r e v b r a s o r t o p . 2015;50(3):356–359
w w w . r b o . o r g . b r
Case
Report
Fracture
of
the
proximal
extremity
of
the
tibia
after
anterior
cruciate
ligament
reconstruction:
case
report
夽
Márcio
de
Oliveira
Carneiro,
Thiago
de
Almeida
Monteiro
∗,
Marcos
Renato
Zenovello
Bueno,
Jorge
Luis
Augustin
Júnior
FaculdadedeMedicinadeSãoJosédoRioPreto(FAMERP),SãoJosédoRioPreto,SP,Brazil
a
r
t
i
c
l
e
i
n
f
o
Articlehistory:
Received26May2014
Accepted27June2014
Availableonline27April2015
Keywords:
Tibialfractures
Anteriorcruciateligament
reconstruction
Autologoustransplantation
a
b
s
t
r
a
c
t
Wereportarareconditionthathasbeenlittledescribedintheliterature:afractureofthe
proximalextremityofthetibiaafteranteriorcruciateligamentreconstructionusingan
autologouspatellarbone-tendongraft.Inthisreport,wediscussthefactorsthatpredisposed
towardthisepisode,thetreatmentandtheevolutionofthecaseafterthesurgicaltreatment.
©2014SociedadeBrasileiradeOrtopediaeTraumatologia.PublishedbyElsevierEditora
Ltda.Allrightsreserved.
Fratura
da
extremidade
proximal
da
tíbia
após
reconstruc¸ão
do
ligamento
cruzado
anterior:
relato
de
caso
Palavras-chave:
Fraturasdatíbia
Reconstruc¸ãodoligamentocruzado
anterior
Transplanteautólogo
r
e
s
u
m
o
Relatamosumacondic¸ãorara,poucodescritanaliteratura,queéafraturadaextremidade
proximaldatíbiaapósreconstruc¸ãodoligamentocruzadoanteriorcomenxertoautólogo
osso-tendãopatelar-osso.Nesterelato,discutiremosfatorespredisponentesaoepisódio,
tratamentoeevoluc¸ãodocasoapóstratamentocirúrgico.
©2014SociedadeBrasileiradeOrtopediaeTraumatologia.PublicadoporElsevierEditora
Ltda.Todososdireitosreservados.
Introduction
Reconstruction surgery on the anterior cruciate ligament
(ACL)performedarthroscopicallypresentsahighrateofgood
夽
WorkdevelopedattheBaseHospital,FaculdadedeMedicinadeSãoJosédoRioPreto(FAMERP),SãoJosédoRioPreto,SP,Brazil.
∗ Correspondingauthor.
E-mails:thiagomonteiro33@yahoo.com.br,goianomonteiro@yahoo.com.br(T.deAlmeidaMonteiro).
results.1 Morethan100,000newcasesareperformedinthe
UnitedStateseveryyear.2However,thisprocedureisnotfree
fromcomplications,3withanincidencerateofbetween1.8%
and24%.4
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.rboe.2015.04.009
rev bras ortop.2015;50(3):356–359
357
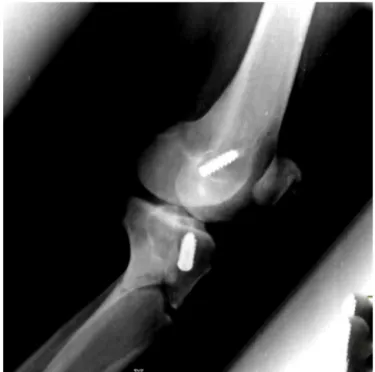
Fig.1–Frontalradiographonkneeshowingfractureof proximaltibia.
The complications that have been described include:
arthrofibrosis,patellarfracture, “Cyclops”lesions,synovitis,
patellartendinitis,paininthegraftdonorareaandosteolysis,3
amongothers. Thecommonestofthese is joint stiffness.4
Fracturingoftheproximaltibiaisaseriouscomplicationthat
hasonlybeendescribedinafewcasesintheliterature.5,6In
thepresentreport,wedescribethiscomplication.
Thiscaseconsistedofafractureoftheproximal
extrem-ityofthetibiathatoccurredinapatient4.5monthsafteran
arthroscopicoperationtoreconstructtheACL.
Case
report
The project for this study was approved by our
institu-tion’sresearchethicscommitteeundertheprotocolnumber
5985/2011.
Thepatientwasa17-year-oldmalewhowasattendedat
ourhospital,withahistory ofspraininghisleft knee after
steppingintoaholeintheasphaltwhencrossingastreet.He
arrivedattheemergencyservicewithaconditionofpainin
hisleft kneeandleg, accompaniedbyfunctionallimitation
andinabilitytobearweightontheaffectedleg.Hesaidthat
hehadundergoneACLreconstructionsurgery4months
previ-ously,inwhichagraftfromtheipsilateralpatellartendonhad
beenused.Radiographsofthekneewereproducedinfontal
andlateralviews,fromwhichanextra-articularfractureofthe
proximaltibiawasdiagnosed.Thefracturelinereachedthe
regionoftheanteriortibialtuberosity(ATT),whichwasthesite
fromwhichtheboneplugforthebone-patellartendon-bone
grafthadbeenharvested(Figs.1and2).Thepatientunderwent
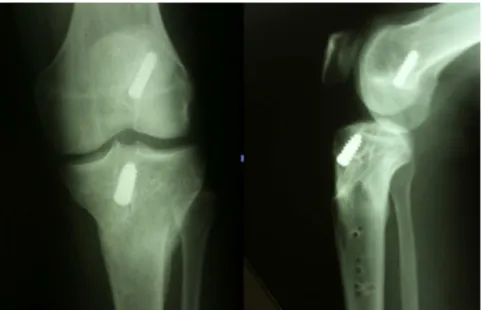
surgicaltreatmentinwhichopenreductionandinternal
fixa-tionusingaplateandscrewswereperformed(Figs.3and4).No
looseningofthetibialinterferencescrewthathadbeenused
intheACL reconstructionwasseen.Thepatientpresented
goodevolutionwiththe treatmentthathad beenproposed
anddidnotpresentany functionalalterationsorany
alter-ationsinspecifictestsforevaluatingthereconstructedACL.
Consolidationofthefracturewasachievedbytheendofthe
Fig.2–Lateralradiographonkneeshowingfractureof proximaltibia.
358
rev bras ortop.2015;50(3):356–359Fig.4–Lateralradiographafteroperation.
fourthpostoperativemonth.Thepatientreturnedtohis
recre-ationalsportsactivitiesandratedhisdegreeofsatisfactionas
high.Oneyearaftertheoperation,theimplantwasremoved
becauseoflocaldiscomfortthatthepatientreported(Fig.5).
Discussion
Fracturing of the tibial plateau at the site of the tibial
tunnel afterACL reconstruction hasonlybeen described a
few timesintheliterature.5,6 Somepublishedstudieshave
reported occurrencesof fractures ofthe tibial plateau
fol-lowingACLreconstructionusingautograftsfromthegracilis
andsemitendinosus.4,5Othershaveusedbone-patellar-bone
grafts6,7andallograftsfromtheAchillestendon.8Thisevent
isprobablyindependentofthegraftused,butthereare
the-oriesstating thatthe bonethat isdrilled through inorder
toconstructthetibialtunnelissubjecttostressthatleads
tofatiguewhentorsionalforcesareappliedduringflexion.8
Thepresenceofatibialtunnelisthoughttoactlikeacortical
defect,whichisafactorpredisposingtowardfractures.5,7 In
thisregard,whenapatellargraftisused,harvestingthebone
plugwouldincreasethesusceptibilityoftheproximaltibiato
fracturing.Thishasbeen welldocumented,sinceacortical
defectdiminishes boneresistanceinsituationsoftorsional
forces.9
Inthecaseinquestion,thecenterofthefracturewasin
thedonorareaoftheboneplug.Thisbonedefectacted
syn-ergicallyinassociationwiththedrillingofthetibialtunnel,
therebyincreasingthezoneoffragilityandallowedtibial
frac-turingduetolow-energytrauma.7,10,11
Concentrationofstressonananteriorpointoftheproximal
tibiacausedbyfixationscrewsthatalterthebone
mechan-icswouldalsobeapredisposingfactor.7 Despitethelackof
specificstudies,abiomechanicalstudybyBrooksetal.found
thatdrilledholeswithdiametersgreaterthan20%ofthebone
width decreasedthetorsionalcapacityby55%.12 One
addi-tionalfactorthatmightplayaroleinfracturedevelopment
following ACL reconstructionis wideningofthe bone
tun-nel,whichmayoccurinupto68%ofthecases.13Thefactor
causingthisisstillunknown,butitisbelievedtobean
autoim-munephenomenoneventhoughnoresearchhasconfirmed
thishypothesis.
rev bras ortop.2015;50(3):356–359
359
Mostauthorshaveoptedtoperformsurgicaltreatmenton
thesefractures,withopenreductionandfixationusingplates
ofavarietyofmodels,eventhoughthisisadifficultsurgical
proceduresecondarytoasurgicalcomplication.Mostofthe
casesdescribedevolvedwellthroughthetreatment.
Inthecasereportedhere,surgicaltreatmentwasalso
cho-sen,withmedialaccesstotheproximaltibiaandpositioning
ofanL-shaped supportplate.Thepatient evolvedwithout
immediateorlatecomplicationsandpresentedfullrangeof
motionandconsolidationofthefracture4monthsafterthe
treatment.
Fracturing of the tibial plateau after arthroscopic ACL
reconstruction is a rare complication that is still little
describedintheliterature.Studieshaveshowngoodevolution
ofthiscomplicationfollowingsurgicaltreatment,eventhough
theprocedurehasahighdegreeoftechnicaldifficulty.Inthe
casereportedhere,thepatientevolvedsatisfactorilyafterthe
operation,withconsolidationofthefractureofthelefttibial
plateau,achievementoffullrangeofmotionofthekneejoint,
areturntoworkactivitiesandevenareturntorecreational
soccerpractice.
Conflicts
of
interest
Theauthorsdeclarenoconflictsofinterest.
r
e
f
e
r
e
n
c
e
s
1. AndersonAF,SnyderRB,LipscombABJr.Anteriorcruciate ligamentreconstruction.Aprospectiverandomizedstudyof threesurgicalmethods.AmJSportsMed.2001;29(3):272–9.
2.OwingsMF,KozakLJ.Ambulatoryandinpatientproceduresin theUnitedStates,1996.VitalHealthStat13.1998;(139):1–119.
3.GrafB,UhrF.Complicationsofintra-articularanterior cruciatereconstruction.ClinSportsMed.1988;7(4):835–48.
4.WienerDF,SiliskiJM.Distalfemoralshaftfracture:a complicationofendoscopicanteriorcruciateligament reconstruction.Acasereport.AmJSportsMed. 1996;24(2):244–7.
5.SundaramRO,CohenD,Barton-HansonN.Tibialplateau fracturefollowinggracilis-semitendinosusanteriorcruciate ligamentreconstruction:thetibialtunnelstress-riser.Knee. 2006;13(3):238–40.
6.DelcoglianoA,ChiossiS,CaporasoA,FranzeseS,MenghiA. Tibialplateaufractureafterarthroscopicanteriorcruciate ligamentreconstruction.Arthroscopy.2001;17(4):E16.
7.MithöferK,GillTJ,VrahasMS.Tibialplateaufracture followinganteriorcruciateligamentreconstruction.Knee SurgSportsTraumatolArthrosc.2004;12(4):325–8.
8.El-HageZM,MohammedA,GriffithsD,RichardsonJB.Tibial plateaufracturefollowingallograftanteriorcruciateligament (ACL)reconstruction.Injury.1998;29(1):73–4.
9.JohnsonBA,FallatLM.Theeffectofscrewholesonbone strength.JFootAnkleSurg.1997;36(6):446–51.
10.MorganE,SteensenRN.Traumaticproximaltibialfracture followinganteriorcruciateligamentreconstruction.AmJ KneeSurg.1998;11(3):193–4.
11.MoenKY,BoyntonMD,RaaschWG.Fractureoftheproximal tibiaafteranteriorcruciateligamentreconstruction:acase report.AmJOrthop(BelleMeadNJ).1998;27(9):629–30.
12.BrooksDB,BursteinAH,FrankelVH.Thebiomechanicsof torsionalfractures.Thestressconcentrationeffectofadrill hole.JBoneJointSurgAm.1970;52(3):507–14.
13.WebsterKE,FellerJA,HameisterKA.Bonetunnel enlargementfollowinganteriorcruciateligament