ISSN 0976-2612, Online ISSN 2278–599X, Vol-7, Special Issue-Number2-April, 2016, pp1201-1206
http://www.bipublication.com
Research Article
The synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles by easy method and analyzing the
pharmaceutical usage of porous iron oxide nanoparticles
*
Fahimeh khakaz, Ali heidary,
Ehsan khodadadi and Atieh yazdani
Department of oganic chemistry, Faculty of basic sciences, Islamic Azad university
Yadegar-E-Imam Khomeini, Shahre Rey Branch ,Tehran ,Iran
*Corresponding author: Email: a.khbz@yahoo.com
Tel: +98-9358675414 ; Fax: +98-2156911760
ABSTRACT:
In this research we have tired to use a simple and fast method for the synthesis of iron nanoparticles and apply it in the drug industry and also we are looking chemistry and pharmacy. Recent research proves iron oxide nanoparticles have the potential of more effective cancer drugs. Iron oxide one of the most important transition metal oxides that feature is unique .The new study used as drug delivery vehicles. The first part of the synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles of iron oxide precursor of a non-magnetic iron sulfate is as targeted. This test has no organic solvent and only in the vicinity of profits and Dyvnayz·h water under the reaction temperature is taken and particles with approximate diameter 10 nm magnetic properties created, The Nano composite is synthesized and the prepared Nano composite is characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and X-ray diffraction (XRD) teqniques. For measuring magnetization values of magnetic nanoparticles, we use a vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) technique. has been investigated by VSM, the results of X- ray diffraction and transmission electron microscopy of single-phase iron oxide particles with a diameter of 10 nm confirms TEM and FTIR results obtained with iron oxide nanoparticles corresponded to the pattern. In the second part of the study synthesis Nano porous particles (PHNP) of iron oxide nanoparticles and more effective use of these nanoparticles in porous doxorubicin, a chemotherapy drug, was investigated.
Keywords: magnetic nanoparticles ,iron oxide, porous nanoparticles, drug delivery, doxorubicin.
[I] INTRODUCTION
Nano science reviews basic principles of molecules and structures with dimensions between approximately 1 and 100 nanometers [1]. For nanotechnology applications in various fields including food, medicine, medical diagnosis, biotechnological communications, computer, energy, environment, transportation. . And housing- is considered[2]. There are many material properties of metal oxides and applications،As long as the materials reach the Nano scale, its properties are formed which
2) Chemical methods (chemical methods than a liquid to aid wet)
3) Mechanical methods
In the physical most of reactions takes place in the gas phase Therefore, methods 1 and 2 the preparation of the arrangement of atoms begin and end with the construction of nanomaterial’s can find stable. But nanomaterial’s made mechanically crushed and deformed as a result of bulk material is concerned.
One of the defects of physical methods using precise, yet expensive tools that are not easily accessible. Production of nanomaterial’s with chemical reactions in the physical method is much cheaper and more accessible and that is why further research in the world nanoparticles are made using chemical methods[4]. The mechanical method with the progress of the reaction, the reaction temperature is increased, resulting in larger particles with the reaction progress and usually cannot use this method with small size of nanoparticles produced. Choose a method of making Nano-materials, Nano-materials is very important, depending on the chemical composition of the initial reaction and so on, which should be considered when manufacturing method of Nano material.
In the preparation of iron oxide nanoparticles factors such as reaction temperature, concentration of the precipitant, salt concentration and physical properties of magnetic iron nanoparticles affect. In this experiment, ferrous sulfate, a precursor of the non-magnetic particles in very simple terms compared to the previous method is obtained, The advantage of this method availability, cheap, fast approaching and reactive components is simple And this test is a simple method for the production of iron nanoparticles.
The trial of particles with nanometer scale, 10 -9 found that Nano-particles obtained by the diffraction X (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), transmission electron microscope (TEM) and magnetic susceptibility meter ( VSM) checked out and See the results of
magnetic iron oxide nanoparticle production with proved Qtr9-10nm.
Over the past decade, functional nanoparticles containing the active components of optical and magnetic widely been studied for multiple applications. This multi-functional nanoparticles with targeting agents bind to drug molecules, the promise of making carrier conduction, the target coordinates with improved sensitivity photographed the day although some chemical agent connection with the performance of different nanoparticles on the surface is often a very efficient synthesis process And the drug and targeting molecules, as well as other functional probes on a surface of the nanoparticles may interfere with the absorption of secondary compounds that target and the nanoparticles.[5-6] Recent studies on magnetic nanoparticles active hollow light with the porous membrane has more. Compared to the integrated particles of similar size, PHNP more level to encapsulate small molecules account, In addition, the porous structures can be programmed as the same particles and biocompatible PHNP can be linked back to a specific targetedand around the area of interest, where drug molecules are released to physically or chemically focus.
This controlled release of drugs with the ability of optical and magnetic imaging, a new type of carrier for simultaneous diagnostic and therapeutic applications for the Nano-porous particles (PHNP) are provided.[7-8-9] Porous iron oxide nanoparticles most recognized multi-functional nanoparticles for biomedical applications offer. Recent advances have led to the formation of iron oxide uniform PHNP and the size, thickness and porosity of the shell structure is designed with a variety of drug molecules and magnetic and optical functions are coordinated.[10]
Placement of the drug in Nano-porous
Placement drug molecules in Nano-porous particles, a process is fast approaching. Pore size, surface chemical properties, surface heterogeneity, building cavities of porous nanoparticles are factors that are effective in the process of absorption of the drug distribution and balance. Solubility, structure, molecular weight, polarity and hydrophobic and hydrophilic properties of drug molecules in drug affect placement process. Porous drug release from nanoparticles
Drug release from nanoparticles of porous, as the reverse process related loading and chemical and structural features of porous nanoparticles, chemical and physical characteristics of incarcerated drug and drug interactions, and the particles depends on the environment. Not only to prevent biodegradation porous membrane pre-release drugs are useful, but it is a continuous release of medication that can be done with external stimuli suddenly they provide.
In this paper, an example of a chemotherapy drug to demonstrate therapeutic importance PHNP examine the application.[11]
[II] MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1.Synthesis of nanoparticles
In this study, a solution of 0.1 M orange iron sulfate was prepared and at a temperature close to 100 ° C, was stirred at a speed of 10,000 rpm And 4 M NaOH solution was added to saturated as it was observed secondary color is black solution which is caused by the formation of iron nanoparticles, Once these steps completed and sediment filtered solution 3 times 2 times 1 times by deionized water and washed by acetone to ensure the absence of impurities And sediment for one hour in an oven at 400 ° C, and iron oxide deposits were observed after this time.
2.2. Oxidation of nanoparticles
After this stage represents the conversion nanoparticles for further oxidation in the presence of oxygen (trim ethylamine -N- oxide) was placed in a high temperature which causes structural defects and then formation of hollow
nanoparticles with a core containing iron oxide Nano-crystalline grains was.
2.3.Placement of the Doxorubicin
Next a chemotherapy drug called doxorubicin, with physical adsorption onto porous particles were then loaded Nano, After coating the porous nanoparticle aqueous dispersion excellent PEG showed that doxorubicin connection to the local water soluble Nano-facilitated, Compared with net doxorubicin, doxorubicin loaded nanoparticles in porous allowing much more control over the behavior and property release less cytotoxic to cancer cells 3-SK-BR's .
[III] RESULTS
3.1.XRD Analysis results
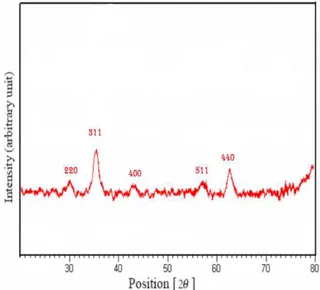
To prove the purity of magnetic nanoparticles obtained from non-magnetic precursor of diffracted X and was analyzed, As shown in [Figure-1].
Fig: 1. XRD of Nano particles iron oxide
can be seen peaks of diffraction peaks index related to magnetite and other impurities In its peak is observed .
3.2.TEM survey results
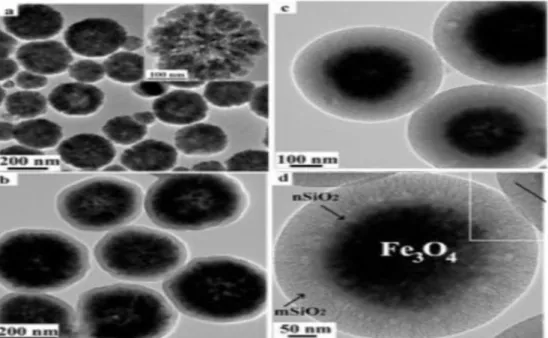
Fig: 2. TEM image of Nano iron oxide
Roy image obtained can be said that iron oxide nanoparticles with a diameter of approximately 10 nm in this experiment is that the results of XRD and magnetic results [Figure-3] agrees.
Single crystals are synthesized nanoparticles are spherical iron oxide nanoparticles in size since smaller than 50 nanometers are single-domain It
can be seen that the single-domain nanoparticles are obtained in this experiment.
3.3.VSM curve
To study the magnetic properties of the particles and see the super paramagnetic properties of particles in fields near zero hysteresis curve Oe (50 to 150 Oe) was measured by VSM [Figure-3].
Fig: 3. hysteresis curves in fields close to zero
As can be seen from this graph as a straight line and passed their origin and field inversion cannot be seen here, which confirmed the iron oxide nanoparticles are paramagnetic properties.
3.4.SEM of porous nanoparticles
Fig: 4. SEM images of hollow nanoparticles of iron oxide after oxidation
3.6. view results optical microscope
After this stage drug Basin two fractions were then loaded onto porous particles by light
microscopy in Nano-porous behavior of the two fractions Basin loaded with doxorubicin net head [Figure -5] were compared
Fig: 5. (A to C) Optical microscopy observation of the behavior of pure doxorubicin (D to C) observation of the behavior of doxorubicin loaded into nanoparticles in porous LM.
As previously mentioned, the two fractions Basin loaded in Nano-capsules allows much more control over the behavior and property release less cytotoxic than the cancer cells.
[IV] DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION In this experiment, the magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles of approximately 10 nm in size of the magnetic material that had been synthesized by the profit that was the precipitating agent. The advantage of this type of synthesis can be fast approaching and the availability and cost of
FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE
The goal of the present study is to develop better understanding a bout the different aspects of Nanoparticle synthesis and chemical, pharmaceutical applications.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors thank the research facilities of yadegar-e-emam university, Tehran ,Iran , for financial support this research project.
REFERENCES
1. Pal S L, Jana U, Manna P. K .,Mohanta G.P., Manavalan R .(2011), Nanoparticle : An overview of preparation and characterization . Jornal of applied pharmaceutical science , 01(06) , pg 228-234
2. Kodama,R .H .(1999) Magnetic nanoparticles , .Magn Mater , 200, pg 359-372
3. Kavitha K.S., Syed Baker , Rakshith D ., Kavitha H. U., Yashwantha Rao H.C., Harini B.P. and Satish S.( 2013) Plants as Green Source towards Synthesis of Nanoparticles. International Research Journal of Biological Sciences , 2 (6) ,pg 66-76
4. Gupta AK , Gupta M,(2005) Synthesis and surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticle for biomedical applications ,Bio materials , 26 , pg 3995-4021 .
5. Larsen,S.C (2004) Surface and monomolecular catalysis, Ed. American Scientific Publishers. 6. Sosa I O,Noguez C, Barrera R(2003).Optical
properties of metal nanoparticles with arbitrary shapes, Journal of Phys Chem.Pg 6269-6275.
7. Sellmyer ( Springer 2005),”Advanced Magnetic Nanostructures”.
8. Salavati-niasari,M.(2005) Journal of Molecular Catalysis Chemical, Pg 229 9. Salavati-niasari,M. ,Shaterian, M., Ganjali,
P., Norouzi . (2007) Jornal of Molcular Catalysis Chemical .Pg 261-147.
10.Salavati-niasari,M . , Zamani, S . Ganjali, P . Norouzi,(2007) Jornal of Molecular Catalysis Chemical, Pg 261-196.
11.WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA. (2008 )Astruc Nanoparticles and Catalysis 12.Manna P. K ,Pal S L, Jana U, X. Cheng, A.T.
Kan , (2004) M.B. Tomson, J. Chem. Eng. Pg 280.
13.Gnanaprakash, G. Morales,S.(2006)” Properties and Biomedical Application of nanoparticles”,Handbook of Magnetic Materials. Vol.16,Elsevier.
14.L.V. Gurgel, O.K. Junior, P.P. Gil, L.F. Gil,(2011) Bio. Tech.vol 99,pg 3077.
15.A.N. Nakagatio, S. Iwamaoto, H. Yano, Appl. (2009) Phys. Mater. Sci. Proc pg. 80- 93. 16.W.W. Zhou, K.B. Tang, S.Y. Zeng, Y.X. Qi,
(2008), Nanotech. vol19.pg 560.
17.E. Tierrablanca, J. Garcia, P. Roman, R. Silva, (2010) Appl. Catalys. Pg 381 -267.
18.J. Lee, Q. Sun, Y. Deng, J. ,(2008) Bio. Mater. vol2, pg 162.