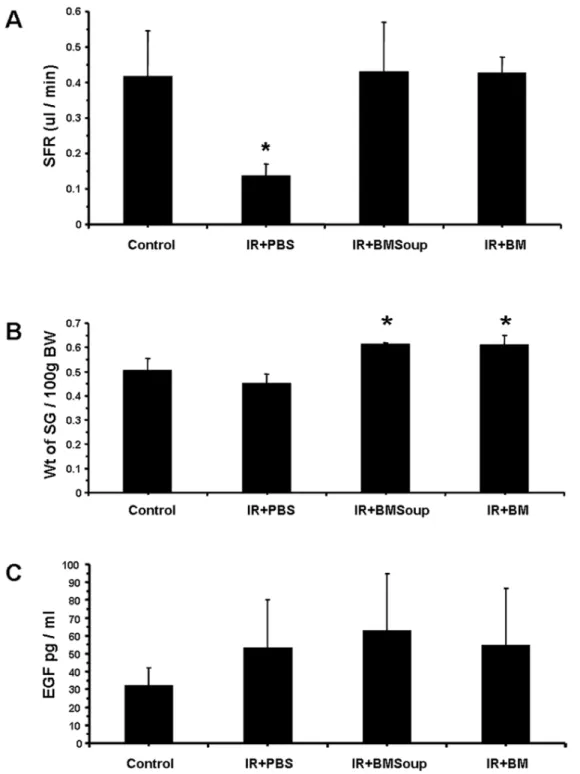
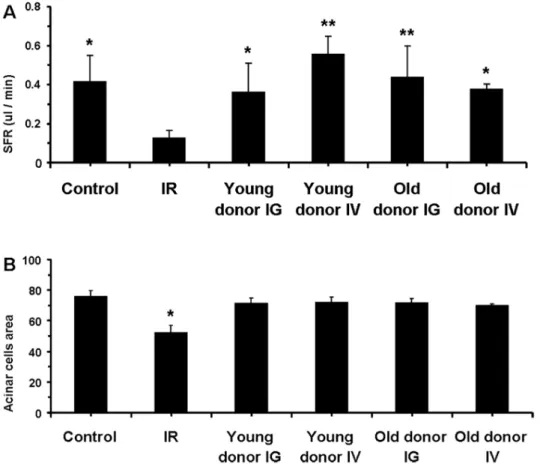
Paracrine effects of bone marrow soup restore organ function, regeneration, and repair in salivary glands damaged by irradiation.
Texto
Imagem


Documentos relacionados
We determined the effects of these epigenetic mechanisms on adipocyte differentiation in mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) derived from bone marrow (BM-MSCs) and adipose tissue
In studies that used a BM implant in the quadriceps of rabbits to study the influence of anti-inflammatory therapies, bone formation was observed in the muscle of control
Immunophenotyping by FC of BM cells showed the presence of clonal plasma cells (40%) expressing CD38, CD138 dim , cy kappa , smkappa, -2 microglobulin and CD81, and were negative
Local transplantation of hypoxia- pretreated BM-MSCs significantly increased the survival of the BM-MSCs in ischemic muscle, markedly increased angiogenesis and improved
The results of this study suggest that inflammation-induced BM exhaustion and a disturbed progenitor cell mobilization response due to reduced levels and activity of MMP-9 in the BM
good proliferation inducer. Figure 2: xCELLigence analysis of DP-MSCs and BM-MSCs. Growth curve of the cells. a1) DP-MSCs, b1) BM- MSCs; doubling time of the DP-MSCs (a2) and
In order to understand the structure based protease inhibition mechanism, solution structural studies of Bm-Aspin has been initiated and in addition to this, the binding of
In this model, irradiated WT mice presented loss of microsatellite markers on BM cells, low white blood cell (WBC) counts, reduced megakaryocyte (MK) and platelet