Arq Neuropsiquiatr 1993, 51(3) :329-332
MAGNETIC RESONANC E IMAGIN G I N
HTLV-I ASSOCIATE D MYELOPATH Y
AÍLTON MEL O * , LUCIAN A MOUR A ** , SOLAN A RIO S * , MARCO S MACHAD O *** , GERS ONI TA COST A * **
SUMMARY — Magneti c resonanc e imagin g o f th e brai n an d spina l cor d wer e carrie d ou t fo r seventeen consecutiv e patient s wit h HTLV- 1 associate d myelopath y (HAM) . Eigh t patient s had brai n abnormalitie s an d fou r ha d decrease d thoraci c spina l cor d diameter . Brai n lesion s were mostl y locate d i n subcortica l an d periventricula r areas . Ou r dat a sugges t tha t diffus e central nervou s syste m lesion s ar e presen t i n patient s wit h HAM.
KEY WORDS : HTLV-1 , myelopathy , leukoencephalopathy , MRI .
Ressonância magnétic a n a mielopati a associad a a o HTLV-1 .
RESUMO — Fora m realizado s exame s d e ressonânci a magnétic a d o crâni o e colun a e m 1 7 pa -cientes co m diagnóstic o clínic o e laboratoria l d e mielopati a po r HTLV- 1 (HAM) . E m oit o pacientes hiavi a anormalidade s cerebrai s caracterizada s po r lesõe s subcorticai s e periventri -culares. Quatr o paciente s apresentava m diminuiçã o acentuad a d o diâmetr o d a medul a espina l torácica. Nosso s dado s sugere m se r a HA M um a patologi a multifoca l qu e envolv e tod o o sistema nervos o centnal .
PALAVRAS-CHAVE: HTLV-1 , mielopatia , leucoencefalopatia , ressonânci a magnética .
It i s no w wel l establishe d tha t HTLV- 1 associate d myelopath y (HAM ) i s a n
endemic diseas e i n th e Southwester n Japan, Caribbean Islands, Central Africa an d
Latin Americ a 7,9,io bu t i t als o ha s bee n describe d i n th e Unite d State s an d
Europe 3,8 characterizin g a diseas e o f wideworl d distribution . Wit h magneti c re
sonance imagin g (MRI) , hig h intensit y signal s hav e bee n observe d mor e frequen
-tly o n T2-weighte d imaging in patient s wh o hav e white matter lesion s a s multiple
sclerosis, leukodystrophies , som e elderl y peopl e an d i n Binswange r subcortica l
arteriosclerotic encephalopath y
2,5,12.Recentl y som e author s hav e describe d
periventricular whit e matte r lesion s i n HA M an d suggeste d possibl e sharin g o f ethio
-pathogenic mechanism s wit h multipl e sclerosi s whic h ha s bee n denie d b y
others
4>
6.
The presen t stud y wa s designe d t o establis h th e type s o f MR I lesions i n
patients wit h HAM .
METHODS
The subject s o f th e presen t stud y wer e 1 7 consecutiv e patient s wh o hav e bee n see n i n a hospital whic h assis t th e lowe r socioeconomi c clas s i n Salvador . Fiv e me n an d 1 2 women , with age s rangin g fro m 1 8 to 5 2 year s old , wer e selecte d accordin g t o accepte d clinica l criteri a of HAM , including progressiv e spasti c paraparesis , urinar y urgenc e o r incontinence , constipa
-* Federa l Universit y o f Bahi a (UFBA ) an d Sant o Antoni o Hospital ; -* -* UFBA; -*-* -* Sã o Rafael Hospita l - Salvador . Aceite : 24-janeiro-1993.
tion an d bac k pai n sometime s associate d wit h superficia l sensitiv e syndrome . Non e o f th e patients ha d concomitan t diabetes , hear t disease s o r arteria l hypertension .
Laboratory. Seru m an d CS F sample s wer e teste d fo r antibodie s t o HTLV 1 usin g com -mercially availabl e enzym e immunoassa y (EIA) . EI A repeatedly reactiv e sample s wer e furthe r examined usin g a HTLV- 1 vira l an d recombinan t protein s a s a n antige n source . Sample s wer e considered serologicall y positiv e i f antibodie s agains t bot h th e ga g (p24 ) an d en v (p21B ) gen e products wer e present . Th e CS F fro m al l participant s wer e teste d fo r th e presenc e o f anti -bodies agains t syphilis , toxoplasmosis , schistosomiasi s an d cysticercosis .
Imaging. Brai n an d spina l cor d MR I wer e performe d wit h a 0.6- t superconductiv e uni t image wit h multi-slice , multi-ech o (SE ) puls e sequence . Brai n MR I was image d i n axia l plane . Sagittal an d corona l image s wer e occasionall y obtaine d a s well . Th e slic e thicknes s wta s 5 mm without interslic e gaps . Th e acquisitio n matri x wa s 256x256 . Th e M R studie s o f cervica l an d thoracic spina l cor d wer e don e wit h multi-slice , multi-echo(SE ) puls e sequenc e an d fiel d echo . The slic e thicknes s wa s 5 mm withou t gaps , o r 3 mm wit h 1 mm interslic e gap . Th e exam s were carrie d ou t i n tw o différents hospitals .
RESULTS
Age a t th e onse t o f neurologi c symptom s a s judge d fro m th e histor y range d betwee n 17 an d 4 5 year s (mea n ag e 32. 4 years).
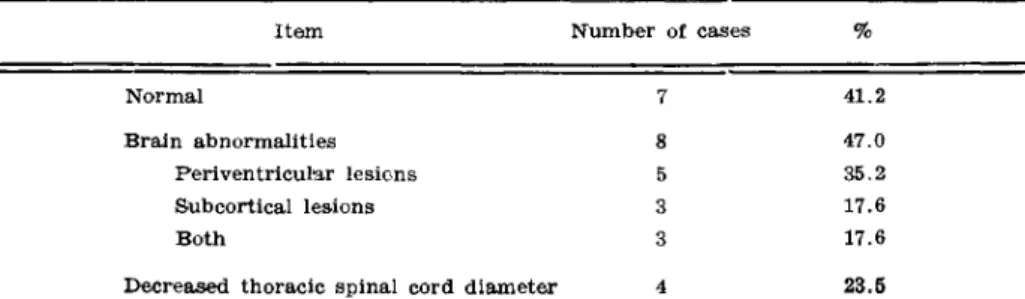
Abnormalities detecte d b y MR I ar e summarize d i n Tabl e 1. Te n (58.8% ) o f 1 7 patient s with HA M had abnormalitie s o n brain , thoraci c spina l cor d o r both .
Among patient s studied , 8 (47% ) ha d brai n abnormalitie s an d 4 (23.5% ) ha d markedl y decreased diamete r o f thoraci c spina l cord . Tw o patient s ha d brai n an d spina l cor d lesions . Five patient s ha d positiv e periventricula r lesions . Subcortica l brai n abnormalitie s wer e foun d in thre e patient s an d thre e share d bot h subcortica l an d periventricula r lesions . Figur e 1 shows: periventricula r brai n radiologi c abnormalitie s i n a 4 5 yea r ol d patien t wit h HA M for 12 years ; severa l larg e an d confluen t lesion s nea r th e anterio r an d posterio r horn s a s wel l as subcortica l lesion s i n a 4 2 ol d woma n wit h HA M for 1 8 years . I n fou r patient s thoraci c spinal cor d thicknes s wa s heavil y reduce d a s show n i n Figur e 2 .
In non e o f th e patient s lesion s i n th e cerebellu m o r brai n ste m wer e foun d
COMMENTS
The presen t case s o f HTLV- 1 associate d myeolapath y showe d a n unifor m
clinical pictur e a s previousl y reporte d 3 bu t som e radiologica l abnormalitie s poin t
to differen t grade s o f a n uniqu e disease . Ou r patient s exhibite d e neurologica l
disorder wit h brain an d spina l cor d involvemen t a s determine d wit h MRI . Brai n
lesions wer e multifoca l bu t predominate d i n periventricula r an d subcortica l area s
of th e brain .
Although intraparenchyma l spina l cor d lesion s hav e bee n previousl y des
-cribed
1 1non e o f ou r patient s ha d thes e kin d o f lesions . The conspicuou s de
crease o f thoraci c spina l cor d diamete r i s probabl y du e t o a hig h degre e o f
demyelination an d degeneratio n o f pyramidal , spinocerebella r an d spinothalami c
tracts, a s ha s bee n foun d i n necrops y studies
1. Th e perivascula r cuffin g o f lym
-phocytes throughou t th e CN S a s ha s bee n pointe d ou t i n necropsies
1suggest s
that vasculiti s coul d b e a featur e o f th e patholog y o f patient s wit h HA M and
explain th e multifoca l lesion s observe d i n thes e patients .
Brain change s i n ou r patient s wer e simila r t o demyelinatio n lesion s foun d
in health y elderly , vascula r problem s an d als o i n primar y disease s lik e multipl e
sclerosis. Considerin g thes e differen t situation s i t i s possibl e tha t differen t me
-chanisms ar e operativ e i n th e MR I findings o f HAM . Brai n lesion s showe d n o
correlation wit h th e ag e o f onse t o f HA M but wer e relate d t o severit y o f symp
-toms.
Meanwhile, furthe r an d controlle d studie s ar e necessar y fo r understandin g
the pathogenesi s o f MR I finding s i n HAM.
REFERENCES
1. Akizuk i S , Nakaaat o O , Higuch i Y , Tanab e K, Setohuch i M , Yoshid a S , Miyazak i Y , Yma- ¬
moto S , Sudo u S , Sannomiy a K , Okajim a T . Necrops y finding s i n HTLV- 1 associate d
myelopathy. Lance t 1987 , 1:156-157 .
2. Berge r J , Tornator e C, Majo r EO , Bruc e J , Shapha k P , Yoshiok a M , Hauf f S , Sheremat a
W, Morto n GF , Land y H . Relapsin g an d remittin g huma n immunodeficienc y viru s asso
-ciated leukoencephalomyelopathy . An n Neuro l 1992 , 31:34-38 .
3. Jansse n RS , Kapla n JE , Khabba z R F e t al . HTLV- 1 associate d myelopathy/tropica l
spastic paraparesi s i n th e Unite d States . Neurolog y 1991 , 41:1355-1357.
4. Karpa s A , Kamp f V , Side n A , Koc h M , Pose r S . Lac k o f evidenc e fo r involvemen t o f
known huma n retroviruse s i n multipl e sclerosis . Natur e 1986 , 322:177-178 .
5. Kobar i M , Meye r JS , Ichij o M , Orave z W T . Leukoaraiosi s correlatio n o f M R an d C T
findings wit h bloo d flow , atroph y an d cognition . AJN R 1990 , 11:273-281 .
6. Koprowsk i H , DeFreita s EC, Harpe r ME , SandbergWollhei m M , Sheremat a WA , Robert
-Guroff M , Saxinge r CW , Wong-Staa l F , Gall o RC . Multipl e sclerosi s an d huma n T-cel l
lymphotropic retroviruses . Natur e 1985 , 318:154-160 .
7. Meirele s A , Moreir a ED , Moreno-Carvalh o OA , Badar ó R , Mel o A . HTLV- 1 associate d
myelopathy i n Salvado r (Northeaster n Brazil) . Ar q Neuropsiquiat r 1992, 50:189-190 .
8. Newto n M , Mille r D , Rudg e P , Cruickshan k K, I>algleis h A , Clayde n S , Mosele y I . Anti
-body t o huma n T-lymphotropi c viru s typ e 1 i n West-Indian-bor n U K resident s wit h spasti c paraparesis. Lance t 1987 , 1:415-416 .
9. Osam e M , Jansse n RS , Kubot a H , Nishitan i H , Igat a A , Nagatak i S , Mar l M , Got o I , Shi-¬
mabukuro H , Khaba z R , Kapla n J . Nationwid e surve y o f HTLV- 1 associate d myelopath y
in Japan : associatio n wit h bloo d transfusion . An n Neuro l 1990 , 28:50-56.
10. Roma n GC . Th e neuroepidemiolog y o f tropica l spasti c paraparesis . An n Neuro l 1988 ,
23(Suppl):S113-S130.
11. Sheremat a WA , Quence r R , Gatt i E , Defreita s E , Harpe r M , Koprowsk i H . Magneti c
resonance imagin g o f tropica l spasti c paraplegia . Neurolog y 1987 , 37(Supp l 1 ) :322.
12. Swiete n JC , Geyske s GG , Deri x MM A e t al . Hypertensio n i n th e elderl y i s associate d
with whit e matte r lesion s an d cognitiv e decline . An n Neuro l 1991 , 30:825-830 .
REFERENCES
1. Akizuk i S , Nakaaat o O , Higuch i Y , Tanab e K, Setohuch i M , Yoshid a S, Miyazak i Y, Yma-moto S , Sudo u S , Sannomiy a K, Okajim a T. Necrops y finding s i n HTLV- 1 associate d myelopathy. Lance t 1987 , 1:156-157 .
2. Berge r J , Tornator e C, Majo r EO , Bruc e J , Shapha k P , Yoshiok a M, Hauf f S , Sheremat a W, Morto n GF, Land y H. Relapsin g an d remittin g humta n immunodeficienc y viru s asso -ciated leukoencephalomyelopathy . An n Neuro l 1992 , 31:34-38 .
3. Jansse n RS , Kapla n JE , Khabba z R F e t al . HTLV- 1 associate d myelopathy/tropica l spastic paraparesi s i n th e Unite d States . Neurolog y 1991 , 41:1355-1357 .
4. Karpa s A , Kamp f V , Side n A , Koc h M , Pose r S . Lac k o f evidenc e fo r involvemen t o f known huma n retroviruse s i n multipl e sclerosis . Natur e 1986 , 322:177-178 .
5. Kobar i M , Meye r JS, Ichij o M , Orave z W T. Leukoaraiosi s correlatio n o f M R an d C T findings wit h bloo d flow , atroph y an d cognition . AJN R 1990 , 11:273-281 .
6. Koprowsk i H, DeFreita s EC , Harpe r ME, SandbergWollhei m M, Sheremat a WA , Robert -Guroff M , Saxinge r CW , Wong-Staa l F, Gall o RC. Multipl e sclerosi s an d huma n T-cel l lymphotropic retroviruses . Natur e 1985 , 318:154-160 .
7. Meirele s A, Moreir a ED, Moreno-Carvalh o OA, Badar o R, Mel o A . HTLV- 1 associate d myelopathy in Salvado r (Northeaster n Brazil) . Ar q Neuropsiquiat r 1992 , 50:189-190 . 8. Newto n M , Mille r D, Rudg e P , Cruickshan k K, I>algleis h A , Clayde n S , Mosele y I . Anti
-body t o huma n T-lymphotropi c viru s typ e 1 i n West-Indian-bor n UK resident s wit h spasti c paraparesis. Lance t 1987 , 1:415-416 .
9. Osam e M, Jansse n RS , Kubot a H, Nishitan i H , Igat a A , Nagatak i S , Mar i M , Got o I, Shi -mabukuro H , Khaba z R , Kapla n J. Nationwid e surve y o f HTLV- 1 associate d myelopath y in Japan : associatio n wit h bloo d transfusion . An n Neuro l 1990 , 28:50-56.
10. Roma n GC. Th e neuroepidemiolog y o f tropica l spasti c paraparesis . An n Neuro l 1988 , 23(Suppl):S113-S130.
11. Sheremat a WA , Quence r R , Gatt i E , Defreita s E , Harpe r M , Koprowsk i H . Magneti c resonance imagin g o f tropica l spasti c paraplegia . Neurolog y 1987 , 37(Supp l 1) :322. 12. Swiete n JC , Geyske s GG , Deri x MM A e t al . Hypertensio n i n th e elderl y i s associate d