Uncertainties in Arctic sea ice thickness and volume: new estimates and implications for trends
Texto
Imagem
Documentos relacionados
Here we investigate the phasing between a South American dust proxy (non-sea- salt calcium flux, nssCa), a sea ice proxy (sea salt sodium flux, ssNa) and a proxy for
In the present study, little auks foraged in the same areas in the presence and nearby absence of sea ice (Fig 1 and S1 Fig), thus questioning the importance of sea-ice habitats
4, we finally compare the magnitude and pacing of past temperature changes reconstructed from deep ice cores to the changes simulated by coupled ocean-atmosphere-sea- ice models
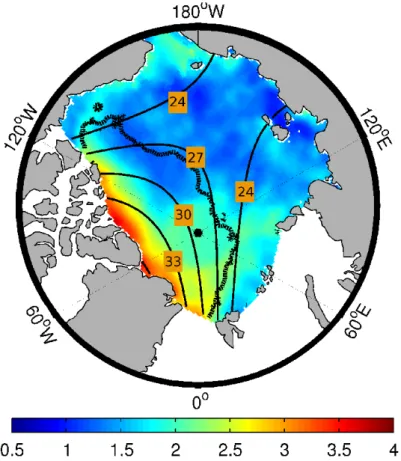
The reconstructions are based on a multilinear regression of forecasted ice concentration, level ice thickness, ridge density, ice speed and an additional factor which is based,
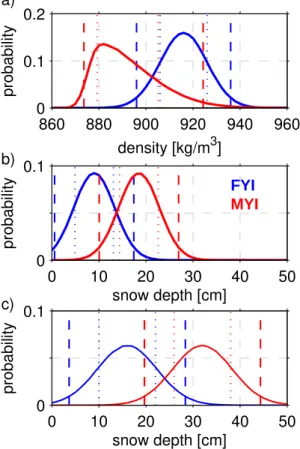
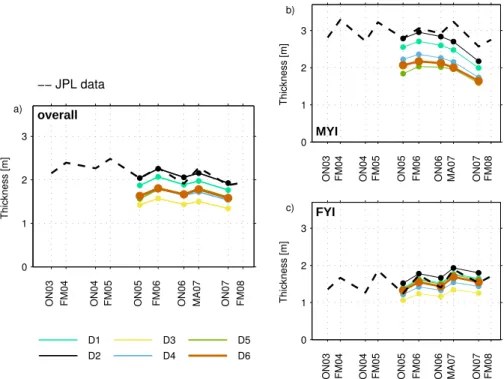
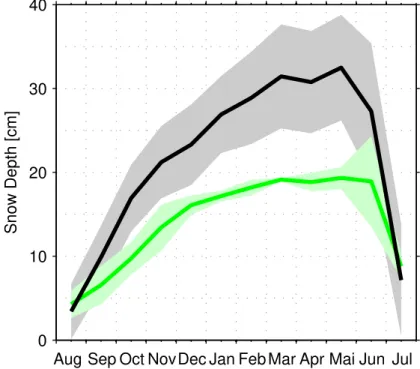
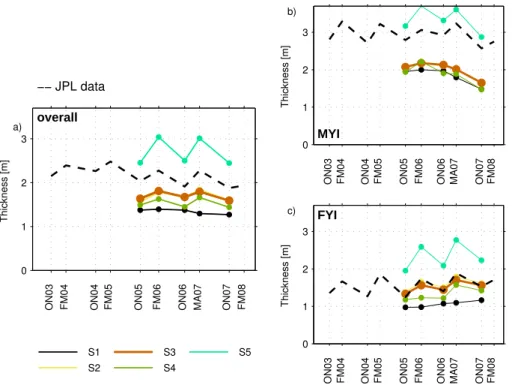
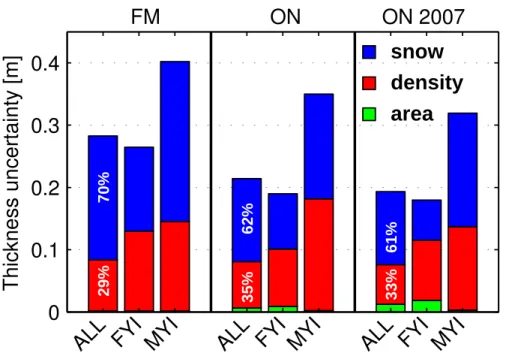
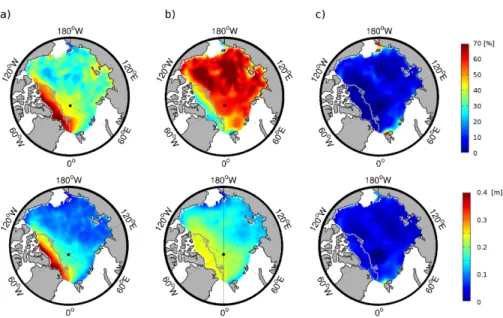
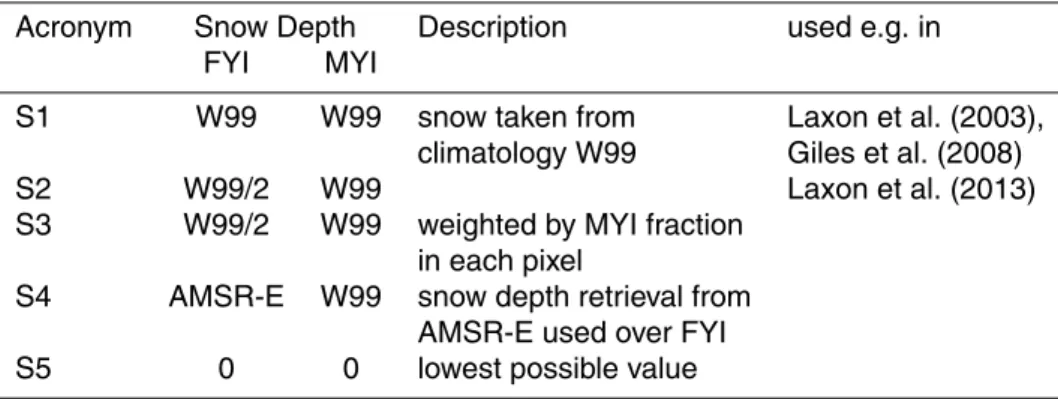
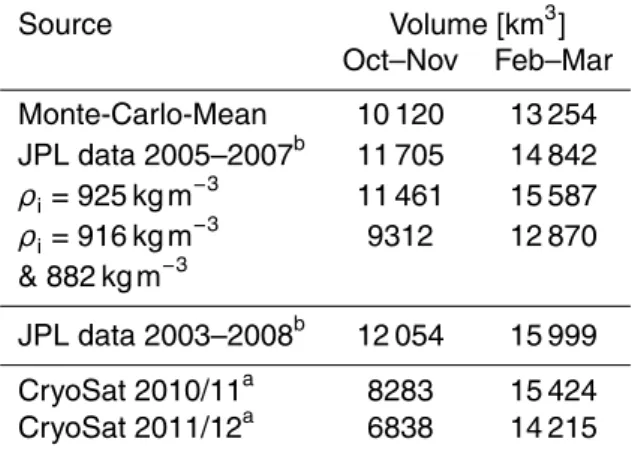
The mean values and uncertainties of snow depth and ice and snow densities, determined for FY ice and MY ice, were used to calculate the total error in ice thickness retrieval
ther investigations of surface structure and snow cover on seasonal sea ice in parallel to measurements of driving pa- rameters like heat flux, radiation, ice temperature and
When we try different values for the ice temperature, snow density, and ice salinity (not shown here), we find that only the ice salinity impacts the modelled brightness
To establish the extent to which a snow cover will mitigate the albedo e ff ect of black carbon in sea ice two di ff erent Arctic snow types (also described by Grenfell and