Vol-7, Special Issue3-April, 2016, pp2292-2298 http://www.bipublication.com
Case Report
Investigating the effect of education based on the promotion of ethical
sensitivity on the nurse caring behavior from patients' perspective
1
Farzaneh Nasiripour, 2Abbas Abbaszadeh*,
3
Fariba Borhani and 4 Mhnaz Ilkhani
1Student Research Committee, School of Nursing and Midwifery, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran 2
Professore, Department of nursing, School of Nursing and Midwifery, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran *Corresponding Author: aabaszadeh@hotmail.com, aabaszadeh@sbmu.ac.ir
3
Associate Professor, medical ethics and law research center, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
4Assistant Professor. Department of nursing, School of Nursing and Midwifery, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
ABSTRACT
Purpose and background: Nursing ethics education to nurses increases their awareness of the ethical aspects of their work and develops their ethical sensitivity towards them. Nursing ethics education, integrates nurses' ethics-based knowledge performance in different conditions. This study was performed to determine the effect of education based on the promotion of ethical sensitivity of nurses on the nurse caring behavior of nurses from patients' perspective in Cardiothoracic Surgery Units.
Methodology: This semi-experimental study was performed on 200 patients admitted to the hospitals of Naft and Mehr of Ahvaz in Iran in 2015-2016. The intervention and control groups were included in the study with random allocation. Data collection was performed by the Wolf's caring behavior questionnaire and the information were analyzed using spss16, descriptive statistics and inferential tests of Mann-Whitney, Spearman and Kruskal– Wallis. Descriptive statistics and inferential tests of Mann-Whitney, chi-square (chi-square test) and covariance ratings.
Findings: The average total scores of caring behavior in the intervention group before and after the intervention were (3.34 ± 0.72) and (4.94 ± 0.59), respectively. The results indicate that the behavior of the nursing care of the nurses from patients' perspective in all areas was significantly higher after the intervention (P< 0 /001).
Conclusion: This study showed that nursing ethics education can improve the ethical sensitivity of nurses and improve the quality of nursing care. The findings of this study could focus on designing training programs to improve ethics in nursing.
Keyword: Ethical principles education, ethical sensitivity, ethics, behavior, behavior of nurses of Iran
INTRODUCTION
The main component of nursing services is to provide care for a patient which requires a great level of ethics in all aspects of the service (1). Care is the essence (2) and main focus of nursing activities. Ethic is an interpersonal process bases on professional development, competence and sensitivity and is considered the foundation of nursing ethics (3). In practice, we must define caring behaviors to measure care
views and actions through which the patient is cared for (6). Nurses are surely a group legally and ethically responsible for caring after a patient (7). Patients expect that a nurse would observe ethical principles during care (8). In this case, a patient will more confidently receive the care of nurses (9). Studies performed in this field show that observation of ethical principles increases performance skills and reveals weaknesses. Moreover, caring will be performed more accurately which decreases existing problems in a unit and eliminates dissatisfaction which eventually creates the motivation to provide quality care and satisfying patients' needs (10). Çetin and Cimen (11) believe that ethical knowledge alone cannot be useful in care and ethical sensitivity should be incorporated with it.
Ethical sensitivity is one of the characteristics that people committed to it see different phenomena from an ethical perspective and it forces caretakers to be aware of verbal and non-verbal behaviors and signs of patients and identify their needs (12). The results of different studies have shown that the ethical sensitivity of nurses, increases their ethical decision making in clinical situations and enables them to become aware of the ethical problems of their profession and find creative solutions to solve them. They will also consider the probable consequences of their performance and take more logical measures in this process (13).
Barati et al. (14) performed to investigate the observation of nursing ethics rites in nurses and patients' perspectives, showed that the levels of the observation of ethical values in nurses and patients' perspective differ. Nurses feel that their performance was ideal with no weaknesses. Of the important barriers to nurses' ethical sensitivity include inappropriate ethics education during university education and internship (15). It can be said that ethics principles education, improves nurses' attitude and decreases their anxiety (16). In Gradi et al. (1), the nurses who took the ethics education course, showed better ethical performances. In another study, it was discovered that educational programs for the development of nurses ethics sensitivity, increases their use of ethical codes.
Borhani et al. (15) showed that holding workshops with follow-ups can significantly influence nurses' ethical sensitivity. Since the majority of nursing articles investigate the effect of ethical principles education on nurses' ethical sensitivity and performance from nurses' perspectives and little investigation has been done about patients' perspective, and since there have been limited studies on nursing ethics education and its effect on nurses' caring behavior in Iran and other countries, therefore this study was performed to investigate the effect of education based on improving ethical sensitivity on the caring behavior of nurses from patients' perspective.
METHODOLOGY
This semi-experimental study was performed on 200 patients admitted to the Cardiothoracic Surgery Units (CSU) of the hospitals of Naft and Mehr of Ahvaz in Iran in 2015-2016. The inclusion criteria include: minimum age of 18, be literate and have the ability to communicate. A minimum 3 days of stay in this unit. Have no communicational problems such as blindness, deafness, inability to speak, and mental disorders. The sample size based on the comparison of two independent samples was calculated to be 50 for each group.
caring behavior scale, the scores of all the items are summed and divided by 42. Therefore, the minimum score for caring behavior is 42 and the maximum score for it is 252. The higher scores of each sub-scale and the overall caring behavior, show better caring behaviors. The validity of each contents of the above tools were assessed in Iran (Hajinezhad et al. 2011, Rafiei et al. 2007) and also for the reliability of these tools calculated using the internal consistency method, the Cronbach's alpha scores are 0.98 and 0.85 respectively.
To ensure the reliability of tools in this research, the internal consistency with Cronbach's alphas has been used. The values for the Cronbach's Alpha of the study for each of the study areas include: respecting others (0.947), confidence in human presence (0.951), positive relationship and orientation (0.895), professional knowledge and skills (0.904), attention to others' experiences (0.983). Given the values of Cronbach's Alpha which are all more than 0.75, it can be concluded that the tools used have an appropriate reliability. The hospitals were divided into the two groups of intervention and control using a lottery. And in each hospital, the CSU was investigated. After receiving permission from the hospital authorities and head nurses of the corresponding units, after introducing ourselves to the nurses and patients of the CSU, their consent for being included in the research was received. Before the intervention, the researcher gave the patients of the intervention and control groups a caring behavior and then two days per week for six weeks, the nurses of the intervention group received an article on nursing ethics principles education by the first writer of the article.
During these six weeks, in all the non-personal education days, for five days per week, every day, a message was sent to the nurses to ensure the consistency of the education. The messages were sent via phone as text messages. Then after the two weeks, the caring behavior questionnaire was given to both groups of the control and intervention groups to be filled. The research data were analyzed using SPSS16, descriptive statistics and inferential tests of Mann-Whitney, Spearman and Kruskal – Wallis ratings.
This research was approved by the Ethics Committee in Research of Tehran Shahi Beheshti University and ethical issues such as receiving permission from the authorities to start the research, explaining the research purpose to the research participants and ensuring them of the confidentiality of the collected data and receiving their consent, were all taken into consideration.
FINDINGS
The findings showed that 49% of the research participants were female and 51% were male. The average age of the study participants was 51.4 and the frequency of the hospitalization times was 4.6. Most of them had less than high-school education or were university graduates (19-26%). 47% of them had good financial status. Most of them were married (70.5%). Those with a good experience (49.2%) constituted the majority of the study participants.
The overall caring behavior score from patients' perspective significantly increased after the intervention (P<0.001). But in the intervention group, no significant change was seen (table 1).
Table 1 – the mean and SD of the overall caring behavior before and after intervention and based on the division of the intervention and control and the inter-group and intra-group test of it.
Overall caring behavior score Control group Intervention group Intergroup test result Mean ± SD Mean ± SD
Before intervention 4.41±0.77 3.34±0.72 P<0.001 After intervention 4.47±0.92 4.94±0.59 P= 0.026 Intragroup test result P= 0.962 P<0.001
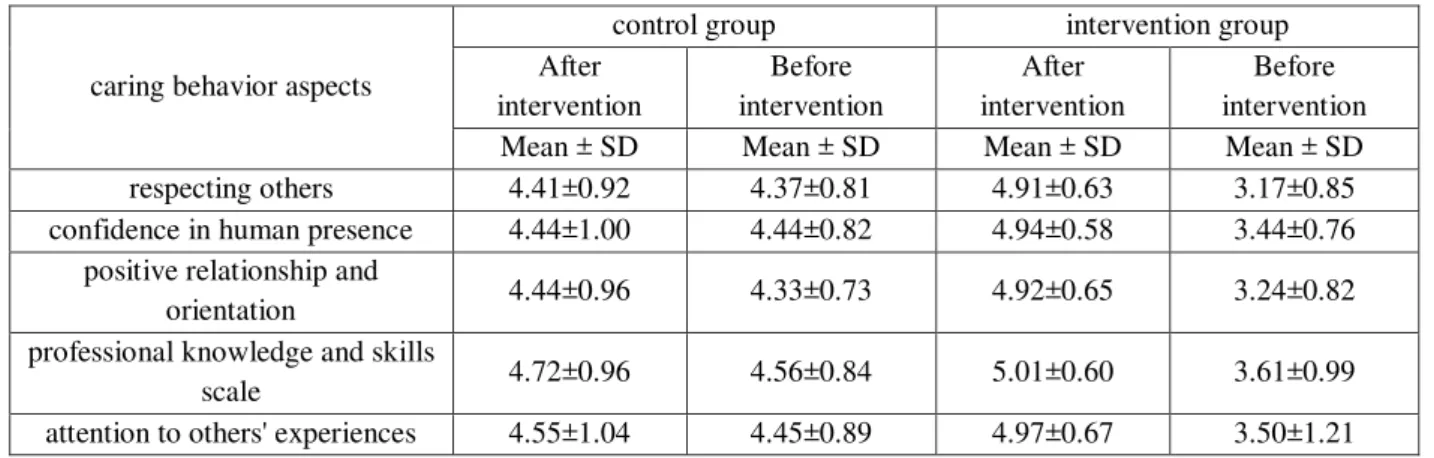
Table 2 - The mean and SD of the scores of the caring behavior aspects before and after intervention in the control and intervention groups
CONCLUSION
The results of this study showed the education based on improving ethical sensitivity was effective on nurses caring behavior from patients' perspective such that the caring behavior increased after educational intervention. Almost all texts on nursing have somehow mentioned the issue of ethics in providing care. Patients expect that nurses observe ethical principles when giving care (10). Since no study was found about education based on improving ethical sensitivity on the caring behavior of nurses from patients' perspective in Iran and other countries, therefore the findings of this research are considered as being important. The results of the present research suggest that the "overall caring score" after intervention (4.94 ± 0.59) was higher than before intervention (3.34±0.72). Izadi et al (17) performed on the correlation between nurses' ethical sensitivity and their caring behavior showed that the score of ethical sensitivity did not have a significant correlation with the caring behavior of nurses. Patients usually have some problems to implement their decision in practice and contextual factors limit their ability to act on decisions which creates problems when it comes to acting in accordance with values and norms. Zakaria et al. (18) performed on the effect of ethics education on nurses' ethical knowledge and behavior showed a positive effect of educational intervention on the ethical behavior of nurses after intervention. Also in Hasanpour et al. (19) performed on the effect of nursing ethics principles on ethical sensitivity, the
intervention group showed a greater ethical sensitivity compared to the pre-intervention group. In Morphi et al. (20) performed on the effect of nursing education on the caring behaviors of nursing students, showed that educational intervention positively affects nurses' caring behavior and improved it. Comparing the results of the present research with the results of other studies performed on the ethical sensitivity and ethical behavior of nurses, shows that educational intervention positively affected nurses caring behavior and improved caring behavior in nurses.
In Izadi et al. (17), Azizfini et al. (22), Sodabe Joolaee et al. (23), Porter et al. (24), and Palese et al. (3), the greatest scope of caring behavior was professional knowledge and skills. It seems that after educational intervention for nurses on providing care to patients, they had a greater ability to use their professional skills and knowledge. Maybe, the technical activities of nurses are more recognized by patients compared to their other nursing activities and are more objective than other behaviors and for this reason, they are more easily scored by patients (3). It should be noted that today, the physical and mental aspects of care are considered. If a nurse neglects the mental aspects of care, it makes the patients to change into a zero therapeutic target (25).
In the present study, after intervention, the lowest level of caring behavior belonged to the item of respecting others. This finding did not match the study results of Joolaee et al. (23), Seyedshohadaei (25), Palese et al (3), but did
intervention group control group
caring behavior aspects Before
intervention After
intervention Before
intervention After
intervention
Mean ± SD Mean ± SD
Mean ± SD Mean ± SD
3.17±0.85 4.91±0.63
4.37±0.81 4.41±0.92
respecting others
3.44±0.76 4.94±0.58
4.44±0.82 4.44±1.00
confidence in human presence
3.24±0.82 4.92±0.65
4.33±0.73 4.44±0.96
positive relationship and orientation
3.61±0.99 5.01±0.60
4.56±0.84 4.72±0.96
professional knowledge and skills scale
3.50±1.21 4.97±0.67
4.45±0.89 4.55±1.04
match the results of Öztunc (26) and Hajinezhad et al (27). It seems that the nurses give more important to their clinical and caring performances and so paid less attention to other caring aspects such as communicating with patients and respecting others. If there is work overload and shortage of nurses, the nurses only focus on their main tasks and neglect other caring dimensions (4). Currently, giving importance to treatment instead of caring, has made nurses fall away from prioritizing high human values. To give great care in nursing, an attitude resulting from sympathy, altruism and considering other people's perspectives is needed (28).
Nurses should provide caring services to patients. The caring behavior of nurses not only counts as the most important factor in the healing process of patients but is also an effective factor for the health estimation of patients. For a higher quality of caring behavior, nurses must be committed to ethical principles in all of their caring aspects. Ethical sensitivity is considered as a foundation for the continuity of observing ethics. Ethical sensitivity education to nurses can help with continued presence of ethics in nurses' caring behavior and help improve caring behavior. Nurses need education during their work to improve their skills. This education enhances their skills and knowledge and enables them to provide better care. Since ethics are an inseparable part of nurses caring behavior, the results from investigating the effect of ethical sensitivity education on nurses can be provided to the authorities of hospitals to provide educational programs on ethical sensitivity to patients. Performing research on nursing can add to the literature on nursing and create new knowledge in various fields. Since the ethical sensitivity of nurses from patients' perspective is less considered, the results of this research can be the basis of subsequent studies with the approach to investigate the effect of empowering nurses on the health estimation of patients.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
This paper is a result of the results of a Master's thesis titled "the effect of education based on
improving ethical sensitivity on the caring behavior of nurses from patients' perspective in the CSU of Ahvaz hospitals approved by Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences and Health Services of Tehran, Iran, with the code :
IR-SMMUPHNM134218. We appreciate the assistance of all the personnel and authorities of the hospitals of Naft and Ahvaz and also the library of the department of nursing and midwifery of Shahid Beheshti University and the Vice President of Research.
REFERENCES
1- Grady C, Danis M, Soeken K. L, O'donnell P, Taylor C, Farrar A and Ulrich C M (2008) Does ethics education influence the moral action of practicing nurses and social workers? The American Journal of Bioethics,
8 (4), 4-11.
2- Omari F.H, Abualrub R, Ayasreh I. R (2013) Perceptions of patients and nurses towards nurse caring behaviors in coronary care units in Jordan. Journal of Clinical Nursing, 22 (21-22), 3183-3193
3- Palese A, Tomietto M, Suhonen R, Efstathiou G, Tsangari H, Merkuris A, Jarosova D, Leino‐kilpi H, Patiraki E, Karlou C (2011) Surgical patient satisfaction as an outcome of nurses’ caring behaviors: a descriptive and correlational study in six European countries. Journal of Nursing
Scholarship,43 (4), 341-350.
4- Zamanzadeh V, Azimzadeh R, Rahmani A, Valizadeh L (2010) Oncology patients' and professional nurses' perceptions of important nurse caring behaviors. Bio Med Central
Nursing, 9 (1), 42-50.[in Persian]
5- Hejazi S. M, Soltani M, Javan, S. A. A, Aminian F and Mehdi S (2012) The Impact of Selected Aerobic Aquatic Exercises on the Depression and Happiness Levels of Patients with Multiple Sclerosis (MS). Life Science
Journal, 9 (4), 234-240. [in Persian]
6- Udomluck S, Tonmukayakul O, Tiansawad S and Srisuphan W (2010) Development of Thai Nurses Caring Behavior Scale. Pacific Rim International Journal of Nursing
Research, 14 (1), 32-44
8- Foroutan B, Abolhassani M, Salihipour S, Karimi A, Dehghanizadeh F, Rezvani N and Soltani Beldaji M (2015) Patients' views on observance of nursing ethics in Imam Hussein Hospital in Shahroud during.
Iranian Journal of Medical Ethics and
History of Medicine, 8 (4), 81-90. [in
Persian]
9- Mahmoudi H, Mohammadi E. and Ebadi A (2015) An explanation of the patients and nurses perception on the concept of emergency caring. International Journal of
Behavioral Sciences, 9 (2), 147-157. [in
Persian]
10- Mohajjel Aghdam A, Hhssankhani H, Zamanzadeh V, Khameneh S. and Moghaddam S (2013) Nurses' performance on iranian nursing code of ethics from patients' perspective. Iran Journal of
Nursing, 26 (84), 1-11. [in Persian]
11- Çetin M, Cimen M (2011) Assessing a group of Physicians ethical sensitivity in turkey. Iranian Journal of Public Health, 40 (3), 89.-97.
12- Borhani F, Alhani F, Mohammadi A, Abbaszadeh A (2009) Professional nursing ethics: it'sdevelopment and challenges. Iran J Med Ethics Hist Med, 2 (3), 27-38. [in
Persian]
13- Kim Y. S, Kang S. W, Ahn J. A (2013) Moral sensitivity relating to the application of the code of ethics. Nursing Ethics, 20 (4), 470-478
14- , Barati A, Ghurchiani F, Gorji H, Khatami Firuz-Abadi A, Dehghani H, Goldoost Marandi F (2013) Observing nursing ethics rites from patients and nurses' perspective in one of the educational-theurapatic hospitals of Tehran University of Medical Sciences. Journal of Medical Ethics, 7 (23),
63-79. [in Persian]
15- Borhani F, Abbaszadeh A, Sabzevari S, Dehestani M (2012) The effect of workshop training and follow-up on the ethical sensitivity of nurses. Journal of
Medical Ethics, 6 (21),11-24. [in Persian]
16- Numminen, O. H. and Leino-kilpi, H (2007) Nursing students ethical decision-making: A review of the literature. Nurse
Education Today, 27 (7), 796-807.
17- Izadi A, Imani H, Noughabi F, Hajizadeh N and Naghizadeh F (2013) Moral sensitivity of critical care nurses in clinical decision making and its correlation with their caring behavior in teaching hospitals of Bandar Abbas. Iranian journal of medical ethics
and history of medicine, 6 (2), 43-56. [in
Persian]
18- -Zakaria AM, Sleem WF, Seada AM (2016) Effectiveness of ethical issues teaching program on knowledge, ethical behavior and ethical stress among nurses.
Journal of Nursing Education and Practice,
6 (7), 125-134.
19- Hassanpoor M, Hosseini M, Fallahi khoshknab M. and Abbaszadeh A (2011) Evaluation of the impact of teaching nursing ethics on nurses' decision making in Kerman social welfare hospitals in.
Iranian Journal of Medical Ethics and
History of Medicine, 4 (5), 58-64. [in
Persian]
20- Murphy F, Jones S, Edwards M, James J, Mayer A (2009) The impact of nurse education on the caring behaviours of nursing students. Nurse Education Today,
29 (2) 254-264.
21- Chan H. S, Chu H. Y, Yen H, Chou L.N (2015) Effects of a care workshop on caring behaviors as measured by patients and patient satisfaction. Open Journal of
Nursing, 5 (2) 89-95.
22- Ismail Azizi-Fini I, Sadat Mousavi M, Mazroui-Sabdani A, Adib-Hajbaghery M (2012) Correlation Between Nurses Caring Behaviors and Patients Satisfaction.
Nursing and Midwifery studies, 1 (1),
36-40. [in Persian]
23- Joolaee S, Hajibabaee F, Jafar Jalal E, Bahrani N (2011) Assessment of patient satisfaction from nursingcare in hospitals of Iran university of medical sciences. Hayat. Journal of Faculty of Nursing and Midwifery, Tehran University of Medical
Sciences; 17 (1), 35-4. [in Persian]
24- Porter C, Cortese M, Vezina M, Fitzpatrick J. (2014). Nurse Caring Behaviors Following Implementation of a Relationship Centered Care Professional Practice Model. International Journal of
Caring Sciences, 7 (3), 818-822
25- Seyedshohadaei M, Oghli S. H, Rafiei F and Zeinali, K. N ( 2015) Investigation Nurses caring behavior working in cancer section based on patients point of view.
World Rural Observation,7 (1), 140- 142. [in
Persian]
International Journal of Caring Sciences, 8 (3), 625- 632
27- Hajinezhad M, Rafii F, Jafarjalal E and Haghani H (2007) Relationship between nurse caring behaviors from patients perspectives & their satisfaction, Iran
Journal of Nursing, 20 (49), 73-83. [in
Persian]
28- Nick Frid L, Hasani P (2014) Investigating the perspective of nursing students of Saaveh Islamic Azad University on the importance of nurses caring behaviors based on Watson-care model. Nursing