The Perception of Entrepreneurial and rd Generation
University in Turkey
(arun Gumus
harun.gumus@cbu.edu.trDeniz Zungun
zungund@hotmail.com Celal Bayar University, Manisa, Turkey)ncreased competition caused by globalization has led to philosophical changes in private and public businesses. This situation has affected educational institutions and they have needed dynamic, innovator and transformational tools in order to survive in competitive
environment. The universities defined as rd Generation Universities need
commercialization, network among universities, close co-operation among institutions and entrepreneurship as well as intellectual and innovative changes. )n this regard, the aim of the research is formed by the analysis of Entrepreneur University concept from the perspective of the academicians that served at managerial positions at the universities in Turkey. The research is limited to the opinions of the academicians that served at top, middle and lower management at randomly chosen universities.
Keywords: Entrepreneurial University, Managerial Academics, rd Generation University,
Economic Structure of GU
JEL classification: L , L , L , M , M , E .
Introduction
The institutions converting with the widespread competition effect of globalization are repositioning themselves in the information era and developing effective strategies on global scale. This change and conversion has also given universities which provide higher education a great shock. Universities are developing long-term strategies related to contemporary radical changes by excluding the traditional definitions in the fields of management and education. At the universities, where competition is escalated, strategies to gain high-grade students and experienced academicians started to arise. Worldwide universities are in the fight of attracting the top-quality students to their campuses by providing them with the opportunities created for the students with the supports of their own business integrations as well as state and local governments. Wissema
emphasizes in their study that the universities, which open up to the world with the effect of globalization, are in a great competition with each other in order to attract high-grade international students.
The universities are the top institutions that the educational and research activities take place. Today, the
functions of the universities are grouped as; education, basic scientific researches and community
services G“r“z, . The universities are functionally organized to perform mainly one function among them
ERDEM, . When these functions are examined, two different characteristics of universities are found;
research universities and mass education universities G“r“z, . )n the near future, it is estimated
that the Council of (igher Education YÖK is going to form new aims and vision for the universities and redefine the universities in Turkey in two groups as research and mass education universities.
)n the traditional university model, the universities were expected to only produce information; however, now they are expected to use the produced information effectively, create resource for new productions and
commercialize the outputs. According to Kiper , universities must subsidize research studies which are
suitable in their way by looking out for universal and/or common good and/or industrial support alongside of their educational functions. Also in the last century, developing and applying the model of relationship based on
mutual interest among these institutions and universities have shown an accelerated increase Kiper, .
the science based university model. )n order to understand this change better, the process of development and change of universities from generation to generation must be examined. The First Generation Universities GU
evolved from de Ridder-Symoens, and later, turned into special academic structures in order to train
more students of good quality professionally. The idea of the discovery and development of new information came out of the philosophy of protection and transfer of accepted information in the transitional period. The Second Generation Universities GU considered the basic laws of science in every thinking process and adopted know-how practices. The Third Generation Universities GU aimed to commercialize know-how practices and created information, when they focused on the scientific studies and educational aims. The main factor forcing universities to change is the fund seeking emerging from increasing costs of researches with the
technological developments Wissema, . Therefore, universities adopted entrepreneurship qualifications in
a progressive pace. The universities try to improve academic entrepreneurship Çetin, and to update the
existing state around entrepreneurship by focusing on scientific projects, overseas education, patent and license applications, long-term industrial collaborations and updating curriculum activities. The leading universities in the world increased the number of industrial collaborations in the way to become Entrepreneur University and the Third Generation University and made this situation permanent with long-term agreements. Thus, a high level of synergy began to form among the institutions which carried on business in two different worlds. The high level of competition and change brought by globalization speeded up the activation of universities and the integration to market conditions. )n this process state and local governments got into the competition of attracting the most qualified students in the world into their universities by supporting GU and the entrepreneurship of universities with their policies. Thus, a serious competition comes into question with
globalization which is specific to worldwide student Wissema, and it triggers seeking of qualified
academicians in a sequence. The increased need of qualified human capital in global environment has given birth
to the obligation of universities to be upgraded to the rd Generation. This formation has triggered universities
becoming entrepreneur in international arena. The gap between the universities, which implement these qualifications, which adapt this philosophy and which increase their competitive capacities, and the universities
that do not have the qualifications of the rd Generation is becoming wider day by day. Entrepreneur universities
are the institutions that are open to change, they have economic freedom, they are autonomous and they complete their industrial integration; and also, they can commercialize knowledge.
G“r“z argues that as modern universities are largely dependent on public funding; their
autonomy will not be possible. G“r“z supports the changeover to entrepreneur university model . Besides
G“r“z defines the contemporary and modern university as follows; it is integrated with the all sections of
society, it is inspected to see in which level it fulfills its accountability towards public in terms of its activities and its activities are led by society, it creates additional funds by utilizing all kinds of facilities, equipments, accumulation of knowledge and manpower with an entrepreneur mind, it has an extraordinarily complex
structure which is managed with modern business techniques. According to Didou-Aupetit , USA and
Canada, which have advanced higher education systems, consider international education as a financial resource to be sold as a service in market logic. Today the universities are being managed professionally as if they are large companies. Universities accept knowledge as goods to be put on market and to be sold. Now, it is the market that determines which lessons will be given, which researches will be supported, which student profile they will serve and which enrollment policies will be adapted. The effects of rapid changes on universities since
the last quarter of th century can be summarized as follows Didou-Aupetit, , Lee, , McBurnie, ,
Tural, , Erdem, ;
i. The effective usage of information technology in researches, in presenting educational services and in
distance education:
ii. Changing relationship among government and universities:
iii. Public institutions of higher education s having rivals:
iv. Facing towards pragmatic university:
v. University autonomy s facing towards the axis of the responsibility of answering to the public:
vi. Accepting universities as knowledge-based societies and resource for economy, and a complex business
rather than accepting them as student-teacher community:
vii. Universities becoming international:
Methodology
Aim of Research
of the relationships between the survey answers and demographic features of the academicians who had administrative functions.
Method and Procedure of Research
)n the study, the relational screening model which analyzes the existence and amount of interaction
between variables has been used. According to Karasar , the relational screening model is a research
approach that aims to define the situation in the past and the situation at present as they are.
)n this study, probabilistic sampling method has been used. )n Turkey, there are universities
registered in the Council of (igher Education YÖK . The groundmass of the study consists of the academic staff that had administrative function at the universities within YÖK. )t is believed that the academicians with
administrative function in their past are the people who can define Entrepreneur University and rd Generation
University concepts, analyze the current situation and offer solutions. Cluster Sampling and Simple Random Sampling methods have been used in the sampling choice. Simple random sampling assumes that the probability of getting into sampling of each factor which forms groundmass equals to the weight to be given to
the each factor in the statistical calculations Arıkan, . Whereas in cluster sampling, the groundmass is
grouped as clusters and random samplings are chosen from each cluster Çömlekçi, . While the survey
questions were being formed for the researched, the opinions of academicians working at Celal Bayar University with administrative function in their past were taken. )n the light of their opinions, a literature review
was made for the subjects of rd Generation University , Entrepreneur University and Competition, Finance
and Collaboration in (igher Education , and totally questions were formed, six of which were demographic,
by making use of sources Ökmen and Bal, , Aslan, , Odabaşı and Odabaşı, , Farsi et al., ,
(eidler and Lengersdorf,
)n questions, five point Likert scale was used in order to determine the approaches and perception
level of administrators related to Entrepreneur University and rd Generation University concepts.
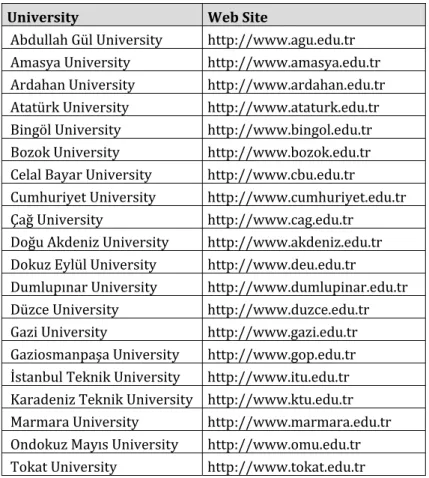
)n this study, universities were chosen randomly among the universities registered in YÖK and their website addresses were taken from the link http://www.yok.gov.tr/web/guest/universitelerimiz Table is chosen.
Table Universities and Web Sites
University Web Site
Abdullah G“l University http://www.agu.edu.tr
Amasya University http://www.amasya.edu.tr
Ardahan University http://www.ardahan.edu.tr
Atat“rk University http://www.ataturk.edu.tr
Bingöl University http://www.bingol.edu.tr
Bozok University http://www.bozok.edu.tr
Celal Bayar University http://www.cbu.edu.tr
Cumhuriyet University http://www.cumhuriyet.edu.tr
Çağ University http://www.cag.edu.tr
Doğu Akdeniz University http://www.akdeniz.edu.tr
Dokuz Eyl“l University http://www.deu.edu.tr
Dumlupınar University http://www.dumlupinar.edu.tr
D“zce University http://www.duzce.edu.tr
Gazi University http://www.gazi.edu.tr
Gaziosmanpaşa University http://www.gop.edu.tr
İstanbul Teknik University http://www.itu.edu.tr
Karadeniz Teknik University http://www.ktu.edu.tr
Marmara University http://www.marmara.edu.tr
Ondokuz Mayıs University http://www.omu.edu.tr
Tokat University http://www.tokat.edu.tr
names , titles , and e-mail addresses of the academicians in administrative function and who were in administrative function in the past were entered in MS Excel© table. The online survey which was designed via Google Drive© was sent to these academicians with personalized e-mail by using title , name and sir name . )t is known in the literature that the percentage of answering e-mails sent for researches by academicians or other individuals is very low. )n the frame of this information, high percentage of reply was aimed with practice of the method of personalized e-mail title, name, sir name and official e-mail address . The e-mails were sent from the Celal Bayar University s official e-mail address in order to minimize the risk of receiving e-mails as
spam for the target group. )n total, surveys were answered in four months period. By using SPSS pack
program, the data obtained from surveys were evaluated in terms of frequency distributions, arithmetic mean, and standard deviation and chi square values. The reliability co-efficient cronbach alpha of the survey
consisting of questions was found , . When the questions , and were taken out and the cronbach
alpha was calculated, the result increased to , .
Findings and Discussion
The research results were analyzed in five categories as follows; demographic information, the views
related to changes and autonomy at universities, the views related to Entrepreneur University and rd
Generation University , the views about university-industry collaborations, and finally the views related to the economic structure of universities. The demographic information of research participants are demonstrated in Table .
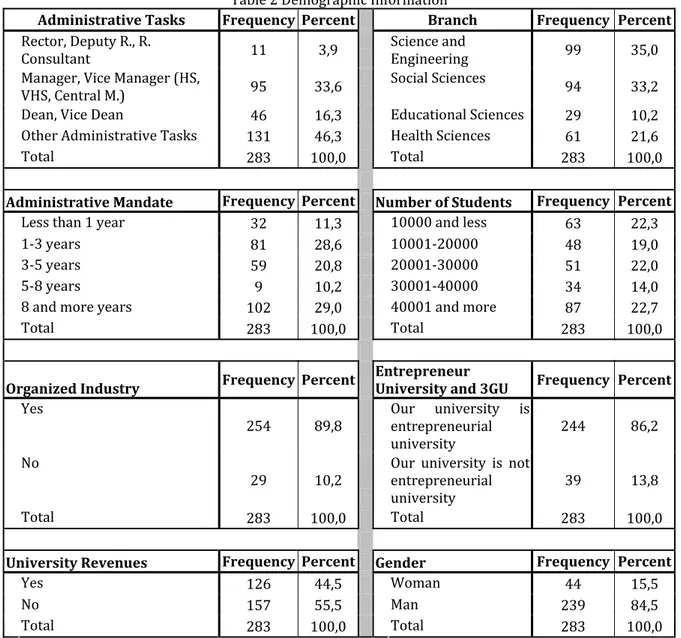
Table Demographic )nformation
Administrative Tasks Frequency Percent Branch Frequency Percent Rector, Deputy R., R.
Consultant , Science and Engineering ,
Manager, Vice Manager (S,
V(S, Central M. , Social Sciences ,
Dean, Vice Dean , Educational Sciences ,
Other Administrative Tasks , (ealth Sciences ,
Total ,
Total ,
Administrative Mandate Frequency Percent Number of Students Frequency Percent
Less than year , and less ,
- years , - ,
- years , - ,
- years , - ,
and more years , and more ,
Total ,
Total ,
Organized Industry Frequency Percent
Entrepreneur
University and 3GU Frequency Percent Yes
,
Our university is entrepreneurial
university ,
No
,
Our university is not entrepreneurial
university ,
Total ,
Total ,
University Revenues Frequency Percent Gender Frequency Percent
Yes , Woman ,
No , Man ,
Total ,
)t is seen that . % of the participants are at senior management Rector, Deputy R, R. Consultant, Manager, Vice Manager, Dean and Vide Dean and are at the position of direct decision makers. )t is revealed that % of the participants are experienced individuals having experience of more than years of administrative function. . % of the participants having experience of more than one year of administrative function will increase the confidence of research data. )t is seen that % of the participants are from the fields of science and engineering, and . % of the participants are from the field of social sciences. )t is confirmed that . % of the universities have side income. There are Organized )ndustry in . % of the area where the universities are located. )t is seen that . % of the participants have conceptual information about Entrepreneur University and GU . )t is obvious that . % of the universities where the participants work have more than students and that there is an equilibrium distribution among answers. The . % of the participants are male and . % of the participants are female; thus, it can be inferred from the statistics that administrative duties are generally assigned to males.
Table . Comments Related to Change and Autonomy at Universities
Items Strongly
Agree Agree
Neither agree
nor disagree
Dis agree
Strongly
Disagree Total Std. D. Mean
Q1. Change is obligatory at
universities. % % , % , % , % , , , ,
Q6. It is positive that state universities depart from their
public nature. % , % , % , % , % , , , ,
Q9. Universities are
autonomous enough. % , % , % , % , % , , , ,
Q14. It is necessary for
universities to earn money. % , % , % , % , % , , , ,
)n Table ., the percentage of sharing idea of the administrator academicians to the propositions related to change and autonomy at universities are shown. The academicians inside the management positions are observed to positively agree with the proposition stating Change is obligatory at universities with a high percentage of . %. )t reveals the fact that universities cannot progress in the present program and they need to reach to the entrepreneur qualifications in order to obtain competitive capacity. )n that sense, change becomes an obligation rather than a choice for universities. For . % of the academicians in management positions, it is a positive situation that public universities leave their public nature. )t can be said that the bulky structure of public is one of the factors for preventing universities from change and improvement. . % of these academicians think that universities are not autonomous enough. When it is thought that the managements making decisions independently are more entrepreneurs, more competitive and more successful, it can be said that the concept of real autonomy is one of the biggest obstacles for the universities in Turkey. Another aspect of autonomy is economic autonomy. When the universities reach at the qualifications of Entrepreneur and rd Generation University, they will generate higher incomes by transferring know-how applications to the market. . % of the participants support this opinion by stating that universities must generate their incomes.
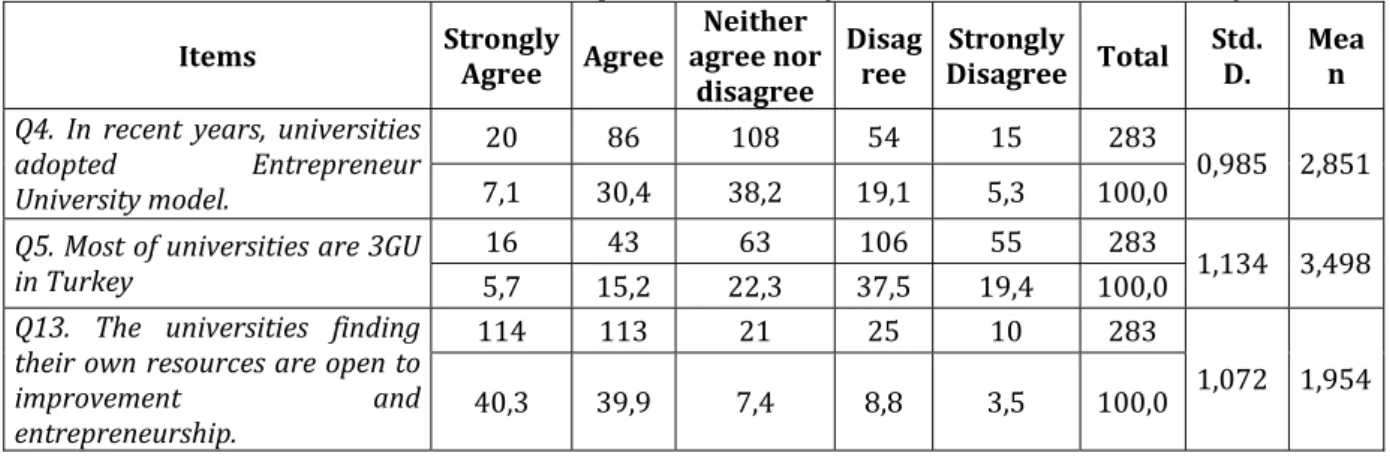
Table . Comments Related to Entrepreneur University and rd Generation University
Items Strongly
Agree Agree
Neither agree nor
disagree
Disag ree
Strongly
Disagree Total Std.
D.
Mea n
Q4. In recent years, universities
adopted Entrepreneur
University model. , , , , , , , ,
Q5. Most of universities are 3GU
in Turkey , , , , , , , ,
Q13. The universities finding their own resources are open to
Table shows the percentage of agreement of the academicians at the managerial positions with the propositions related to Entrepreneur University and rd Generation University . According to Etzkowitz , universities must work with industrial zone in an integrated way and must adapt the entrepreneur university model in order to improve the quality of academia. , % of the academicians with administrative function have the opinion that universities adapted the Entrepreneur University model in the last few years.
(owever, it can be seen that . % of them do not agree with this propositions and . % of them are
undecided. )t can be inferred that universities fail to satisfy in terms of adapting Entrepreneur University model and developing plan, program and strategies in this direction. The aims of the rd Generation Universities are not only education but also revealing research and know-how . The role of these universities is creating value rather than defending the truth or discovering the nature. As method, GUs focus on modern science and interdisciplinary studies and they are led by scientists and entrepreneurs. . % percent of the academicians at the managerial position do not agree with the proposition stating A great part of the universities in Turkey are rd Generation Universities . Most of the universities in Turkey are doubtful if they have updated themselves from GU to GU or not. . % of the participants think that the universities generating their own incomes are the ones that are open to progress and entrepreneurship. Universities with the entrepreneur characteristics can provide economic development by planning projects, patents, and by integration with startup companies and industrial zone rather than needing state subsidy.
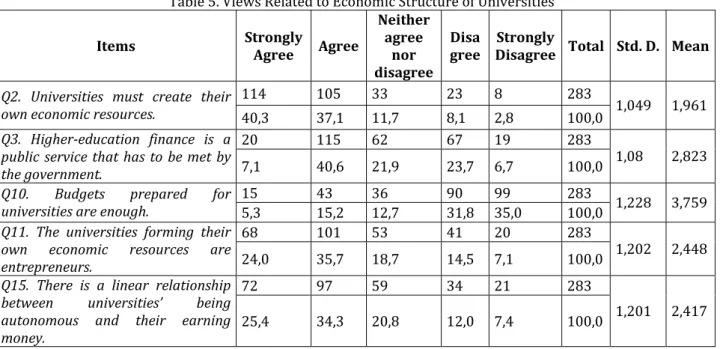
Table . Views Related to Economic Structure of Universities
Items Strongly
Agree Agree
Neither agree
nor disagree
Disa gree
Strongly
Disagree Total Std. D. Mean
Q2. Universities must create their
own economic resources. , , , , , , , ,
Q3. Higher-education finance is a public service that has to be met by
the government. , , , , , , , ,
Q10. Budgets prepared for
universities are enough. , , , , , , , ,
Q11. The universities forming their own economic resources are
entrepreneurs. , , , , , , , ,
Q15. There is a linear relationship between universities’ being autonomous and their earning
money. , , , , , ,
, ,
Table shows the percentage of agreement of the academicians at the managerial positions with the
propositions about the economic structure of universities. With a high percentage as such . %, the
academicians at the managerial positions at universities agree with the proposition stating Universities must generate their own economic resources . . % percent of the participants agree with the proposition The finance of higher education is a public service that needs to be satisfied by the government . . % of the participants think that the budget given to the universities is not sufficient. When the universities in Turkey are compared to the worldwide universities in the budget basis, the budgets of the universities in Turkey are by far
low. For instance, İstanbul University, which receives the highest budget in Turkey, receives only . $
annually Maliye-Bakanlığı, . The budgets of the universities in USA receive billion dollars. For example, the
annual budget of (arvard University is billion $. . % of the participants define the Entrepreneur
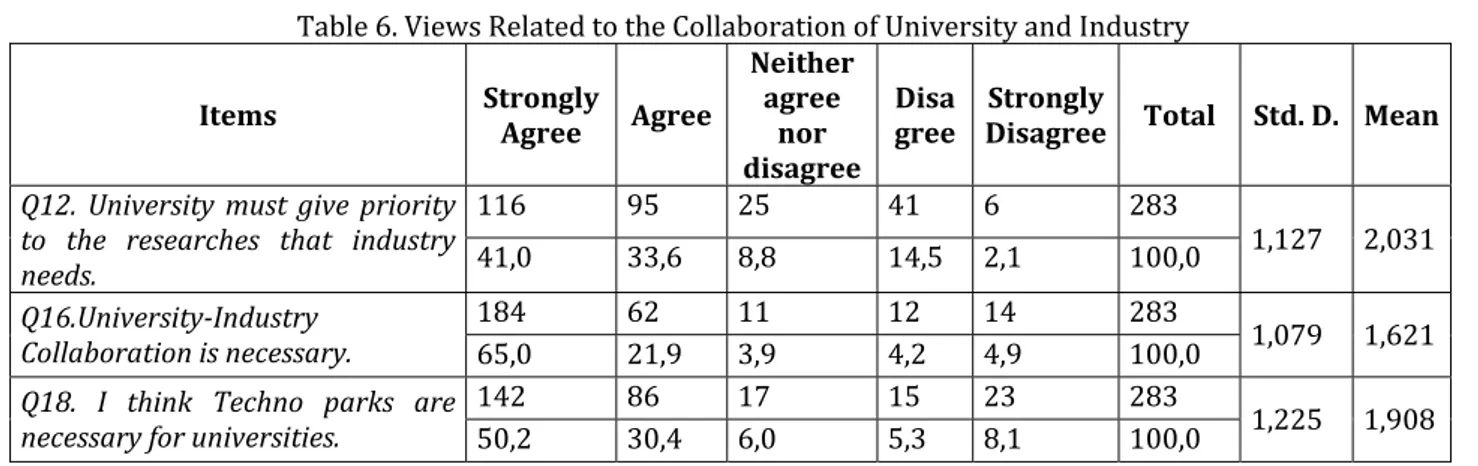
Table . Views Related to the Collaboration of University and )ndustry
Items Strongly
Agree Agree
Neither agree
nor disagree
Disa gree
Strongly
Disagree Total Std. D. Mean
Q12. University must give priority to the researches that industry
needs. , , , , , , , ,
Q16.University-Industry
Collaboration is necessary. , , , , , , , ,
Q18. I think Techno parks are
necessary for universities. , , , , , , , ,
Table shows the percentage of agreement of the academicians at the managerial positions with the propositions about universities having collaboration with the industry. The academicians with administrative function agree with the proposition Universities must give priority to the researches that are needed by the
industry with a percentage of . %. Most of the participants . % argue that university-industry
collaboration is a necessity. . % of the participants express that Techno-Parks are necessary for universities.
Conclusion
The universities in many developed countries completed the industry integration and built a system on creating value and making profit by integrating the concept of know-how to their research philosophy. These universities embraced the global world university qualifications and synthesized modern science with interdisciplinary approaches. These qualifications, which are defined with GU, built a vision for the universities and formed a frame including competitiveness, creating their own economies, entrepreneur, having international network, focused on synergy and practices for the universities. Entrepreneur University model, which is one of the components of this frame, has been accepted as the lead in the economic growth of the countries Farsi et al., and has been supported by government and state policies in most of the countries. Some interesting results related to the Entrepreneur University and GU concepts, which were analyzed from the perspective of the academicians at the managerial position at the universities in Turkey, were revealed. )n this study, the opinions of the academicians at the managerial positions related to these concepts were received and important observations about the situations of the universities in Turkey were made. The participants deduced that the universities in Turkey were not able to improve in the present situation and they needed to reach at the point of entrepreneur and GU qualifications in order to obtain international competitive capacity. )n this regard, change and improvement are obligation rather than choice for the universities. Nevertheless, the most important finding which can trigger this is universities defecation of the bulky structure of public. Most of the academicians with administrative function emphasized that the universities were not autonomous enough, and the current situation about finance and budget had to be changed. A different aspect of autonomy is that universities generate fund and resources. This aspect makes Entrepreneur University model easy to be adapted. Besides, almost all of the participants support collaboration between university and industry, and think that techno-parks are significant for the university and market integration.
)t is found as a result of the researches that academicians with administrative functions embraces Entrepreneur University model which attributes importance to the university-industry collaboration and they lean towards future collaborations in this direction. (owever, it can be inferred that the universities are insufficient in adapting Entrepreneur University model and making plan, program and strategies in this direction. )f the government develops a policy in this frame and supports universities, the transition to rd
Generation Universities will be easier. The number of participants managerial academicians and the
limited number of questions in the survey form which are constraints of this study must be taken into account in the process of evaluation. There were similar studies in this field before; nonetheless, lack of an extensive study from the perspective of academicians at the various managerial positions makes this subject authentic in its field.
)n the future studies, analysing universities in Turkey by making distinctions of private-public universities
Reference
1. ARıKAN, R. 2004. Araştırma teknikleri ve rapor hazırlama, Ankara, Asil Yayın Dağıtım.
2. ASLAN, G. 2010. Öğretim Üyelerinin Girişimci Üniversite ve Üniversite Sanayi İşbirliği Kavramlarına İlişkin Görüşleri. Eğitim
Bilim Toplum Dergisi, 8, 7-22.
3. ÇETIN, M. 2007. Bolgesel Kalkinma ve Girisimci Universiteler. Ege Academic Review, 7, 217-238.
4. ÇÖMLEKÇI, N. 2001. Bilimsel araştırma yöntemi ve istatistiksel anlamlılık sınamaları. Ankara: Bilim Teknik Yayınevi.
5. DE RIDDER-SYMOENS, H. 2003. A history of the University in Europe: Volume 1, universities in the middle ages, Cambridge
University Press.
6. DIDOU-AUPETIT, S. 2002. Küreselleşme, NAFTA ve Meksika’da Yüksek Öğretim Sistemi: Konular, Tehditler ve Reformlar.
Kuram ve Uygulamada Eğitim Bilimleri, 2, 81-92.
7. ERDEM, A. R. 2005. ÜNİVERSİTENİN VAR OLUŞ NEDENİ (ÜNİVERSİTENİN MİSYONU)*. Pamukkale Üniversitesi Eğitim
Fakültesi Dergisi, 17, 75-86.
8. ERDEM, A. R. 2006. Dünyadaki yükseköğretimin değişimi. Selçuk Üniversitesi Sosyal Bilimler Enstitüsü Dergisi, 15, 299-314.
9. ETZKOWITZ, H. 2012. Triple Helix Clusters: Boundary Permeability at University—Industry—Government Interfaces as a
Regional Innovation Strategy. Environment and Planning C: Government and Policy, 30, 766-779.
10. FARSI, J. Y., IMANIPOUR, N. & SALAMZADEH, A. 2012. Entrepreneurial university conceptualization: case of developing
countries. Global Business and Management Research: An International Journal, 4, 193-204.
11. GÜRÜZ, K. 1994. Türkiye'de ve dünyada yükseköğretim, bilim ve teknoloji, Türk Sanayicileri ve Işadamları Derneği.
12. GÜRÜZ, K. 2001. Dünyada ve Türkiye’de Yükseköğretim (Tarihçe ve Bugünkü Sevk ve İdare Sistemleri), Ankara, ÖSYM
Yayınları.
13. HEIDLER, J. & LENGERSDORF, D. 2015. The entrepreneurial University from the Perspective of Gender Studies: between
Awakening and Perseverance. Feministische Studien, 33, 154-156.
14. KARASAR, N. 2002. Bilimsel Araştırma Yöntemi Ankara: Nobel Yay. Ekim.
15. KIPER, M. 2010. Dünyada ve Türkiye'de üniversite-sanayi işbirliği: ve bu kapsamda üniversite sanayi ortak araştırma
merkezleri programı (ÜSAMP), TTGV.
16. LEE, M. N. 2004. Global trends, national policies and institutional responses: Restructuring higher education in Malaysia.
Educational Research for Policy and Practice, 3, 31-46.
17. MALIYE-BANALıĞı 2015. GENEL BÜTÇE KAPSAMINDAKİ KAMU İDARELERİ 2015 YILI BÜTÇESİ ÖDENEK TEKLİF
TAVANLARI.
18. MCBURNIE, G. 2002. Transnational education, quality and the public good: case studies from South-East Asia.
19. ODABAŞı, H. & ODABAŞı, Y. 2004. Girişimci üniversitelere doğru. Cumhuriyet Bilim Teknik Dergisi, 18, 20-21.
20. ÖKMEN, M. & BAL, V. 2013. Üniversite Yönetimlerinin Girişimci Üniversite Kavramına İlişkin Görüşleri. Journal of Higher
Education/Yüksekögretim Dergisi, 3.
21. TURAL, N. K. 2002. Küreselleşmenin üniversite üzerine etkileri: Çeşitli ülkelerden örnekler. Eğitim Araştırmaları, 6, 99-120.
22. WISSEMA, J. G. 2009. Towards the third generation university: managing the university in transition, Edward Elgar