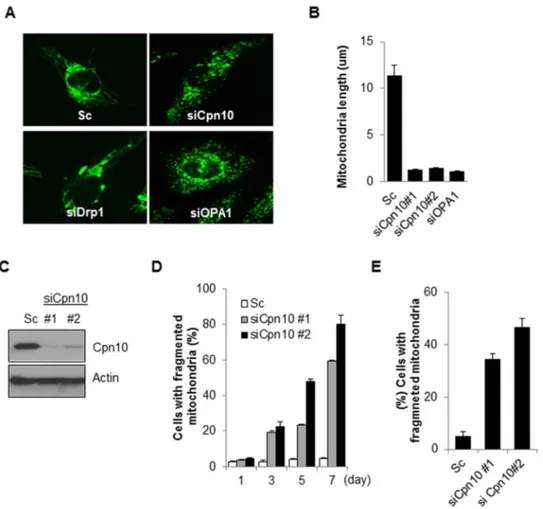
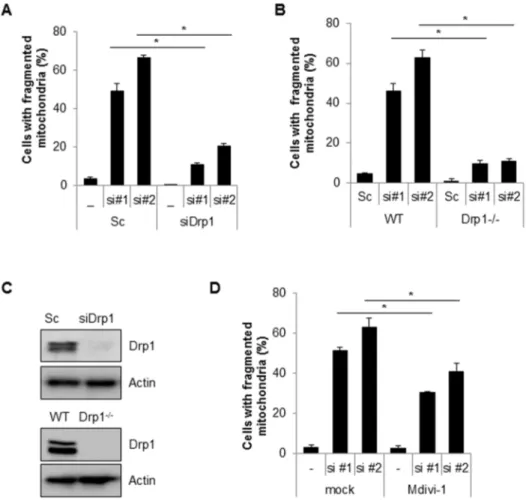
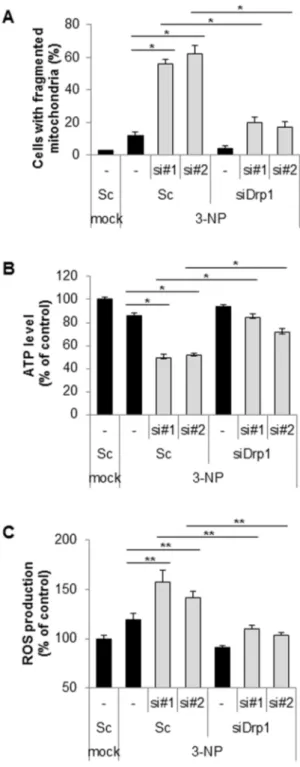
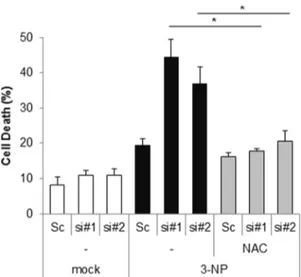
Suppression of Cpn10 increases mitochondrial fission and dysfunction in neuroblastoma cells.
Texto
Imagem
Documentos relacionados
Considering that citrate synthase plays an important role in brain energy metabolism and that mitochondrial dysfunction has been implicated in the pathogenesis of MODS, in
In addition to a lack of dystrophin, studies are emerging that are painting a picture of a more intricate connection between mitochondrial dysfunction and DMD where increased
The results indicated that treadmill training had a protective effect against damage and dysfunction, attenuated the increase in DOX-induced apoptosis, and increased
Although we presented preliminary data, our studies suggest that parkin up- regulation by TUDCA induced PARIS down-regulation in mice midbrain and in human neuroblastoma cells,
Considering that increased serum lactate levels suggest mitochondrial dysfunction, we then evaluated the effect of acute fructose administration on Krebs cycle enzyme activities
The types of mitochondrial dysfunction in cancerous thy- roid follicular cells can be classified as follows: (1) defective OxPhos arising from somatic alterations in mitochondrial
To investigate the potential effects of maternal diabetes on mitochondrial biogenesis in cumulus cells, we first evaluated mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) content in cumulus cells
Suppression of endogenous cardiomyocyte dMfn with the RNAi induces mitochondrial fragmentation, shown as smaller organelles and a leftward shift in the size distribution (A)