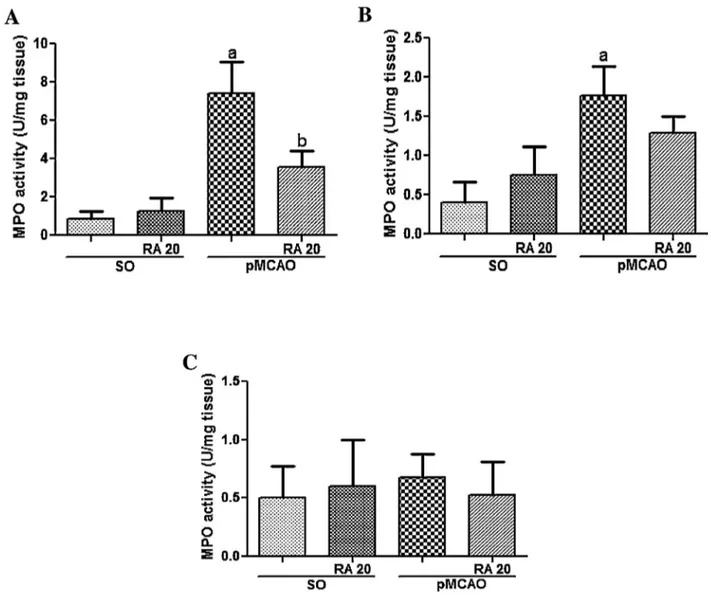
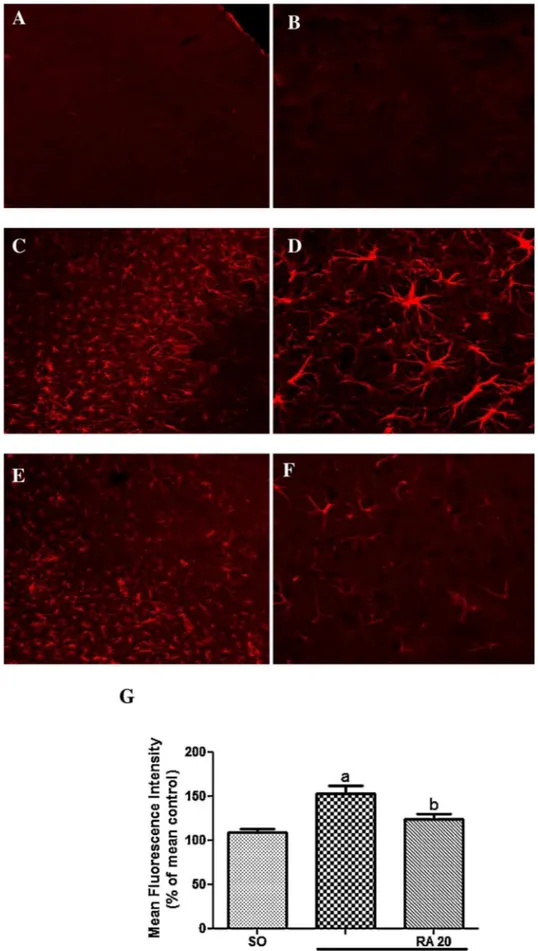
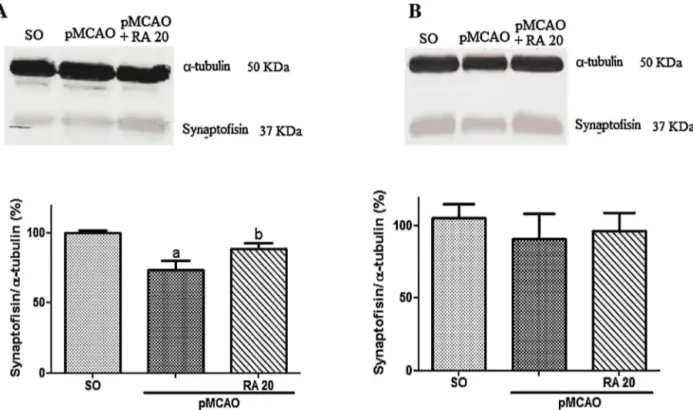
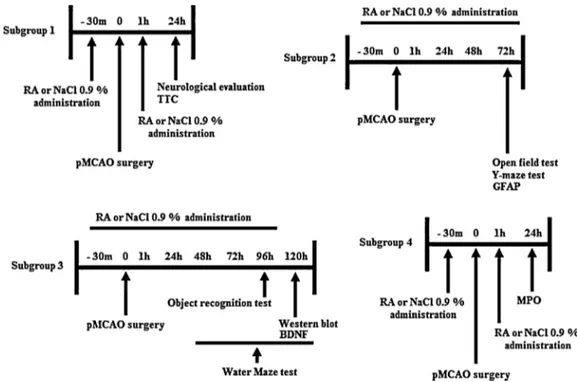
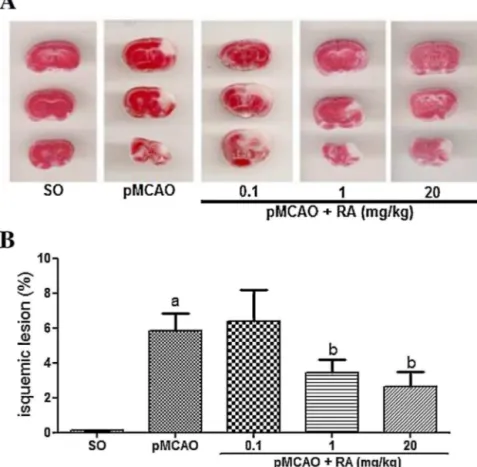
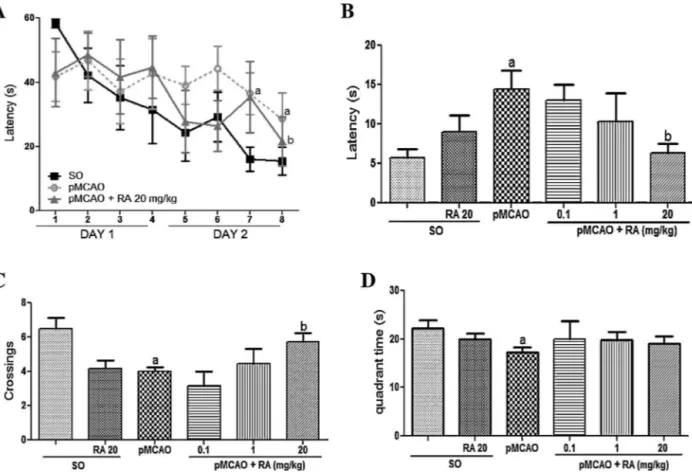
Rosmarinic acid prevents against memory deficits in ischemic mice
Texto
Imagem

Documentos relacionados
The mechanisms involved in improving memory deficits of LSPC and LC combinations were associated with the improvement of antioxidant defense ability of brain, serum and
Hypothesis/Purpose: Thus, the present study was designed to explore whether eriodictyol has neuropro- tective effects against the neuronal damage, motor and memory deficits induced
A permissão para utilizar as IFRS para as contas individuais das empresas cotadas é verificada particularmente em países com um forte sistema de financiamento de
“Os salários pagos pela empresa são semelhantes ao mercado deste ramo” foi o quarto questionamento, gerando as seguintes respostas: 10,7% discorda parcialmente; 32,1% não
Este trabalho visa o estudo de motores de regras e sua utilização no Sistema de Dotação de Material do Exército Brasileiro, de forma a facilitar a definição e execução das
In hippocampal neurons, c- jun phosphorylation by hNGFP61S/R100E, as well as by hNGFR100E, determined with a site-specific anti- phospho c- jun antibody, was reduced by 30% with
The 6-OHDA-lesioned rats showed contralateral rotations towards the lesion side, which was accompanied by learning and memory deficits in a passive avoidance test and a decrease
Of the 13 subjects in this group who converted to dementia, 84.6% had baseline deficits in episodic memory and other cogni- tive functions (global cognitive functioning, working