less, 21% with history of service from 6 to 10 years, 25.5% with history of service from 11 to 15 years and 47.5% remaining had history of serving more than 15 years .In terms of education level, 7% had an associate's degree, 41% had bachelor's
degree, 50% master's and 2% had doctoral degree or higher.
4.2Inferential statistic: Since the most important component in this area is making decision
considering multiple considerations
simultaneously, so multi-criteria decision-making methods (MCDM) have allocated highest usage to self. Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) is a multi-criteria decision-making techniques) Razavi and Alaghebandan, 2007), which it has been used in this study.
4.3Fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Process
normalized method of Sati and was developed by using Fuzzy triangular numbers, was welcomed by researchers (Zanjirchi, 2011).
Steps of doing this method are as follows:
Step 1: drawing a hierarchical tree. In this stage at first, hierarchical structure of decision by using target levels, criteria and sub-criteria to be traced. This tree has been shown in Figure 1.
Step 2: forming matrix of paired comparisons. At this step we form adaptive matrix in accordance with the decision tree and use of experts’ opinions and then inconsistency rate is calculated according to the method of Gogoos and Boucher (1998). Step 3: this step is step of calculation of arithmetic mean of opinions.
Step 4: the total number elements of the row is calculated at this step.
Step 5: This step is step of normalization of the weights of rows.
Step 6: degree of probability of being greater is determined at this step.
Step 7: This step, step of weights vector is normalized.
Step 8: This step, in combination weights in order to obtain priority (Zanjirchi, 2011).
4.4Computation of fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy ProcessBy using Chang method
By using the hierarchical tree (Figure 1) and by following the steps of fuzzy process that was mentioned above, Under experts' opinions (by converting verbal phrases to the triangular numbers according to Table 1) aggregation, and in order to ensure compatibility of matrices inconsistency rate is calculated according to the method of Gogus& Boucher, 1998 and then weight of each of the criteria for levels of two and three of hierarchical structure is calculated. To calculate the final weight we multiply each of third level sub criteria in weight of standard to related to the second level.Tables 3 and 4, show the weight of sub criteria for level of 2 and 3. Paired comparison matrix to barriers of e-commerce is consistent with CRm = 0.038 and
CRg = 0.054.degree of sub criteria priority for level 2 to barriers of e-commerce is as follows: 1. Human being, educational and cultural 2. Informational 3.Customs representative, trade and tax 4.Technical and Hardware 5.Financial software 6.legal, Legal and Security.Matrix of Paired comparison to drivers of e-commerce is consistent with CRm = 0.077 and CRg = 0.063.degree of sub criteria priority for Level 2 to drivers of e-commerce includes: 1. availability 2. Education and making culture 3.Leading plans of Bank 4. Government and public support.Matrix of Paired comparison to organizational agility is consistent with CRm = 0.038 and CRg = 0.054. Degree of sub criteria priority for Level 2 to agility of the organization is: 1. competence, 2. technologies used, 3. speed, 4. Accountability, 5. Flexibility.Summary of results obtained from research and degree of sub criteria priority level 3 to relevant sub criteria in level 2, has been shown in Tables of 3 and 4 and 5.According to Table 6, it can be seen that human factors with a weight of 0.188, informational factors with weight of 0.186 and Customs representative and commercial and fiscal factors with the weight of 0.181 have the most important role among barriers of electronic commerce. Software factors and legal factors respectively are barriers with less weight. According to Table 7, factor of availability with a weight of 0.373And education factor and making culture with 0.321 weights. And factor of programs leading for banks are with a weight of 0.306 of the most important drivers of e-commerce. And factor of government support is of other factors with less weight.
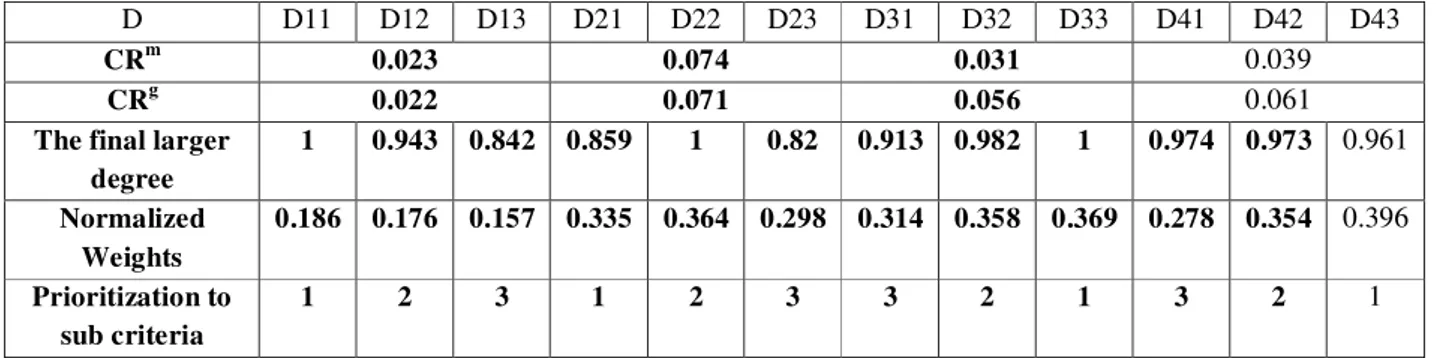
Table 3: degree of sub priority criteria for Level 3 to relevant sub criteria in Level 2(drivers of e-commerce) D43 D42 D41 D33 D32 D31 D23 D22 D21 D13 D12 D11 D 0.039 0.031 0.074 0.023 CRm 0.061 0.056 0.071 0.022 CRg 0.961 0.973 0.974 1 0.982 0.913 0.82 1 0.859 0.842 0.943 1
The final larger degree 0.396 0.354 0.278 0.369 0.358 0.314 0.298 0.364 0.335 0.157 0.176 0.186 Normalized Weights 1 2 3 1 2 3 3 2 1 3 2 1 Prioritization to sub criteria
Table 4: degree of sub priority criteria in Level 3 to relevant sub criteria related in Level 2 (Barriers of e-commerce)
B63 B62 B61 B53 B52 B51 B43 B42 B41 B33 B32 B31 B23 B22 B21 B13 B12 B11 B 0.058 0.05 0.077 0.015 0.084 0.038 CRm 0.079 0.76 0.051 0.047 0.094 0.074 CRg 0.939 0.937 0.961 0.728 0.695 1 0.94 0.795 0.966 0.931 0.952 1 0.613 0.784 1 0.982 1 1 The final larger degree 0.245 0.244 0.25 0.156 0.149 0.214 0.254 0.215 0.261 0.323 0.33 0.347 0.256 0.327 0.417 0.329 0.335 0.335 Normalized Weights 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 3 2 1 3 2 1 3 2 1 Prioritization to sub criteria
Table 5: degree of sub priority criteria in Level 3 to the relevant sub criteria in level 2 (organizational agility)
A53 A52 A51 A43 A42 A41 A33 A32 A31 A23 A22 A21 A13 A12 A11 A 0.028 0.012 0.046 0.087 0.05 CRm 0.054 0.023 0.068 0.061 0.076 CRg 0982 1 1 0.931 0.962 1 0.939 1 0.937 1 0.94 0.966 0.695 0.728 1
The final larger degree 0.329 0.338 0.342 032 0341 0.356 0.245 0.261 0.244 0.27 0.254 0.261 0.149 0.156 0.214 Normalized Weights 3 2 1 3 2 1 2 1 3 1 3 2 3 2 1
Prioritization to
sub criteria
Table 6: The final weight of sub-criteria to criteria of e-commerce barriers
B63 B62 B61 B53 B52 B51 B43 B42 B41 B33 B32 B31 B23 B22 B21 B13 B12 B11 B 0.069 0.051 0.098 0.077 0.056 0.096 0.01 0.023 0.048 0.06 0.063 0.021 0.035 0.037 0.036 0.052 0.057 The final decisive weight of sub criteria for Level 3
0.188 0.186 0.114 0.181 0.161 0.171 The final decisive weight of sub criteria for Level 2
Table 7: The final weight of sub-criteria to criteria of the drivers of e-commerce
D43 D42 D41 D33 D32 D31 D23 D22 D21 D13 D12 D11 D 0.079 0.075 0.074 0.084 0.068 0.045 0.089 0.1 0.098 0.08 0.082 0.086
The final decisive weight of sub criteria
for Level 3
0.306 0.289
0.373 0.321
The final decisive weight of sub criteria
Table 8: final weight of sub-criteria to standard of organizational agility
A53 A52 A51
A43 A42
A41 A33
A32 A31 A23
A22 A21 A13
A12 A11 A
0.05 0.056 0.078
0.081 0.208
0.089 0.087
0.12 0.098 0.048
0.57 0.096 0.045
0.019 0.06
The final decisive weight of
sub criteria for Level
3
0.154 0.172
0.189 0.179
0.188 The final
decisive weight of
sub criteria for Level
2
In Figure 2, the final weights of sub criteria in level 2, according to Tables 6 and 7, has been drawn and indicate the prioritization of sub criteria in level 2, with breakdown of barriers criteria and drivers of e-commerce.
Figure 2: The final weights of sub criteria in level 2
And ultimately final weights of sub criteria for level 3, without breakdown of barriers criteria and drivers of e-commerce have been shown in the bar graph 3.
5. CONCLUSION:
Research findings show that for the first sub-question entitled "What are deterrent factors of e-commerce in the bank?" Human factors with weigh of 0.188, information factors with weigh of 0.186, and customs, commercial and tax factors with weigh of 0.181 have the most important role among barriers of e-commerce. Software factors and legal factors are of the barriers with fewer weights, respectively. For the second sub-question entitled "What are the driving factors in e-commerce in the bank?"Availability factor with weight of 0.373 and education and culture-making factor with weight of 0.321, and bank leading programs factor with weight of 0.306 are of the most important drivers of e-commerce. Government support factor is of the other factors with less weight. For the third sub-question entitled "What are the factors of organizational agility indices in bank?"Competence factor with weight of 0.189, technology factor with weight of 0.188, speed factor with weight of 0.179 are of the most important criteria compared to agility index in e-commerce. Factors of responsiveness and flexibility are of the other effective factors. For the fourth sub-question entitled "Which of the deterrent and driving factors are more important?" Deterrent factors (barriers) of e-commerce in the bank in order of priority are: 1- human, educational, cultural, 2- informational, 3- customs, commercial, and tax, 4- technical and hardware, 5- financial and software, 6 - legal, juridical, and security. Human, educational, and cultural, informational, customs, commercial and tax components have the greatest weight. This means these barriers should be turned into strengths for advancement of e-commerce. Also, from the aspect of the driving factors (drivers) of e-commerce in bank in order of priority are: 1- availability, 2- education and culture-making, 3- bank leading programs, 4- government and people support. Components of availability, education and culture-making have the greatest weight, so that they have the largest
share in expansion of e-commerce in organizations.
5.1: Suggestions for conducting future researches:
- Identification of barriers and drivers of e-banking.
- Evaluation of barriers posed in establishment of e-commerce in Iran by various industrial sectors. - Evaluation of knowledge management in development of e-commerce in Iran.
- This research to be conducted in larger population.
- Evaluation of success measurement criteria in implementation of e-commerce in Iran by various sectors
- Evaluation and comparison of companies that use e-commerce system and those who traditionally continue to work.
6. REFERENCES:
1. Agarwal, A., Shankar, R. &Tiwari, M. K., (2007), Modeling agility of supply chain. Industrial Marketing Management. Vol. 36. No. 4. Pp. 443-457
2. Burrough, P. A., R.A. Macmillan., W. Van Deursen., (1992), Fuzzy classification methods for determinig land suitability from profile observation and topography, J. Soil Sci., 43: 193-210
3. Erl H. P., (2000). The Emergency Of Electronic Commerce and Electronic Forms Of Money. Master Thesis, Technical University 4. Gogus O., Boucher T. (1998). Strong
transitivity, rationality and weak monotonicity in fuzzy pairwise comparisons, Fuzzy Sets and Systems, Volume 94, Issue 1, Pages 133-144 5. Goldman, S., & Nagel, R., (1993),
Management, Technology, and Agility: The Emergence of new Era in Manufacturing. International Journal of Technology Management. Vol. 8. No. 1/2. Pp. 18-35
6. Gunasekaran, A., (1998), Agile
manufacturing: enablers and an
Journal of Production Research. Vol. 36. No. 5. Pp. 1223-1247
7. Huang, C., &Nof, S. Y., (1999), Enterprise agility: a view from the PRISM lab. International Journal of Agile Management Systems. Vol. 1. No. 1. Pp. 51-59
8. Ives, C., (2000), E-Business and E-Commerce, Managing Information Journal, January / February
9. John. R. and Coupland. S., (2007). "Type-2 Fuzzy Logic: A Historical View," Computational Intelligence Magazine, IEEE, Vol. 2, pp. 57-62, 2007
10.Kalakota, R. and Whinston, A., (1997), Electronic Commerce. A Manager's Guide, Addison Wesley, Reading, MA
11.L. A. Zadeh, (1965). "Fuzzy Sets," Information and Control, Vol. 8, pp. 338-353 12.Lin, C., Chiu, H. & Tseng, Y., (2006), Agility
evaluation using fuzzy logic. International Journal of Production Economics. Vol. 101. No. 2. Pp. 353-368
13.McKenzie, Jane & Aitken, Paul, (2012), Development of digital product catalogue for enabling agility in a manufacturing organization, Strategic HR Review, Vol. 11, Issue: 6, pp. 12-31
14.Sokol, P. K., (1995), From EDI to EC: A Business Initiative. New York: McGraw-Hill 15.Yüksel, ì. & Da Hdeviren, M. (2010). Using
the fuzzy analytic network process (ANP) for Balanced Scorecard (BSC): A case study for a manufacturing. Systems with Applications, 37, 1270-1278
16.Zain, M., Rose, R. C., Abdullah, I. &Masrom, M., (2005), The relationship between information technology acceptance and organizational agility in Malaysia. Information & Management. Vol. 42. No. 6. Pp. 829-839 17.Zimmerman, H. (1982). Fuzzy set theory and
its application. Bostan: Kluwer-Nijhoff
18.Azar, A., and H. Faraji. 2010, management science phase, Tehran: Kind
19.AkhavanSaffar, M., 2012, check the quality of internet banking websites in the country using
fuzzy algorithms. Iranian Journal of Medical Information
20.Babaei, A., 2002, the benefits of information technology, strategy, No. 122
21.Jafarnejad, Ahmed, Ali Sajjadinia, Safavid Mir Mahalleh, Golestan, Seyyed Rahim, thus Qshlajvqy, M., 2002, to assess barriers and implementing e-commerce solutions in the development of Iran's carpet exports, Quarterly Journal of Commerce, Autumn, Issue 52, pp. 34-1
22.Khani, J., 2007, e-commerce, magazine, message management, Issue 25, pp. 85-67. 23.Zanjirchi, SM, 2011, AHP fuzzy, Tehran:
SaneiShahmirzadi
24.Taheri, cm, familiarity with the theory of fuzzy sets Mashhad University Jihad Press, second edition, 2008
25.Kohzadi, Noruzi, 2001, e-banking: Prerequisites, constraints and ways to implement it in Iran, Monetary and Banking Research Institute, pp. 366-343
26.Mahdavi, Mohammad hosseinShamsiRezai dust, in 2007, the need for e-commerce business in Iran due to its role in the productivity of leading countries, Journal of Knowledge & Development, Issue 21, pp. 120-97