1
Universidade de Lisboa
Faculdade de Medicina de Lisboa
The place of DPP-4 inhibitors in the
treatment algorithm of diabetes type 2: a
Systematic Review of Cost-effectiveness
Studies
Alexandre Baptista
Or i ent a dor : P r of Dr . Jul ia n P er el ma n C o-Or i ent a dor : P r of. Dr . Ant óni o Va z C a r nei r o
Diss er t a çã o esp ec ia l me nt e ela b or a da pa ra obt ençã o do gr a u de M est r e em Epi de mi ol ogia
2
“ A impressão desta dissertação f oi aprovada pelo Conselho
Científico da Faculdade de Medicina de L isboa em reunião
de 29 de Julho de 2015”
3
Table of Contents
Page
Abbr evia t i ons a nd Acr onyms 3
Abst r a ct 4
Ba c kgr ou nd 6
C l i nica l E vi denc e a b out dia b et es 6
Epi de mi ol ogy of D ia b et es 7 Bur den of D is ea s e 8 Mor ta lit y 9 Mor bidit y 11 P or tugu es e Da ta 12 Ec onomi c B ur den of D is ea s e 12 C ost s 14
Dir ect c osts 14
I ndir ect c osts 14
T r ea t ment - I nhib it or s of DP P 4 15 T r ea t ment a l gor it hm 15 R el eva nc e of t he st u dy 16 Met hods a nd da t a 20 R esu lt s 25 Gr ey lit er a tur e 37
C ost ef f ectiven ess models 37
Dis cuss i on 40
C onc lus i ons 45
F undi ng 45
C onf l i ct s of i nt er est st a t ement 45
R ef er enc es 46 Annex es 50 F i gur es F i gur e 1 7 F i gur e 2 8 F i gur e 3 9 F i gur e 4 10 F i gur e 5 10 F i gur e 6 12 F i gur e 7 16 F i gur e 8 17 F i gur e 9 18 F i gur e 10 19 F i gur e 11 24 F i gur e 12 25 F i gur e 13 25 F i gur e 14 26 T a bles T a ble 1 11 T a ble 2 13
4
4-T T r ea t ing T o T a r get i n T yp e 2 D ia b et es
AC E Acar bo se C ard io va scu lar
Eva lu at io n
ADOP T A D ia b et es Out c omes P r ogr ess i on
T r ia l AF OR R D At or va st a t i n i n F a ct or ia l wit h O mega
-3 F a t t y Ac i ds R is k R edu ct i on i n Dia b et es
AR Q H Agenc y f or Hea lt hca r e R es ea r c h a nd
Qua l it y
C I C onf i denc e I nt er va l
IC ER Incr em ent a l C ost -Ef f ect i ven ess
R a t io
IDF I nt er na t i ona l D ia b et es F eder a t i on
hmR H ea lt h Ma r ket R es ea r c h
LDS Lip id s in D ia bet es St ud y
MA Ma r ket i ng Aut hor iza t i on
NIC E Na t i ona l I nst it ut e f or H ea lt h a nd
C l i nica l Ex c el l enc e
OHE Off i c e of H ea lt h Ec onomi c s
P IC OS : P opu la t i on, I nt er vent i on, C ompa r a t or , Out c omes, S t udy D esi gn
P R IS MA Pre ferred Repo rt ing It ems fo r
S yst e mat ic R e view s a nd Met a-Ana lys e s
P S A P r oba bi l ist i c S ens it i vit y Ana l ys is
Q AL Y Qua lit y - Adjust ed L i f e Yea r
R C T Ra ndomi z ed C ont r ol l ed T r ia l
T EC OS T r ia l Eva lua t i ng C a r di ova scu la r
Out c omes W it h S it a gl ipt i n
UKP DS UK P r osp ect i ve D ia b et es S t udy
UKC R C Unit ed K i ngdom C l i nica l R es ea r c h
C ola bor a t i on
5
Summary and Update
Regarding this work an actualization has been made to the thesis delivered in January of 2015. As this is a field of rapid evolution a new systematic review has been made in May 2015 with the retrieval of new studies published in the years of 2014 and 2015. This new review did not change the methods and conclusions from the former one.
The objectives are to conduct a systematic review of cost-effectiveness, cost-utility and cost-benefit studies of DPP-4 inhibitors for diabetes treatment versus other antidiabetics.
Regarding the methods three investigators searched the CRD York, Tufts CEA Registry, MEDLINE databases through May 2015. We revised all potentially relevant titles and abstracts, and subsequently screened full-text articles, according to inclusion criteria. The studies should be available as a full-text publication and published in English, French, Spanish, or Portuguese. A critical appraisal of the methodology and reporting was performed using the 35 item version of the BMJ checklist.
Regarding the results a total of 295 studies were identified, of which 20 after the 2nd screening. Compared to sulphonylureas, the ICER varied between €924-13,931/QALY for saxagliptin, €5,949-20,350/QALY for sitagliptin and €9,072/QALY for vildagliptin, all as add-on to metformin. Compared to insulin, saxagliptin presented an ICER of €6,100/QALY (with sulphonylurea) and €6,790/QALY (with metformin). Compared to sitagliptin, liraglutide had an ICER that varied between €10,436-32,869/QALY as second line therapy. Finally, a study on GLP-1 agonists established an ICER of €37,463/QALY versus DPP-4 inhibitors. The majority of the studies were based on clinical trials of high quality; differences in ratios were essentially due to differences in the costs of resources across countries.
6 Finally the conclusions are that according to commonly accepted thresholds, DDP-4 inhibitors are cost-effective versus sulphonylureas, and liraglutide versus sitagliptin for diabetes type 2. Recent evidence demonstrates that GLP-1 agonists are cost-effective versus DPP-4 inhibitors, possibly questioning the national current therapeutic guidelines. Keywords Diabetes Cost-effectiveness studies DPP-4 inhibitors Systematic reviews
Em 2013 estima-se que 382 milhões de pessoas tinham diabetes a nível global. (1). De acordo com a Federação Internacional da Diabetes, 5.1 milhões de pessoas morreram de diabetes em 2013. Os países onde a prevalência é maior entre os 20-79 anos de idade são os de médios e altos recursos.
Os inibidores das DPP-4 são medicamentos relativamente novos. A Sitagliptina, saxagliptina, linagliptina, vildagliptina e alogliptina estão aprovadas pela FDA e pela EMA, enquanto outros aguardam aprovação de AIM ou estão em desenvolvimento. A guideline do NICE para a diabetes tipo 2 sugere adicionar um inibidor das DPP-4 em vez de uma sulfonilureia como tratamento de segunda linha, com metformina em primeira linha, se existe um risco considerável de hipoglicemia ou se a sulfonilureia está contra-indicada ou não é tolerada. Esta recomendação é baseada numa revisão sistemática da Cochrane, com um pequeno número de ensaios, todos publicados antes de 2009, e apenas relacionados com sitagliptina e vildagliptina.
7 Além disso, esta guideline não incorpora considerações de custo-efectividade relativas aos novos inibidores das DPP4, que são no entanto essenciais como um instrumento para ajudar a decisão de alocação de recursos. A importância é enfatizada em contextos correntes de recessão económica e de pressão nos budgets públicos já de si apertados, e considerando os altos burdens epidemiológico e económico da doença em questão.
O objectivo deste estudo foi conduzir uma revisão sistemática de estudos custo-efectividade, custo-utilidade e custo-beneficio de inibidores das DPP4 versus outros antidiabéticos como tratamento da diabetes tipo 2, e perceber as suas implicações para guidelines, politicas e futura pesquisa.
Métodos
Esta revisão seguiu a metodologia recomendada pelo PRISMA statement e pelo CRD da University of York para revisões sistemáticas de avaliações económicas.
A revisão de literatura foi baseada numa pesquisa de artigos de jornais científicos e de abstracts em Medline e na base de dados do CRD de 1996 até á presente data e NHS EED, base de dados de avaliações económicas e o registo do Tufts até ao presente. O Google scholar foi também pesquisado. Os termos de pesquisa foram: sitagliptina, vildagliptina, saxagliptina, linagliptina, alogliptina e inibidores das DPP-4, custo efectividade, custo-utilidade e custo benefício.
Primeiro, três investigadores reviram independentemente todos os títulos potenciais e abstracts (1ª screening) e subsequentemente reviram artigos em texto completo (2º screening), de acordo com critérios de inclusão pré-estabelecidos. Os critérios de inclusão seguiram a abordagem PICOS. Seguimos o flowchart do PRISMA no relatório da selecção de estudos como sugerido pelo statement do PRISMA.
8 Estudos custo efectividade, custo utilidade e custo benefício estavam disponiveis como publicações de texto completo e publicadas em Inglês, Francês, Espanhol ou Português. Excluímos as avaliações económicas incompletas – analises custo consequência (4 estudos); Estudos de Patient Reported Outcomes (PRO) (1 estudo); os estudos em sub-populações que não podem ser generalizados para sub-populações (2 estudos); os relatórios de agencias que não foram submetidos a revisão por peer review (36 estudos); estudos fora do âmbito (162) e apenas abstracts (66) como é habitual em revisões sistemáticas. O 2nd screening levou á exclusão de 4 estudos que foram considerados fora de âmbito. Segundo, os três investigadores usaram um template standard de abstração de dados para revisões sistemáticas de avaliações económicas, para extrair independentemente dados de cada estudo. Os desacordos foram resolvidos por discussão.
Terceiro, uma avaliação crítica da metodologia e relatório foi realizada focando em assuntos de qualidade chave, como os métodos de derivar os dados de efectividade, medida e avaliação de dados de recursos, medida e avaliação de benefícios de saúde (utilidades); método de sintetizar os custos e efeitos, análise da incerteza e validade externa. Para fazer isso, usámos a versão de 35 itens da checklist da BMJ. Uma percentagem em score foi atribuida para cada estudo calculando as respostas afirmativas na checklist.
Finalmente, reportamos um sumário de estatísticas e síntese (descritiva) qualitativa de estudos identificados na forma de tabelas de sumários. Uma síntese comparativa qualitativa foi realizada para explorar relações entre e dentro dos estudos.
9 A pesquisa de literatura identificou inicialmente 303 citações. Destas, 24 estudos custo efectividade foram aceites depois do primeiro screening e 20 foram aceites depois do 2nd screening.
Os estudos foram todos realizados em países de altos e médios recursos.
Os países de altos recursos foram os USA, Suécia, Alemanha, UK, Áustria, Finlândia e Canadá. Os países de médios recursos foram a Grécia, Espanha, Portugal, Argentina, Brasil, e Polónia. Quatro estudos recolhidos têm uma perspectiva da sociedade e dezasseis têm uma perspectiva do 3º pagador. A maioria dos estudos foi baseada num RCT. A Saxagliptina foi avaliada em 7 estudos, a sitagliptina em 11 e a vildagliptina em 1, todos como adição á monoterapia com metformina e em segunda linha. Quatro dos estudos da saxagliptina foram também avaliados em combinação com a sulfonilureia. A insulina glargina foi avaliada versus a sitagliptina. Os dois agonistas dos receptores das GLP-1 (liraglutide and exenatide) mais a metformina foram também avaliados versus 3 inibidores das DPP-4 (sitagliptina, saxagliptina, e vildagliptina) no que diz respeito ao custo efectividade.
O treshold da OMS foi usado em países sem treshold oficial (Argentina). Estes critérios definiram uma estratégia como custo efectiva quando o ICER é menos de três vezes o PIB per capita, e como muito custo efectiva quando o ICER é menor do que o PIB per capita [11].
Finalmente, os estudos incluídos nesta revisão eram de alta qualidade (score médio de 0.720 numa escala até 1 e num intervalo entre 0.485 e 0.885).
O ICER para o liraglude versus sitagliptina (ambos adicionados a metformina, e usados em segunda linha) variaram entre €10,436/QALY a €32,869/QALY. Actualmente, excepto no caso dos EUA, todos os estudos obtiveram valores abaixo dos € 20,000/QALY. Por outro lado, a maior parte dos estudos foram baseados nas mesmas
10 medidas dos benefícios, de forma que a a efectividade incremental era bastante similar entre estudos, no que diz respeito a custos de terapia, existiram variações largas entre paises (entre €30,222 nos UK até valores acima de €100,000 na Suécia, para o tratamento com o liraglutide), mas novamente o custo incremental eram bastante similares, explicando o porque dos ratios não diferiram muito. Além disso, os países adoptaram taxas de desconto próximas. Para os EUA o maior ICER foi devido ao maior ICER devido ao menor preço do tratamento com a sitagliptina.
Saxagliptina foi comparada com sulfonilureias maioritariamente, quando adicionada a metformina, em pacientes não controlados com monoterapia com metformina. Os valores de ICER variaram entre 924 a €13,931/QALY. De novo os USA foram um outlier neste caso com um ratio muito menor de €924/QALY. A efectividade incremental nos EUA foi muito maior do que noutros países, onde os valores foram similares. Isto foi essencialmente devido aos menores benefícios das sulfonilureias nos EUA. Um estudo unicamente, comparou a saxagliptina com a pioglitazona, em combinação com a metformina, e descobriu que a saxagliptina é dominante. Finalmente, também num estudo único, observou-se que a saxagliptina em comparação com a insulina teve um ICER de €6,790/QALY em combinação com a metformina e de €6,100/QALY em combinação com a sulfonilureia.
O ICER da sitagliptina versus as sulfonilureias variou entre €5,949/QALY a €20,350/QALY. As comparações entre países permitiu observar que as variações ratios entre os ratios foram essencialmente devido as diferenças entre custos incrementais, entre €5,949/QALY em Portugal a €20,350/QALY na Áustria. As diferenças nos sistemas de saúde, uso de recursos e preços de medicamentos nos diferentes países são explicações para estas diferenças.
11 Um estudo único foi obtido para a vildagliptina comparado com sulfonilureias, todos adicionados a metformina, em pacientes não controlados com monoterapia com metformina. A vildagliptina tem um ICER de €9,072/QALY comparado com as sulfonilureias no SNS Português.
Finalmente, a insulina glargina foi comparada com a sitagliptina como adicionados a metformina, e foi classificado como dominante nos settings Canadianos.
Os agonistas dos GLP-1 (exenatide and liraglutide) foram comparados aos inibidores dos DPP-4 como adicionados a metformina, com um ICER de €37,463/QALY em settings Suecos.
Conclusões
Os inibidores das DPP-4 representam benefícios substanciais no tratamento da diabetes tipo 2, mas também um desafio relevante para os sistemas de saúde devido aos seus altos preços. Há assim claramente uma necessidade de realizar avaliações destas novas terapias, para conduzir os tomadores de decisão nas suas decisões no que diz respeito a co-pagamentos, guidelines terapêuticas e estratégias de comparticipação. Esta revisão sistemática de literatura demonstra que a evidência em custo efectividade é ainda recente e escassa mas é consistente e baseada em estudos de grande qualidade global. Em particular, a maioria dos estudos foi baseada em RCTs publicados para a medida das consequências, e nos preços unitários oficiais e recursos especificos de cada país usado para custos. Os resultados providenciaram evidência do custo efectividade dos inibidores das DPP-4 para a diabetes tipo 2 quando comparados com as sulfonilureias de acordo com tresholds específicos de cada país ou de acordo com os tresholds da OMS. De acordo com os resultados os inibidores das DPP-4 o liraglutide foi custo efectivo quando comparado com a sitagliptina.
12
Dissertation de livere d in Ja nuar y 2015
ABSTRACT
T he place of DPP-4 inhibitors in the treatment algorithm of
diabetes type 2: a Sys tematic Review of Cost -effectiveness
Studies
Al e xand re B apt ist a 1, I nês T e i xe ir a 2, S óni a Ro ma no2, A ntó ni o V a z Car ne iro 3, J ul i an Pe re l man4
1 F a cult y of M edi c i ne of Lisb on
2 C ent r e f or H ea lt h E va lua t i on & R es ea r c h ( C EF AR ), Na t i ona l Ass ocia t i on of P ha r ma c i es ( ANF )
3 C ent er f or Evi denc e- Ba s ed M edi c i ne (C E MBE), F a cult y of M edi c i ne a t t h e Uni ver s it y of L isb on
13
Objective: To conduct a systematic review of effectiveness, utility and
cost-benefit studies of new inhibitors of DPP-4 for diabetes treatment versus other antidiabetics.
Methods: Three investigators searched the CRD York, NICE Health Technology
Assessment, Tufts CEA Registry, MEDLINE (PubMed) databases, and grey literature through 2014. Revision of all potentially relevant titles and abstracts (1st screening), and subsequently screened full-text articles (2nd screening), according to inclusion criteria. Restricted to studies with a lifetime or near-lifetime horizon and adopting either a societal or a healthcare perspective. The studies should be available as a full-text publication and published in English, French, Spanish, or Portuguese. A critical appraisal of the methodology and reporting was performed using the 35 item version of the BMJ checklist.
Results: A total of 59 studies were identified and 13 were accepted (2nd screening). Saxagliptin was assessed in 7 studies, sitagliptin in 5 and vildagliptin in 1. Liraglutide was cost-effective versus sitagliptin as second line therapy (12,401 to 29,957 €/QALY). Saxagliptin (842 to 13,931 €/QALY), sitagliptin (5,949 to 20,350 €/QALY) and vildagliptin (9,072 €/ QALY) were also cost-effective versus sulphonylureas as second line therapy, all as add-on to meformin. Saxagliptin is dominant versus pioglitazone with metformin. Saxagliptin was also cost-effective versus insulin (5,831 €/QALY with sulphonylurea and 6,491 €/QALY with metformin).
Conclusion: According to commonly accepted thresholds in high income countries,
there is consistent evidence about the cost-effectiveness of DDP-4 inhibitors as second line therapy for diabetes type 2. Though, more evidence is necessary to define which DDP-4 inhibitor is the most cost-effective.
14
Background:
D ia bet es me llit us is a gro up o f met a bo lic d is e as es c haract er ize d b y hyp erg lyc e mia res u lt ing fro m de fe ct s in insu lin s ecret io n, ins u lin act io n, o r bot h. The c hro nic hyp erg lyc e mia o f d ia bet es is a sso c iat ed w it h lo ng-t erm d a mag e, d ys fu ncng-t io n, a nd fa ilure o f var io us o rga ns, esp ec ia lly ng-t he e yes, k id ne ys, ner ves, heart , and blo o d ve ss e ls.
T ype 1 d ia bet e s is c haract er ize d by β- ce ll de st ruct io n, usu a lly lead ing t o a bso lut e insu lin d e fic ie nc y. T his fo r m o f d ia bet es, w hic h ac co unt s fo r o nly 5–10% o f t ho se w it h d ia bet es, pre v io us ly e nco mp as sed b y t he t er ms ins u lin-d epe nd e nt d ia bet es, t yp e I d ia bet es, o r ju ve n ile-o nset d ia bet es, resu lt s fro m a ce llu lar- med iat ed aut o immune de st ruct io n o f t he β-ce lls o f t he p a ncre as. Ge st at io na l d ia bet es me llit us is d e fined a s a ny degre e o f g lu co se int o ler a nce w it h o ns et o r first reco gnit io n dur ing preg na nc y (1) T ype 2 D ia bet es Me llit u s re su lt s fro m in su lin re s ist a nce, a co nd it io n i n whic h ce lls fa il t o use ins u lin pro per ly, s o met ime s a lso w it h a n a bso lut e ins u lin de fic ie nc y. T his fo r m w as pre vio us ly re ferred t o as no n ins u lin-depe nd e nt d ia bet es me llit u s (NIDD M) o r "adu lt -o nset d ia bet es ". (2) T yp e 2 d ia bet es co mpr is e s 90% o f p eo p le w it h d ia bet es aro und t he wo r ld ( 3), a nd is large ly t he resu lt o f e xce ss bo d y w e ig ht and p hys ic a l inact iv it y. Pat ie nt s w it h t yp e 2 d ia bet es ha ve a hig her pre va le nc e o f o bes it y (part icu lar ly a bdo mina l o be s it y), hyp ert e ns io n, a nd lip id d iso rders, a s we ll as a n incr ea sed r isk o f macro vascu lar d ise as e in co ro nar y, per ip hera l, a nd cere br a l art er ia l c ir cu lat io ns, t ha n peo p le w it ho ut d ia bet es. (4) M icro vas cu lar co mp lic at io ns o f d ia bet es inc lud e ret ino pat h y, w hic h ca n le ad t o lo ss o f vis io n, nep hro pat h y ( lead ing t o rena l fa ilure), neuro pat hy (w it h a n increa sed r is k o f fo o t u lcer s, a mput at io ns, a nd fo o t defo r mat io ns), a nd aut o no mic neuro pat hy, ca us in g card io va sc u lar, ga st ro int est ina l, g e nit o urinar y, a nd se xu a l d ys fu nct io n. D ia bet es ma y ha ve a s er io u s e mo t io na l a nd so c ia l imp act o n a ffe ct ed ind iv idua ls a nd t he ir fa milie s, a nd has ma jo r eco no mic imp lic at io ns fo r so c iet y as a w ho le in bo t h de ve lo p ed a nd de ve lo p ing co unt r ies (4)
1. Clinical evidence about diabetes
Regard ing c lin ic a l e v ide nce a nd mo re spec ific a lly co mp let ed c lin ica l t ria ls , t he D ia bet es Tr ia ls U nit o f t he U n iver s it y o f O xfo rd, a re fere nce in t he fie ld w it h a re le va nce o f 100% acco rd ing ly w it h t he U n it e d King do m C lin ic a l Re se arc h Co la bo rat io n (U KC RC) Re g ist ered C lin ic a l Tr ia ls U nit N et wo rk, t he mo st re le va nt w as t he U K Pro spe ct ive D ia bet e s St ud y (UKP DS). This wa s a la nd ma rk ra ndo mis ed, mu lt ice nt re t ria l o f g lyc ae mic t herap ie s in 5,102 pat ie nt s w it h new ly d ia g no sed t ype 2
15 d ia bet es. It ran fo r t we nt y ye ars (197 7 t o 1997) in 23 U K c lin ic a l s it e s a nd s ho wed co nc lus ive ly t hat t he co mp lic at io ns o f t yp e 2 d ia bet es, prev io us ly o ft e n regarded a s ine vit a ble, co u ld be reduc ed b y impro vin g blo o d g luco se a nd/o r blo o d pressur e co nt ro l. (5)
2. Epidemiology- B urden of disease
There are s e vera l det er mina nt s t hat co nt ribut e t o t he incre as e o f t he nu mber o f per so ns w it h d ia bet es. Amo ng t he m are: gro wt h and ag e ing o f t he po pu lat io n, ur ba niz at io n, t he incre as e o f t he pre va le nc e o f o be s it y a nd sed e nt ar is m. (6)
G lo ba lly, as o f 201 3, a n est imat ed 382 millio n peo p le wo r ldw id e had d ia bet es ac co rd ing ly w it h dat a fro m ID F. (7)
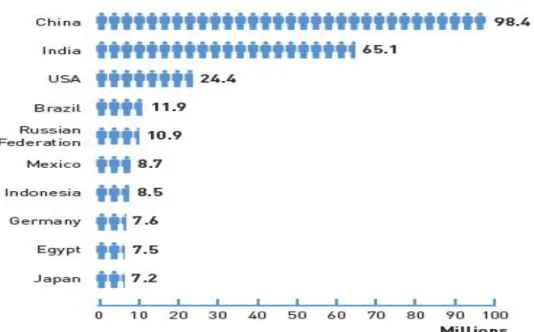
Figu re 1 - Inte rnationa l Diab etes Fede r ation (IDF) At la s 2013 (7)
98, 4 millio n p eo p le in C h ina a nd a bo ut 11, 9 millio n peo p le in Braz i l had d ia bet es t ype 2. Mo re t ha n 80% o f d ia bet es d eat hs o ccur in lo w- a nd midd le - inco me co unt r ies (8). Wo r ld H ea lt h Orga n izat io n ( WHO) pro ject s t hat d ia bet es w ill be t he 7t h le ad ing cau s e o f de at h in 2030. ( 9) Hea lt h y d iet , regu lar p h ys ic a l a ct ivit y, ma int a in ing a no r ma l bo d y w e ig ht a nd a vo id ing t o bacco use c a n pre ve nt o r dela y t he o nset o f t ype 2 d ia bet es. I f t hes e incre as ing t re nds co nt inu e, by 2 035, so me 592 millio n p eo p le w ill ha ve d ia bet es. The large st incre as es w ill t ake p lac e in t he reg io n s where de ve lo p ing e co no mie s ar e predo min a nt . (7)
16
M orbidity
In fig ure 2 it is po ss ib le t o see t he preva le nc e o f peo p le w it h d ia bet e s aro und t he wo r ld.
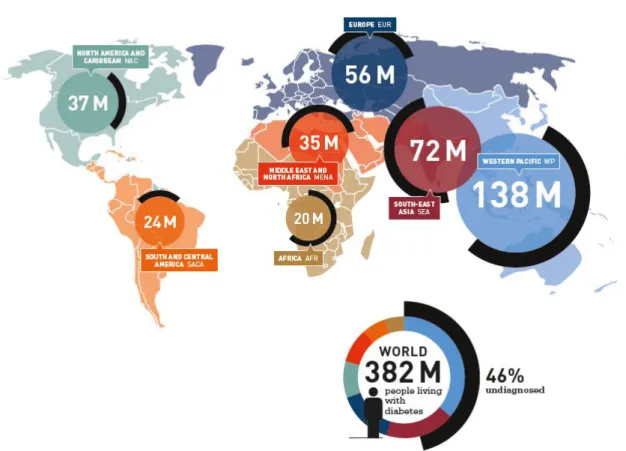
In 2 013 t here were 382 millio n p eo p le living w it h d ia bet es a nd 46% o f t he m wer e u nd ia g no sed. Fro m t he se, 13 8 millio n live d in t he We st er n Pac ific a nd 72 millio n live d in So ut h East As ia. T he la rge ma jo r it y o f t he peo p le liv ing w it h d ia bet es in t he se ar eas ar e u nd iag no s ed.
Figu re 2 - Inte rnationa l Diab etes Fede r ation (IDF) At la s 2013 (7) .
Furt her mo re t he At las o f 2 013 pr e se nt s t he pro ject io ns o f t he nu mber o f peo p le w it h d ia bet es (20-75 ye ars) bet wee n 2013 a nd 2035.
17
Figu re 3 - IDF At la s 2013 (7)
The incr ea se in t he nu mbe r o f peo p le w it h d ia bet es is go ing t o be hig he r in A fr ica ( incre as e by 109, 1%) a nd lo w er in Euro pe ( incr ea se by 2 2, 4 %) as it is po s s ib le t o see in figure 3. (7)
M orta lity
WHO pro je ct s t hat d ia bet es deat hs w ill d o uble bet we e n 2005 a nd 2 030. (10) Acco rd ing t o t he I nt ernat io na l D ia bet es Fed erat io n 5, 1 millio n peo p le d ie d due t o dia bet es in 2 013.
18
Figu re 4 - Inte rnationa l Diab etes Fede r ation Atla s 2013 (ID F) (7)
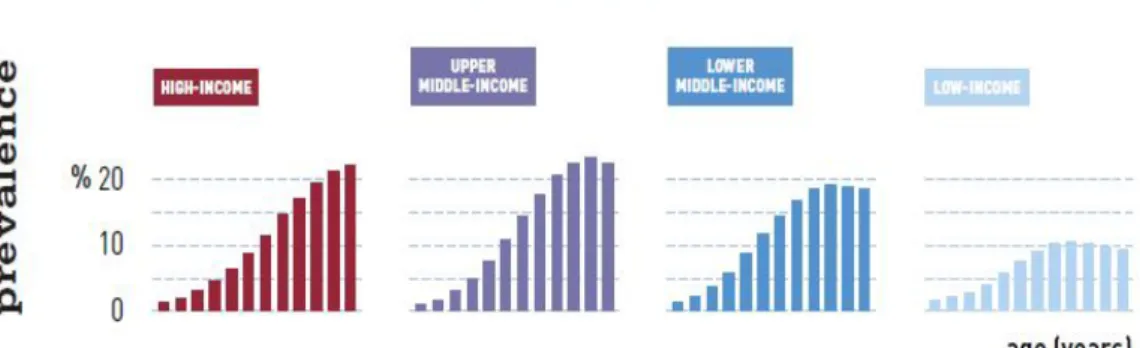
Upper midd le- inco me a nd hig h – inco me g ro ups are t he gro ups where t here is hig her pre va le nce o f d ia bet es (20-79 years) at a g lo ba l le ve l a s is it po s s ib le t o see in figure 4.
Figu re 5 - Inte rnationa l Diab etes Fede r ation Atla s 2013 (7)
Mo reo ver ha lf o f t he peo p le w ho d ie fro m d ia bet es are u nder t he a ge o f 60 as it po ss ib le t o underst a nd in figure 5.
19
Tab le 1 - Eu ro stat (11)
On t a ble 1 we co mp are t he mo rt a lit y rat es in d iffer e nt Euro pea n co unt r ie s t o co nc lu de t hat t he U K pres e nt s t he lo wer mo rt a lit y rat e a mo ng t he co unt r ies s e lect ed. Po rt uga l pr ese nt s o ne o f t he h ig he st va lue s o f mo rt a lit y w it h 22, 9 deat hs per 100 00 0 inha b it a nt s. The Euro pea n (27 co unt r ie s) a verag e is o f 12, 0 deat hs per 1 00 000 inha bit a nt s. In Po rt uga l t here ha s bee n no po s it ive o r ne gat ive e vo lut io n o f deat hs by d ia bet es in t he last 10 ye ars. The nu mber ha s re ma ine d st able.
20
Po rtugue se D ata
The pre va le nce o f d ia bet es in Po rt uga l in 20 12 wa s o f 12, 9 % o f t he Po rt uguese po pu lat io n w it h age s bet wee n 20 a nd 79 ye ars o ld. T her e ha s bee n a n incr ea se in t he pre va le nce o f d ia bet es (as it wa s 11, 7% in 2009). Regard ing mo rt a lit y d at a t here ha s bee n a de crea se o f 15% o f po t ent ia l life ye ars lo st in t he p er io d bet wee n 2 0 06 a nd 2012 in t he po pu lat io n w it h les s t ha n 70 ye ars o ld. (12)
3. Econo mic B u rden o f dise as e
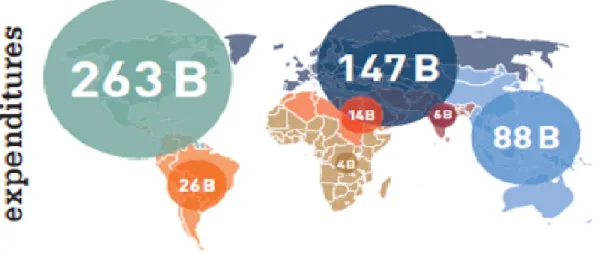
Figu re 6 - Inte rnationa l Diab etes Fede r ation (IDF) At la s (7)
A lo o k at he a lt h sp e nd ing o n d ia bet es b y reg io n re ve a ls hu ge d is par it ie s in re spo ns es t o t he ep ide mic. Two reg io ns s pe nt mo re o n d ia bet es t ha n a ll o t her reg io ns: No rt h Ame r ica a nd Car ibbe a n, w it h a n e st imat ed USD 263 billio n- e qua l t o near ly ha lf t he wo rld ´s he a lt h e xpe nd it ure o n d ia bet es ; a nd Euro pe w it h USD 147 billio n. Desp it e t he ir gro w ing d ia bet es po pu lat io ns, sp e nd ing in So ut h-East -As ia a nd Afr ic a acco u nt ed fo r les s t ha n 1% o f a ll g lo ba l hea lt h e xpe nd it ure o n t he d is ea se.(7)
21
Tab le 2 - Top 10 count rie s with the hi ghest he a lth e xpenditu re s fo r diabetes a s mea su red by the national total, pe r pe rson with diabetes , and percentag e of the nationa l hea lth e xpenditure on diabete s in 2010
So urce: Euro st at (11)
One co u nt r y, t he U nit ed St at es o f Amer ica (US A), sp e nt USD 19 8 billio n, o r 52.7% o f g lo ba l e xpe nd it ure fo r d ia bet e s a s s ho w n in t a ble 2 . Ind ia, t he co unt r y w it h t he la rge st po pu lat io n o f peo p le liv ing w it h d ia bet es, spe nt a n e st imat ed US D 2.8 billio n, o r le ss t ha n 1% o f t he g lo ba l t ot a l a nd so do es no t ent er in t he to p 10 co unt r ie s in t he t able . (11)
An a ver age o f USD 7,383 per per so n w it h d ia bet es w ill be spe nt o n d ia bet es-re lat ed care in t he US A but les s t ha n USD10 per per so n wer e spe nt in B uru nd i, Cô t e d’Ivo ire a nd M ya n mar. (11)
Costs:
Co st s ca n d iv ided in t wo t ype s u s ing a hea lt h eco no mic s ap pro ach: t he d ire ct co st s and t he ind irect co st s.
Di rect co sts:
D ire ct co st s t o ind iv idu a ls a nd t he ir fa milie s inc lud e med ic a l c are, drugs, ins u lin a nd o t her supp lie s. Pat ie nt s ma y a lso ha ve t o bear o t her perso na l co st s, suc h as incr eas ed pa yme nt s fo r hea lt h, life a nd aut o mo bile ins ura nce. D ir ect co st s t o t he hea lt hcare s ect o r inc lud e ho sp it a l ser vic e s, phys ic ia n s erv ice s, la bo rato ry t est s and t he da il y ma nage me nt o f d ia bet es – w hic h inc lu de s a va ila bilit y o f pro duct s suc h as ins u lin, s yr ing es, o ra l hypo g lyc ae mic age nt s a nd blo o d-t est ing equ ip me nt . Co st s ra nge fro m re lat ive ly lo w-co st it e ms, suc h as pr imar y-care co nsu lt at io ns a nd ho sp it a l o ut pat ie nt ep iso des, t o ver y hig h-co st it e ms, su c h as lo ng ho sp it a l inpat ie nt st a ys fo r t he t reat me nt o f co mp lic at io ns.
D ire ct hea lt h care co st s o f d ia bet es are d iffere nt in a nnua l he a lt h car e bud get s, depe nd ing o n lo c a l d ia bet es pre va le nc e a nd t he so p hist icat io n o f t he t reat me nt ava ila ble.
22 This var iat io n is pr imar ily dr ive n b y t he d ia bet es pre va le nce o f ea c h co unt r y, w hic h is dr ive n in t urn by t he inc ide nce o f new d ia bet es c as e s a nd by t he rat es o f sur viva l a ft er d ia bet es o nset
Also , t he hig her t he so phist ic at io n o f t he t reat me nt a va ila b le t he hig he r w ill be t he co st s. Desp it e t he co st -e ffect ive nes s o f so me in no vat iv e t reat me nt s t here is a budget impa ct a llo ca t ed to t he m. The bud get imp act a llo cat ed t o so me co st -e ffe ct ive t reat me nt s ca n be t o o hig h t o be suppo rt ed by t he hea lt h s yst e m budget s o f so me co u nt r ie s. So , t here ar e co unt r ie s w it h d iffere nt re so urces a nd d iffere nt po rt fo lio s o f t reat me nt a va ila b le.
A co st -o f- illne s s st ud y t hat co vered Euro pea n co u nt r ie s e st imat ed a nnua l d ire ct med ic a l co st s per pat ie nt o f € 2834 and t ot a l co st s o f € 29 billio n in 2002[1 3]. In 2012, t he co st o f d ia g no sed d ia bet es in t he U nit ed St at es was $17 6 billio n fo r d ire ct med ic a l co st s (ho sp it a l a nd e me rge nc y care , o ffic e vis it s a nd med ic at io ns). (14)
Indi re ct cost s - costs o f lo st productivit y
A nu mber o f d ia bet es p at ie nt s ma y no t be a ble t o co nt inue wo rk ing o r wo rk as e ffe ct ive ly a s t he y co u ld be fo re t he o ns et o f t he ir co nd it io n. S ic k ne ss, a bse nc e, d is a bilit y, pre mat ure ret ire me nt o r pre mat ure mo rt a lit y ca n c aus e lo s s o f pro duct ivit y.
Est imat ing t he co st to so c iet y o f t his lo ss o f pro duct ivit y is no t eas y. Ho wever, in ma ny c as es w here e st imat es ha ve be e n made, t he se co st s o f lo st pro duct io n ma y be as great o r e ve n great er t ha n d irect he a lt h car e co st s. This ma y be bec au se t here is limit ed acce s s t o hig h qua lit y c are w it h, co nse que nt ly, a hig h inc id e nc e o f co mp lic at io ns, d is a bilit y a nd pre mat ure mo rt a lit y. Fa milie s t oo , o f co urse, su ffer lo ss o f ear ning s a s a resu lt o f d ia bet es a nd it s co ns eque nce s.
The Amer ic a n D ia bet es As so c iat io n est imat ed t hat t he US e co no my lo st $69 billio n USD in r educ ed pro duct ivit y in 2012. Averag e med ic a l e xpe nd it ures a mo ng p eo p le w it h d ia bet es ar e 2.3 t ime s hig her t ha n a mo ng t ho se w it ho ut dia bet es. A s ig nifica nt po rt io n o f t he U.S. hea lt h care do lla r go es t o t reat ing peo p le w it h d ia bet es. Mo re t ha n $1 in $10 is spe nt d ir ect ly o n d ia bet es a nd as so c iat ed co mp licat io ns, a nd $1 in $ 5 is spe nt o n car ing fo r peo p le w it h d ia bet es. (14)
Suc h lo s se s are per hap s re lat ive ly la rge r in po o rer co unt rie s be cau s e pre mat ure deat h due t o dia bet es o ccurs at mu c h yo u ng er age s. (15)
4. T reat ment - Inhibito rs o f DPP4
Treat me nt o f d ia bet es t yp e 2 is in it ia lly w it h d iet a nd e xerc is e, w it h o ra l drugs be ing a dded if t hat is ins u ffic ie nt , o r whe n t he co nd it io n pro gresse s, as is co mmo n. T he U K Pro sp ect ive D ia bet es St ud y (U KPDS) s ho wed t hat in ma n y pat ie nt s, T2DM, is a pro gress ive d iso rder w it h
23 d imin is h ing bet a ce ll fu nct io n o ver t ime . Ma ny pat ie nt s pro gres s fro m life st yle c ha ng es t o ora l mo no t herap y, the n to co nt inuat io n o f t ablet s, a nd in a t hird o f ca se s, t o insu lin t hera p y, w it h o r w it ho ut co nt inue d t ablet t reat me nt suc h a s met fo r min.
Inhib it o rs o f d ipept id yl p ept ida se 4, a lso ca lled DPP-4 inh ib it o rs o r g lipt ins, ar e a c la s s o f o ra l h ypo g lyc e mics t hat blo c k DPP-4. G luc ago n incr ea se s b lo o d g luco se le ve ls, a nd DP P-4 inhib it o rs reduc e g luca go n a nd blo o d g luco se le ve ls . The me c ha nis m o f DPP-4 inh ib it o rs is t o incr ea se inc ret in le ve ls (G LP-1 a nd GI P),(16, 17, 18)] whic h inh ib it g lu cago n re le as e, w hic h in t urn increa s es ins u lin s ecret io n, decre as e s gast r ic e mpt ying, a nd de crea se s blo o d g lu co se le ve ls
The y c a n be u sed t o treat dia bet es me llit u s t ype 2.
DPP-4 inh ib it o rs are r e lat ive ly new o ra l hypo g lyc e mic drug s. S it a g lipt in, vild ag lipt in, sa xag lipt in, linag lipt in a nd a lo g lipt in ar e curre nt ly appro ved b y t he US Fo o d and Drug Ad min ist rat io n a nd t he Euro pea n Med ic ine s Age nc y, w hile o t hers are awa it ing ap pro va l o r are in de ve lo p me nt .
T reat ment A lgo rithm
It is re co mme nd ed b y t he AH RQ (19) t ha t met fo r min s ho u ld be t he first line t herap y. DPP-4 inh ib it o rs are re co mme nded fo r u se w he n met fo r min a lo ne do es no t co nt ro l H bA1c le ve ls.
In Po rt uga l t he D irec ção Gera l de Saúd e ( DGS) ha s is s ued a gu ide line in 2011 w her e t he t reat me nt a lgo r it hm fo r t he us e o f DDP4 inh ib it o rs ha s bee n de fine d a nd fir st - line met fo rmin is reco mme nde d. (20) Ne vert he le ss, a mo ng t he re fere nce s is t he Nat io na l I nst it ut e fo r Hea lt h a nd C lin ic a l E xc e lle nce (NICE) gu id e line fo r t he co st -e ffect ive ne s s re le va nce o f t hes e med ic at io ns. (21).
The NICE c lin ic a l gu ide line fo r t yp e 2 d ia bet es sugg est s ad d ing a DPP-4 inh ib it o r inst ead o f a su lfo nylur ea a s sec o nd line t reat me nt t o first lin e met fo r min if t here is a co ns id era ble r isk fo r h ypo g lyc ae mia o r if a su lfo nylur ea is co nt ra ind ic at ed o r no t t oler at ed. This reco mme nd at io n, ho we ver, is ba sed o n a s ma ll nu mber o f t ria ls a nd a Co c hra ne s yst e mat ic revie w, a ll pu blis he d be fo re 2009 a nd it is co nc er ning o n ly s it ag lipt in a nd vildag lipt in. (22)
Also , as s ho w n in fig ure 8 t he Amer ic a n D ia bet es As so c iat io n ( AD A) a nd t he Euro pea n As so c iat io n fo r t he St u d y o f D ia bet es (E ASD) ha ve a c lear a lgo r it hm o f t reat me nt (23) I n t his a lgo r it h m o f t reat me nt t he DPP-4 inh ib it o r are re co mme nded fo r us e in t wo -drug co mb inat io ns a s add-o n to met fo r min. T he c haract er ist ic s o f t hes e drugs are int er med iat e e ffic ac y, lo w r is k o f hypo g lyce mia, neut ra l imp act o n BMI, rare ma jo r s ide e ffect s a nd hig h co st s. Ne vert he le ss, co st -effe ct ive nes s ru le s are no t co ns id ered.
24
Figu re 7 - A me ri can Diab etes As soc iation ( ADA) and Eu ropea n As sociation fo r the Study of Diab etes (E ASD) alg o rith m of t re atment
5. Relevance of the study
The DPP-4 inh ib it o rs c la ss wa s co ns id ere d due t o it s eco no mic imp act in t he nat io na l hea lt h s yst e m e xpe nse s. ( 24) The curre nt gu id e line s reco mme nd met fo r min as first line t herap y fo r T2DM pat ie nt s.
In se co nd line t her ap y a co mbinat io n o f met fo r min a nd DPP 4 inh ib it o rs is a po ss ib ilit y o f t reat me nt as s ho wn in figure 8. It revea ls e ffic ac y in c lin ica l set t ing s, prese nt lo w r is k o f hypo g lyc ae mia, are neut r a l regard ing w e ig ht ga in a nd pre se nt rare s ide e ffe ct s. But t he y ar e e xpe ns ive.
25 The rat io o f t he co ns u mpt io n o f D PP-4 inh ib it o rs versu s o t he r a nt id ia bet ic drug s is a lread y o ne o f t he per fo r ma nce ind icat o rs fo r t he e va luat io n o f t he Pr imar y Care ce nt res t yp e 2 in Po rt uga l. (25) It is impo rt ant t o ha ve dat a a bo ut it s co st -e ffe ct ive ne s s in o rder t o under st and ho w t o a llo c at e reso urce s in t his c la s s o f drugs in t ime s o f budg et co nst ra int in t he he a lt h s yst e ms. To do t hat it is ne eded t o st ud y t he p lace o f DPP-4 inh ib it o rs in t he d ia bet es treat me nt a lgo r it hm. There is a lr ead y so me e vid e nc e but it is d is per sed a nd d iffic u lt t o co mp are a nd so a s yst e mat ic re view is impo rt ant in t he se set t ing s.
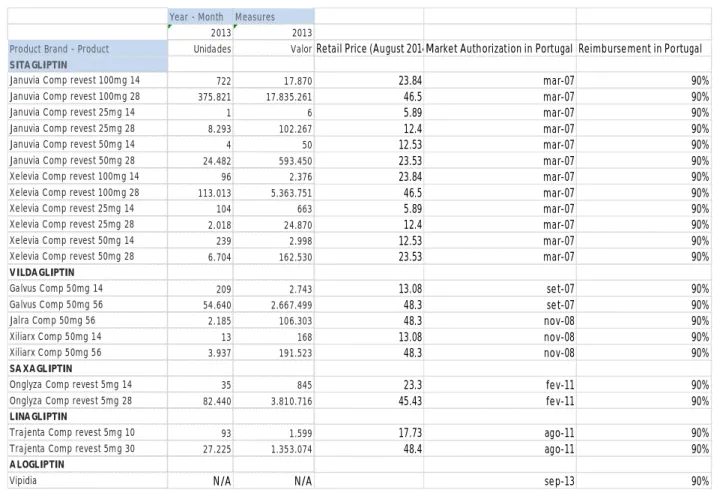
Figu re 8 - Consu mption, Pri ce, M a rket Autho ri zation Ho ld e r and Reimbu rs e ment o f D PP-4 Inhibito rs in Po rtuga l in 2013 ( Sou rce hmR e Infomed)
Year - Month Measures
2013 2013
Product Brand - Product Unidades ValorRetail Price (August 2014)Market Authorization in Portugal Reimbursement in Portugal SITAGLIPTIN
Januvia Comp revest 100mg 14 722 17.870 23.84 mar-07 90%
Januvia Comp revest 100mg 28 375.821 17.835.261 46.5 mar-07 90%
Januvia Comp revest 25mg 14 1 6 5.89 mar-07 90%
Januvia Comp revest 25mg 28 8.293 102.267 12.4 mar-07 90%
Januvia Comp revest 50mg 14 4 50 12.53 mar-07 90%
Januvia Comp revest 50mg 28 24.482 593.450 23.53 mar-07 90%
Xelevia Comp revest 100mg 14 96 2.376 23.84 mar-07 90%
Xelevia Comp revest 100mg 28 113.013 5.363.751 46.5 mar-07 90%
Xelevia Comp revest 25mg 14 104 663 5.89 mar-07 90%
Xelevia Comp revest 25mg 28 2.018 24.870 12.4 mar-07 90%
Xelevia Comp revest 50mg 14 239 2.998 12.53 mar-07 90%
Xelevia Comp revest 50mg 28 6.704 162.530 23.53 mar-07 90%
VILDAGLIPTIN
Galvus Comp 50mg 14 209 2.743 13.08 set-07 90%
Galvus Comp 50mg 56 54.640 2.667.499 48.3 set-07 90%
Jalra Comp 50mg 56 2.185 106.303 48.3 nov-08 90%
Xiliarx Comp 50mg 14 13 168 13.08 nov-08 90%
Xiliarx Comp 50mg 56 3.937 191.523 48.3 nov-08 90%
SA XAGLIPTIN
Onglyza Comp revest 5mg 14 35 845 23.3 fev-11 90%
Onglyza Comp revest 5mg 28 82.440 3.810.716 45.43 fev-11 90%
LINAGLIPTIN
Trajenta Comp revest 5mg 10 93 1.599 17.73 ago-11 90%
Trajenta Comp revest 5mg 30 27.225 1.353.074 48.4 ago-11 90%
ALOGLIPTIN
Vipidia N/A N/A sep-13 90%
The DPP-4 inh ib it o rs are e xpe ns ive mo lecu le s. So , in 20 13 s it ag lipt in va lue s 24,106,092 euro s, vildag lipt in va lu es 2,968,236 e uro s, sa xag lipt in va lue s 3,811,560 euro s a nd linag lipt in va lues 1,354,673 euro s.
As it is po ss ib le t o und erst a nd fro m figur e 9 t he t ot a l sa le s va lu e in 201 3 o f t he DPP-4 inh ib it o rs was o f 32,24 0,561 euro s. Furt her mo re, t he re imbur se me nt is o f 90% w hat mea ns t hat 29,016,505 euro s were sp e nt by t he st at e in 2 013 in t he se mo le cu le s.
26
Fig.9 - Con sumption, Pric e, M arket Autho ri zation Ho ld e r an d Reimbu rs e ment o f DPP-4 Inhibito rs c o mbination s in Po rtug a l in 20 13 (Source hmR e In fo med)
Year - Month Measures
2013 2013
Product Brand - Product Unidades ValorRetail Price (May 2014)Market Authorization in Portugal Reimbursement in Portugal
Metformin + Sitagliptin
Janumet Comp revest 1000mg+50mg 14 403 5.440 13.25 jul-08 90%
Janumet Comp revest 1000mg+50mg 56 581.435 28.473.749 47.82 jul-08 90%
Janumet Comp revest 850mg+50mg 14 147 1.937 12.9 jul-08 90%
Janumet Comp revest 850mg+50mg 56 116.601 5.639.609 46.49 jul-08 90%
Velmetia Comp revest 1000mg+50g 14 274 3.703 13.25 jul-08 90%
Velmetia Comp revest 1000mg+50g 56 158.519 7.761.112 47.82 jul-08 90%
Velmetia Comp revest 850mg+50mg 14 51 675 12.9 jul-08 90%
Velmetia Comp revest 850mg+50mg 56 34.843 1.688.146 46.49 jul-08 90%
Metformin + Saxagliptin
Komboglyze 1000 mg + 2,5 mg 56 comp 46.57 nov-11 90%
Komboglyze 1000 mg + 2,5 mg 14 comp 12.92 nov-11 90%
Komboglyze 850 mg + 2,5 mg 56 comp 47.99 nov-11 90%
Komboglyze 850 mg + 2,5 mg 14 comp 12.81 nov-11 90%
Metformin + Linagliptin
Jentadueto 1000 mg + 2,5 mg 60 comp N/A 50.64 jul-12 90%
Jentadueto 1000 mg + 2,5 mg 10 comp N/A 9.53 jul-12 90%
Jentadueto 850 mg + 2,5 mg 60 comp N/A 50.64 jul-12 90%
Jentadueto 850 mg + 2,5 mg 10 comp N/A 9.53 jul-12 90%
Metformin + Alogliptin
Vipdomet 1000 mg + 12,5 mg 56 comp N/A 48.21 sep-13 90%
Vipdomet 1000 mg + 12,5 mg 14 comp N/A 13.36 sep-13 90%
Vipdomet 1000 mg + 12,5 mg 56 comp N/A 48.21 sep-13 90%
Vipdomet 1000 mg + 12,5 mg 14 comp N/A 13.36 sep-13 90%
Metformin + Vildagliptin
Eucreas Comp revest 1000mg+50mg 10 460 4.583 9.49 nov-07 90%
Eucreas Comp revest 1000mg+50mg 60 498.613 26.755.416 50.45 nov-07 90%
Eucreas Comp revest 850mg+50mg 10 137 1.396 10.73 nov-07 90%
Eucreas Comp revest 850mg+50mg 60 120.632 6.610.514 53.45 nov-07 90%
Zomarist Comp revest 1000mg+50mg 10 195 1.949 9.49 dec-08 90%
Zomarist Comp revest 1000mg+50mg 60 279.691 15.007.426 50.45 dec-08 90%
Zomarist Comp revest 850mg+50mg 10 31 314 10.73 dec-08 90%
Zomarist Comp revest 850mg+50mg 60 74.570 4.084.601 53.45 dec-08 90%
Icandra Comp revest 1000g+50mg 10 11 108 9.49 dec-08 90%
Icandra Comp revest 1000g+50mg 60 166.691 8.939.268 50.45 dec-08 90%
Icandra Comp revest 850mg+50mg 10 25 258 10.73 dec-08 90%
Icandra Comp revest 850mg+50mg 60 40.961 2.242.118 53.45 dec-08 90%
The DPP-4 inh ib it o rs us ed in co mb inat io n ar e e xp e ns ive mo le cu le s a nd met fo r min + s it ag lipt in va lu es 43,574 ,372 euro s a nd met fo r min + vild ag lipt in va lue s 63,647,95 1 euro s. As we ca n se e in fig ure 10 w e ca n co nc lud e t hat a bo ut 107, 222, 323 w ere spe nt in 2013 in t hes e fixe d co mbinat io ns. So t he Po rt uguese N HS s pe nt 90% o f t his va lu e t hat is 96, 500, 090 e uro s in t he se fixe d co mbinat io ns in 2013. T his is a conservative assumption as there are persons with low level of income that have 95% of reimbursement of the drug for diabetes.
27 I f we su m t he s a le s o f DPP-4 inh ib it o rs so ld as s ing le mo le cu le a nd a s fixe d co mbinat io ns it is po ss ib le t o und erst a nd t hat t hese nu mber s represe nt 139, 46 2, 884 euro s o f t he t ot a l va lue spe nt by t he Po rt uguese NHS in a nt id ia bet ic s in 2013. T he Po rt ugues e NHS sp e nt a bo ut 229, 5 millio n euro s in a ll t yp e o f me d icat io n fo r d ia bet es in 2 013 (26).
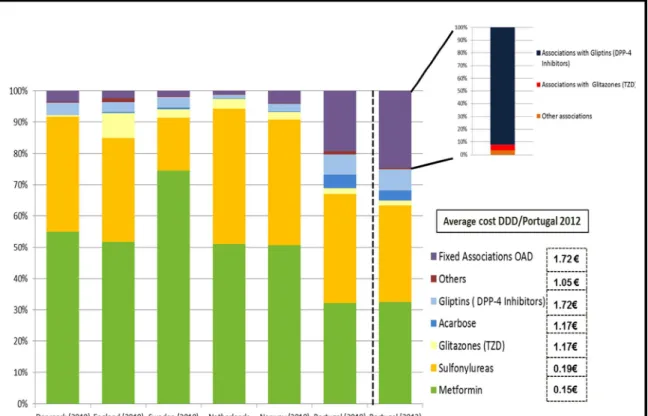
Figu re 10 - Dist ribution of O ra l Antidiabetic D rug s Consu mptio n (%D DD) in Po rtuga l in 2012 (22)
As s ho w n in figure 10 t he DPP-4 inh ib it o rs cause a great imp act in t he e xpe nd it ures o f t he d iffe re nt he a lt h s yst e ms but t he y ha ve a part icu la r hig h impa ct in t he Po rt uguese hea lt h s yst e m. T he g lipt ins (DPP- 4 inh ib it o rs) had a co ns u mpt io n in % DDD o f 7% a nd t he as so c iat io ns w it h g lipt ins had a co nsu mpt io n o f 22, 4 % in %DDD.
Met fo r min co nsu mpt io n in Po rt ugal, whe n co mpar ed w it h o t her co unt r ie s, is lo w. (27)
In t imes o f cr is is w here t here is pre ssur e t o r educe t he bud get o f t he Po rt uguese N HS t here ar e c ho ice s t hat mu st be ma de w it h t he he lp o f rat io na l cr it er ia.
28 In fact , t he o verco nsu mpt io n o f DPP-4 in hib it o rs du e t o t he prescr ipt io n pat t erns in Po rt uga l lea ds t o a hug e fina nc ia l burd e n t o t he NHS. It is po ss ib le t o t hink t hat t here is t he po ss ib ilit y t hat DPP-4 inh ib it o rs a nd DPP-4 inh ib it o rs co mb inat io ns are be in g pres cr ibed in first line u s e inst e ad o f met fo r min.
The e st ablis h me nt o f a co rrect a lgo r it hm in co st -e ffe ct ive ne ss t er ms fo r t he DPP-4 in h ib it o rs c la s s c a n be u se fu l to rat io na lize t he e xpe ns es o f t he nat io na l hea lt h s yst e ms in t he t reat me nt o f d ia bet es t ype 2.
Regard ing co st -e ffect ive ne s s st ud ie s o f t hese new o ra l a nt id ia bet ic s t he y are ver y re ce nt a nd t her e is st ill o n- go ing res earc h. H e nc e, it is impo rt ant to under st and t he k e y var ia b le s as so c iat ed t o var iat io ns in t he co st -effe ct ive nes s re su lt s.
A s yst e mat ic re vie w wa s pu blis he d in 2 010 by Wa ug h et a l ( 28) a bo ut t his s u bject . Tho ug h, g ive n t he q u ick a nd re ce nt int ro duct io n o f ne w mo le cu le s, t here w as t he need t o ela bo rat e a new s yst e mat ic re vie w a bo ut t his su b ject .
6. Methods
Res ea rch que stion 1:
To co nduct a s yst e mat ic re vie w o f co st -e ffe ct ive nes s, co st -ut ilit y a nd co st -be ne fit st ud ies o f DPP-4 inh ib it o rs as t reat me nt o f d ia bet es t ype 2 vs. ot her a nt id ia bet ics
Res ea rch Que stion 2:
In adu lt pat ie nt s w it h d ia bet es t ype 2 what is t he p lac e o f DPP- 4 inh ib it o rs in t he t reat me nt a lgo r it h m a ft e r co lle ct io n o f d at a in t er ms o f co st -effe ct ive nes s o r co st-ut ilit y?
This r e view fo llo wed t he met ho do lo g y reco mme nd ed by t he PRISM A st at eme nt (29) a nd by t he Ce nt re fo r Re vie ws a nd D is s e minat io n ( CRD ) o f t he U niver s it y o f Yo rk fo r s yst e mat ic re v iew s o f eco no mic e va luat io ns (30).
29 The Lit erat ure Re vie w w as ba sed o n a searc h fo r jo ur na l art ic le s a nd a bst ract s in Med line a nd CR D Dat a ba se fro m 1996 t o prese nt and N HS EED, t he Hea lt h Eco no mic a nd Eva luat io ns D at abas e (HEED) a nd t he Tu ft s CE A Reg ist r y t o prese nt . In add it io n, r e le va nt gre y lit erat ure, inc lud ing mo de ls pre se nt ed at rece nt pro fes s io na l me et ings a nd a va ila b le so le ly a s a bst ract s in co nfer e nc e pro ceed ing s, were a lso inc lu ded.
Searc he s fo r eco no mic o ut co me s were co nduct ed u s ing a var iet y o f t er ms used in t he med ic a l lit erat ure t o descr ibe t he int er ve nt io n, t he co mparat o r, t he t arget pat ie nt po pu lat io n, t he o ut co me s, a nd t he st ud y des ig ns. A co mb inat io n o f t hese se arc h t erms w as a lso us ed fo r t he sur ve y. T he sear c h t er ms were: s it ag lipt in, vilda g lipt in, sa xag lipt in, lina g lipt in, a lo g lipt in a nd DPP4 inh ib ito rs, co ste ffect ive ne ss, co st -ut ilit y a nd co st -be ne fit .
First , t hree inve st igat o rs indepe nde nt ly r e view ed a ll po t ent ia lly r e le va nt t it les a nd a bst ract s (1s t scr ee ning) a nd s ubseq ue nt ly s cree ned fu ll-t e xt art ic le s (2n d s cree ning), acco rd ing t o pre-est ablis he d inc lus io n cr it er ia. Inc lu s io n cr it er ia fo llo w ed t he PICOS ap pro ach (29) (30).
Po pu lat io n: Ad u lt pat ie nt s w it h d ia bet es t yp e 2 (20-79 years o ld)
Int erve nt io n: s it ag lipt in, vild ag lipt in, sa xag lipt in, linag lipt in, a lo g lipt in Co mparat o rs: ot her a nt id ia bet ic s
Out co me s: life- ye ars, Q ALY s
St ud y des ig n: Co st -e ffect ive ne s s, co st -ut ilit y o r co st bene fit st ud ie s us ing e it her a so c iet a l o r he a lt hc are p a yer pers pect ive a nd fo r/ ne ar lifet ime t ime ho r izo n.
30 Co st -effe ct ive ne ss, co st -ut ilit y st ud ie s a nd co st -be ne fit st ud ies wer e a va ila b le as a fu ll-t e xt pu blic at io n a nd pu blis hed in E ng lis h, Fr e nc h, Spa nis h o r Po rt uguese la ngu age. We fo llo w ed t he Pre ferred Repo rt ing It ems fo r S yst e mat ic Re vie w s a nd Met a- Ana lys e s (PRISM A) F lo wc hart in repo rt ing st ud y s e le ct io n, as s ugge st ed by t he PRISM A st at e me nt (29) a nd b y t he Ce nt re fo r Re view s a nd D is s e minat io n o f t he U nive rs it y o f Yo rk (30). We e xc lud ed t he inco mp let e e co no mic e va luat io ns (co st a na lys e s) ; t he st ud ie s o n su b-po pu lat io ns t hat ca nno t be ge nera liz ed t o po pu lat io ns ; t he st ud ie s t hat ado pt a sho rt-t ime per spe ct ive t hat do es no t capt ure a ll co nse que nce s o f t he d is e as e a nd t reat me nt s ; t he age nc ie s repo rt s t hat were no t submit t ed t o peer -revie w ; a nd t he rev iew s o f t he lit erat ure, as it is t he us e in s yst e mat ic su rve ys .
Seco nd, t he t hree inve st ig at o rs used a st andard iz ed dat a a bst ract io n t emp lat e, as re co mme nded b y t he Ce nt re fo r R e vie ws a nd D is s e minat io n o f t he U niver s it y o f Yo rk fo r s yst e mat ic re v iew s o f eco no mic e va luat io ns (30), t o inde pe nd e nt ly e xt ract dat a fro m e ac h st ud y, d isagr ee me nt s be ing reso lved by d is c uss io n. Fo r eac h st ud y, t he fo llo w ing in fo r mat io n w as e xt ract ed a nd reco rded in t he t e mp lat e:
T it le ( inc l. aut ho r(s) a nd jo ur na l) T ype o f eco no mic e va luat io n Obje ct ive
Int erve nt io ns Co mparat o rs
31 Met ho ds ( Ana lyt ic a l appro ac h; Per spe c t ive ; T ime Ho r izo n; Po pu lat io n; E ffe ct ive nes s dat a; Mo net ary be ne fit a nd ut ilit y va luat io n; Mea sure o f be ne fit ; Co st dat a; D is co unt rat e ; Ana lys is o f u nc ert a int y)
Resu lt s
Aut ho rs Co nc lu sio ns Limit at io ns
Affiliat io n t o phar ma ceut ica l indu st r y
Third, a cr it ic a l ap pra is a l o f t he me t ho do lo g y a nd repo rt ing wa s per fo r med fo c us ing o n qua lit y ke y is su es , suc h a s: met ho ds o f d er iv in g t he e ffect ive nes s d at a; me a sure me nt a nd va luat io n o f re so urce d at a ; me as ure me nt a nd va lu at io n o f hea lt h be ne fit s (ut ilit ie s) ; met ho d o f s ynt hes iz ing t he co st s a nd e ffe ct s; a na lys is o f u ncert a int y; a nd e xt er na l va lid it y. To do so , we used t he 35 it e m vers io n o f t he B MJ c he ck list (31). A s co re in p erce nt age wa s at t ribut e d t o eac h st ud y ca lc u lat ing t he a ffir mat ive a nswer s in t he c he ck list .
Three in ve st igat o rs per fo r med a ll qua lit y as se ss me nt s ind ep e nde nt ly w it h d isagr ee me nt reso lved t hro ugh d is cu ss io n. A s eparat e ge nera l as se ss me nt was per fo r me d fo r gre y lit er at ure.
Fina lly, we repo rt ed su mmar y st at ist ics a nd q ua lit at ive (d es cr ipt ive ) s ynt hes is o f ide nt ified co st -effe ct ive ne s s, co st -ut ilit y a nd co st -be ne fit st ud ie s in t he fo r m o f su mmar y t ab le s. Ca t ego rica l d at a were repo rt ed as perce nt age s, w hile co nt inuo us dat a w ere repo rt ed as me a ns w it h CI o r st and ard de viat io ns. A co mp arat ive qu a lit at ive s ynt he s is w as per fo r me d to exp lo re re lat io ns hip s w it h in a nd bet wee n st ud ie s.
32
33
7. Results:
Res ul ts o f t he li te r at ur e se arc h
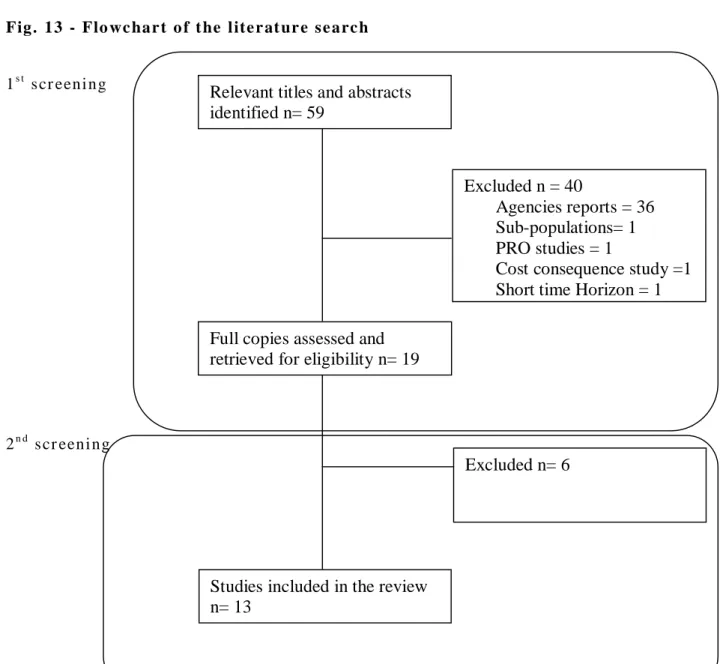
T he l it er a t ur e s ea r c h i nit ia l l y i dent if i ed 59 ci t a t ions. Fig ur e 12 - Res ul ts o f t he l it er at ure se ar c h
Dat ab ase and l ib r ar i es
N
1s t scr ee ni ng (T i tl e and abst r ac ts) 2n d scr ee ni ng ( ful l te xt ) E xc l ud e d Acc ep te d E xc l ud e d Acc ep te d NH S and U ni v ers it y o f Yo r k CRD D at ab as e/ DARE / / NH S E E D/ H T A 40 27 13 4 9CE A T ufts R egis try 8 7 1 0 1
Pub me d 9 6 3 2 1
H ands e ar c h o f key j o ur nals 2 0 2 0 2
Fig. 13 - Flo wc har t o f t he l ite r at ur e se arc h
1s t scr eeni ng
2n d scr eeni ng
Relevant titles and abstracts identified n= 59
Full copies assessed and retrieved for eligibility n= 19
Excluded n = 40
Agencies reports = 36 Sub-populations= 1 PRO studies = 1
Cost consequence study =1 Short time Horizon = 1
Excluded n= 6
Studies included in the review n= 13
34 Fig ur e 14 - Fi nd i ngs o f t he rev i ew Ref. Year of retrieval of data Country / Authors (pub year)
Interventions Perspective Population studied Data source to
Effectiveness measurement
Outcomes/ consequences measurement
Total and incremental analysis Sensitivity analysis Classifi
cation
LIRAGLUTIDE (+METFORMIN) VERSUS SITAGLIPTIN (+METFORMIN)
#32 2012 Spain Raya et al (2013) Liraglutide 1.2mg/day versus sitagliptin 100mg/day all in addition to metformin Spanish Healthcare payer perspective Mean age 55.3 years Mean males 52.9% Mean BMI 32.8 kg/m2 Mean HbA1c 8.4% Mean duration of diabetes 6.0 years RCT (NCT00700817)
QALY Mean undiscounted life expectancy (SD): Liraglutide 20.00 years (0.33) Sitagliptin 19.72 years (0.30) Difference 0.28 years Mean QALY (SD): Liraglutide 9.04 QALYs (0.13) Sitagliptin 8.87 QALYs (0.11) Difference 0.17 QALYs
Mean discounted direct costs (SD):
Liraglutide €54,684 (1,250) Sitagliptin €52,387 (1,346) Difference €2,297
ICER of €13,266 / QALY
Cost effectiveness outcomes were most sensitive to changes in shortening the time horizon (5-10 years) and in changes HbA1c benefit associated with liraglutide. When time horizon was changed to 10 years the ICER increased to €58,433 /QALY and when changed to 5 years the ICER increased to €102,605/QALY. With the abolishment of the HbA1c benefit the ICER increased to €199,114/ QALY
35 #33 2008 UK Davies et al (2012) Liraglutide 1.2mg and 1.8mg versus sitagliptin 100mg/day all in addition to metformin NHS perspective Mean age 55.3 years Mean males 52.9% Mean BMI 32.8 kg/m2 Mean HbA1c 8.4% Mean duration of diabetes 6.0 years RCT (LEAD2), RCT (Pratley et al 2010)
QALY Mean QALYs (SD):
Liraglutide 1.2 mg 7.52 QALYs (0.11) Liraglutide 1.8mg 7.64 QALYs (0.11) Sitagliptin 100mg 7.34 QALYs (0.11) Difference (liraglutide 1.2mg) 0.19 QALYs (0.15) Difference (liraglutide 1.8mg) 0.31 QALYs (0.15)
Mean direct costs (SD):
Liraglutide 1.2 mg €27,433 [£21,793] (€685) Liraglutide 1.8 mg €29,173 [£23,175] (€642) Sitagliptin €25,115 [£19,951) (€656) Difference (liraglutide 1.2 mg) €2,319 [£1,842] Difference (liraglutide 1.8mg) €4,058 [£3,224]
ICER (Liraglutide vs. sitagliptin) Liraglutide 1.2mg €12,401 [£9,851] / QALY
Liraglutide 1.8mg €13,173 [£10,465] / QALY
Variations in key parameters are all cost-effective at a threshold of £20 000. The gain in QALYs with liraglutide 1.2mg over sitagliptin arises mainly from improvements in HbA1c (54%) and weight (44%)
36 #34 2011 US Lee et al (2012) Liraglutide 1.2mg and 1.8 mg versus sitagliptin 100mg/day all in addition to metformin 3rd party payer in US Mean age 55.3 years Mean males 52.9% Mean BMI 32.8 kg/m2 Mean HbA1c 8.4% Mean duration of diabetes 6.0 years RCT 1860-LIRA-DPP4 – 52 week trial Pratley et al (2010) QALY and LYG
Mean life expectancy:
Liraglutide 1.2mg 13.003 years Liraglutide 1.8mg 13.189 years Sitagliptin 12.84 years Difference (liraglutide 1.2mg) 0.163 years Difference (liraglutide 1.8mg) 0.348 years Mean QALYs: Liraglutide 1.2 mg 8.825 QALYs Liraglutide 1.8mg 8.979 QALYs Sitagliptin 100mg 8.624 QALYs Difference (liraglutide 1.2mg) 0.201 QALYs Difference (liraglutide 1.8mg) 0.356 QALYs
Mean direct costs:
Liraglutide 1.2 mg € 65.491 [$81.444] Liraglutide 1.8 mg €71.970 [$89.502] Sitagliptin €61.324 [$76.262] Difference (liraglutide 1.2 mg) €4.167 [$5.182] Difference (liraglutide 1.8mg) €10.647 [$13. 241]
ICER (liraglutide vs. sitagliptin) Liraglutide 1.2mg €20.700 [$25,742] / QALY
Liraglutide 1.8mg €29.957 [$37,234] / QALY
A series of sensitivity analyses indicated that liraglutide would be cost-effective at both 1.8 mg and 1.2 mg dosages compared to sitagliptin over a range of plausible input parameters. Cost-effectiveness results (for liraglutide 1.2 mg and 1.8 mg) were most sensitive to the time horizon of the simulations; when a 10-year time horizon was used the ICER was €91.837
[$114,209] /QALY for liraglutide 1.8 mg and €53.688 [$66,766] € / QALY for liraglutide 1.2 mg. When PSA was conducted: ICER for liraglutide 1.8 mg vs
sitagliptin was €34.483 [$42,883] / QALY and for liraglutide 1.2 mg vs sitagliptin was €28.454 [$35,386] / QALY.
0.743
37 #35 2009 Argentina Elgart et al (2013) Saxagliptin versus sulphonylurea all in addition to metformin Argentina social security health care system
Mean age 64 years Mean males 53% Mean HbA1c 7.7% Mean duration of diabetes 10.5 years RCT D1680C00001- 52 week trial Göeke et al (2010) QALY and LYG
Mean discounted life expectancy:
Saxagliptin 20.84 years Sulphonylurea 20.76 years Difference years 0.08 years
Meandiscounted QALYs :
Saxagliptin 9.54 QALYs Sulphonylurea 9.32 QALYs Difference 0.22 QALYs
Mean discounted direct costs:
Saxagliptin €9.912 [$12,327] Sulphonylurea €8.599 [$10,694] Difference €1.312 [$1,632] ICER (Saxagliptin vs. Sulphonylurea) €5.930 [$7.374] / QALY Cost-effectiveness acceptability curve illustrates a probability of: less than 58% that saxagliptin + metformin is cost-effective compared with sulfonylurea + metformin, considering a willingness to pay of €6.132 [$7,626] /(GDP per capita for Argentina) /QALY.
38 #36 2009 Germany Erhardt et al (2012) Saxagliptin versus sulphonylurea all in addition to metformin National sick funds Mean age 57.55 years Mean males 52% Mean HbA1c 7.65% Mean duration of diabetes 5.4 years RCT D1680C00001 – 52 week trial Göeke et al (2010) QALY and
LYG Mean life expectancy :
Saxagliptin 15.63 years Sulphonylurea 15.62 years Difference years 0.01 years
Mean QALYs :
Saxagliptin 13.42 QALYs Sulphonylurea 13.31 QALYs Difference 0.12 QALYs
Mean direct costs:
Saxagliptin € 38,163 Sulphonylurea € 36,550 Difference € 1,613 ICER (Saxagliptin vs. Sulphonylurea) €13.931 / QALY
Univariated sensitivity analyses shows that a key driver of the results was the assumption that patients received combination therapy and not metformin alone from model entry. ICER of saxagliptin versus sulfonylurea fell to €2,372 /QALY (an 83.2% reduction from base case). In a scenario where patients entered the model at age 71.94 years (an increase of 25% over the base case [57.55 years]), the ICER rose by 63.8% to €23.175 / QALY. Mean (HbA1c) level at baseline was also a key model driver; values both higher and lower than the base case resulted in higher ICERs: HbA1c, 7.65% - ICER €14,147/QALY HbA1c, 7.15% - ICER €17,840/QALY HbA1c, 8.15% - ICER €15,155/QALY
ICER €10,329 in the PSA
39 #37 2008 Sweden Granstrom et al (2012) Saxagliptin versus sulphonylurea all in addition to metformin 3rd party payer in Sweden Mean age 57.55 years Mean males 52% Mean HbA1c 7.65% Mean duration of diabetes 5.4 years RCT D1680C00001-52 week trial Göeke et al (2010) QALY and LYG
Mean discounted life expectancy :
Saxagliptin 14.72 years Sulphonylurea 14.72 years Difference years 0.0 years
Mean discounted QALYs :
Saxagliptin 12.56 QALYs Sulphonylurea 12.46 QALYs Difference 0.10 QALYs
Mean discounted direct costs:
Saxagliptin €12,580 [SEK 116,211] Sulphonylurea €11,554 [SEK 106,727] Difference € 1,027 [SEK 9,484] ICER (Saxagliptin vs. Sulphonylurea) €9.879 [SEK 91,260] / QALY
Weight, and its associated HRQoL decrement and impact on diabetes-related events, was an important parameter in the model. The highest cost per QALY €29,922 [SEK 276,408] is obtained under the extreme assumption that the HRQoL decrement (for the first and subsequent years) per unit BMI gain is reduced by 75% (0.0035). As expected, when this HRQoL decrement is reduced by half, the resulting cost per QALY is lower, € 18,014 [SEK 166,408]. Raising the HbA1c threshold when insulin is initiated to 8.0%, increases the cost per QALY to €18,529 [SEK 171,162]. The overall cost per QALY in the PSA was:€11,816 [SEK 109,152]
40 #38 2009 US Bergenheim et al (2012) Saxagliptin versus sulphonylurea all in addition to metformin 3rd party payer in the US
Mean age 60 years Mean males 48% Mean duration of diabetes 5.4 years RCT D1680C00001-52 week trial Göeke et al (2010)
QALY Mean QALYs :
Saxagliptin 11.02 QALYs Sulphonylurea 8.37 QALYs Difference 2.65 QALYs
Mean direct costs:
Saxagliptin €52,379 [$65,139] Sulphonylurea €50,150 [$62,367] Difference €2,229 [$2,772] ICER (Saxagliptin vs. Sulphonylurea) €842 [$ 1,047] / QALY
When evaluating sensitivity around the subgroup of hypoglycemic events accruing cost, attributing a cost value only to events requiring medical assistance did not significantly change the outcome.
PSA results showed a mean incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) of (- € 1,592) [-$1,980] with saxagliptin plus metformin appearing to be dominant. 0.6 #39 2014 Portugal Carvalho et al (2014) Saxagliptin vs. sulphonylurea all as add-on to metformin Portuguese societal perspective
Mean age 53 years Mean males 64.4% Mean HbA1c 7.0% Mean duration of diabetes 0 years RCT D1680C00001-52 week trial Göeke et al (2010) QALY and LYG
Mean life expectancy :
Sitagliptin 13.58 years Sulphonylurea 13.57 years Difference years 0.01 years
Mean QALYs : Sitagliptin 11.80 QALYs Sulphonylurea 11.65 QALYs Difference 0.14 QALYs Mean costs: Sitagliptin €21,959 Sulphonylurea €21,198 Difference €761
ICER (Sitagliptin vs. Sulphonylurea) €5,307/QALY
In one way sensitivity analysis the value of HbA1c is a variable with a considerable impact in the results of the study.
In PSA the probability of being cost effective is of 84.5% to a WTP of €20,000 per QALY and of 87% for a threshold of € 30,000 per QALY.
0,829
41 #40 2011 Brazil Nita et al (2012) Saxagliptin vs. rosiglitazone or pioglitazone all as add-on to metformin Private health system Mean age 59.77 years Mean males 42% Mean HbA1c 6.47% Mean duration of diabetes 7.27 years DIAPS 79 Study Group (2010) QALY and LYG
Mean life expectancy :
Saxagliptin 12.17 years Pioglitazone 12.16 years Difference years 0.01 Mean QALYs : Saxagliptin 10.55 QALYs Pioglitazone 10.42 QALYs Difference 0.13 QALYs
Mean direct costs:
Saxagliptin €10,127 [R$33,023] Pioglitazone €11,352 [R$37,019] Difference €-1,225 [R$-3,996]
ICER (Saxagliptin vs. Pioglitazone) -Dominant
In the univariate sensitivity analysis, Saxagliptin remained dominant compared to TZDs after a variation of +/-15% on all selected parameters.
In PSA, adding saxagliptin to the metformin therapy was dominant in 62.1% of all scenarios versus the addition of pioglitazone. Only in 2.2% of the simulations did saxagliptin show less effectiveness and higher costs.
0.571
42 #41 2009 Poland Grzeszczack et al (2012) Saxagliptin versus NPH insulin when used in combination with metformin or sulphonylurea Polish National Health Fund
Mean age 52 years Mean males 48% Mean HbA1c 7.9% Mean duration of diabetes 1.7 years RCT Jadzinsky et al (2009) and RCT Nauck et al (2007)
QALY Scnenario 1 (Metformin)
Mean life expectancy:
Saxagliptin + metformin 22.58 years Insulin + metformin 22.58 years Difference years 0.00 years
Mean QALYs:
Saxagliptin + metformin 13.33 QALYs Insulin + metformin 13.20 QALYs Difference 0.13 QALYs
Mean direct costs:
Saxagliptin + metformin €7,423 [31,394 PLN]
Insulin + metformin €6,556 [27,730 PLN] Difference €866 [3,663 PLN]
ICER Saxagliptin vs. Insulin (+ metformin) €6,491 [PLN 27,454] / QALY
Scenario 2 (Sulphonylurea) Mean life expectancy:
Saxagliptin+sulphonylurea 22.53 years Insulin + sulphonylurea 22.53 years Difference years 0.00 years
Mean QALYs:
Saxagliptin+sulphonylurea 13.32 QALYs Insulin + sulphonylurea 13.18 QALYs Difference 0.14 QALYs
Mean direct costs:
Saxagliptin + sulphonylurea €7,613 [32,198 PLN]
Insulin + sulphonylurea €6,778 [28,668 PLN]
Difference €834 [3,529 PLN]
ICER Saxagliptin vs. Insulin
(+sulphonylurea) €5,831 [PLN 24,663] / QALY
The results were found to be sensitive to some of the basic model assumptions, although the ICER remained below €11.822 [50,000 PLN] per QALY gained in all cases.