w w w . r b o . o r g . b r
Original
Article
Evaluation
of
the
results
and
complications
of
the
Latarjet
procedure
for
recurrent
anterior
dislocation
of
the
shoulder
Luciana
Andrade
da
Silva
a,∗,
Álvaro
Gonc¸alves
da
Costa
Lima
b,
Raul
Meyer
Kautsky
b,
Pedro
Doneux
Santos
a,
Guilherme
do
Val
Sella
a,
Sergio
Luiz
Checchia
a,caShoulderandElbowGroup,SantaCasadeSãoPaulo,SãoPaulo,SP,Brazil
bDepartmentofOrthopedicsandTraumatology,SantaCasadeSãoPaulo,SãoPaulo,SP,Brazil
cDepartmentofOrthopedicsandTraumatology,FaculdadedeCiênciasMédicasdaSantaCasadeSãoPaulo(FCMSCSP),SãoPaulo,
SP,Brazil
a
r
t
i
c
l
e
i
n
f
o
Articlehistory:
Received7August2014 Accepted22September2014 Availableonline11November2015
Keywords: Jointinstability Shoulderdislocation Shoulder
a
b
s
t
r
a
c
t
Objective:Evaluate theresults andcomplicationsofLatarjetprocedurein patientswith anteriorrecurrentdislocationoftheshoulder.
Methods:Fifty-one patients(52shoulders)withanterior recurrentdislocation,surgically treatedbyLatarjetprocedure,wereanalyzedretrospectively.Theaveragefollow-uptime was22months,range12–66months;Theagerangewas15–59yearswithameanof31; regardingsex,42(82.4%)patientsweremaleandnine(17.6%)werefemale.Thedominant sidewasaffectedin29(55.8%)shoulders.Regardingtheetiology,48(92.3%)reportedtrauma andfour(7.6%)hadthefirstepisodeafteraconvulsion.
Results:Theaverageelevation,lateralrotationandmedialrotationoftheoperatedshoulder were,respectively,146◦(60–80◦),59◦(0–85◦)andT8(T5gluteus),withstatisticalsignificance fordecreasedrangeofmotioninallplanes,comparedwiththeotherside.ThescoresofRowe andUCLAwere90.6and31.4,respectively,inthepostoperativeperiod.Elevenshoulders (21.2%)hadpoorresults:signsofinstability(13.4%),non-union(11.5%)andearlyloosening ofthesynthesismaterial(1.9%).Therewasacorrelationbetweenpoorresultsandconvulsive patients(p=0.026).
Conclusion:WeconcludethattheLatarjetprocedureforcorrectionofanteriorrecurrent dis-locationleadstogoodandexcellentresultsin82.7%ofcases.Complicationsarerelatedto errorsintechnique.
©2014SociedadeBrasileiradeOrtopediaeTraumatologia.PublishedbyElsevierEditora Ltda.Allrightsreserved.
∗ Correspondingauthor.
E-mails:lucalu@terra.com.br,ombro@ombro.med.br(L.A.daSilva). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.rboe.2015.09.009
Avaliac¸ão
dos
resultados
e
das
complicac¸ões
em
pacientes
com
instabilidade
anterior
de
ombro
tratados
pela
técnica
de
Latarjet
Palavras-chave:
Instabilidadearticular/cirurgia Luxac¸ãoglenoumeral Ombro
r
e
s
u
m
o
Objetivo: Avaliarosresultados e ascomplicac¸ões dacirurgia de Latarjetem pacientes acometidospelainstabilidaderecorrenteanteriordeombro.
Métodos: Foramanalisados,retrospectivamente,51pacientes(52ombros)comdiagnóstico deluxac¸ãorecidivanteanterior,operadospelatécnicadeLatarjet.Otempomédiode segui-mentofoide22meses,variac¸ãode12a66meses;afaixaetáriavarioude15a59anos,com médiade31;emrelac¸ãoaosexo,42(82,4%)pacienteseramdomasculinoenove(17,6%) dofeminino.Oladodominantefoiacometidoem29(55,8%)ombros.Quantoàetiologia,48 (92,3%)referiramtraumaequatro(7,6%)tiveramoprimeiroepisódioapósumquadrode convulsão.
Resultados: Asmédiasde elevac¸ão,rotac¸ãolateral erotac¸ãomedial ativasdomembro operadoforam, respectivamente,de 146◦ (60◦a 180◦),59◦ (0◦ a85◦)e T8(T5a glúteo), houvesignificânciaestatísticaquantoàdiminuic¸ãodaamplitudedemovimentoemtodos os planos, quando comparado com olado contralateral (não operado). As médias de pontuac¸ãodeRoweeUCLAforamde90,6e31,4,respectivamente,noperíodopós-operatório. Onzeombros(21,2%)apresentarammausresultados:sinaisdeinstabilidade(13,4%), pseu-doartrose(11,5%)esolturaprecocedomaterialdesíntese(1,9%).Houvecorrelac¸ãoentre mausresultadosepacientesconvulsivos(p=0,026).
Conclusão: OprocedimentodeLatarjetparacorrec¸ãodaluxac¸ãoanteriorrecidivantelevaa bonseexcelentesresultadosem82,7%doscasos.
©2014SociedadeBrasileiradeOrtopediaeTraumatologia.PublicadoporElsevier EditoraLtda.Todososdireitosreservados.
Introduction
Differentsurgicalprocedureshavebeendescribedfortreating recurrent anterior shoulder dislocation.1 The capsulolabral repairdescribedbyBankart2andmodifiedbyRoweetal.3is oneofthemaintechniquesusedtotreatthisconditionand itcanbedonearthroscopicallyorasanopenprocedure,with goodresultsfrommostpatients.1Incasesinwhichthe dis-location occursin morethan onedirectionand/orthere is anincreaseincapsulevolume,capsuloplastycanbechosen. ThistechniquewasdescribedbyNeerand Foster4 andwas subsequentlyrevisedbyBigliani.5
However,soft-tissuerepairalonedoesnotseemtobean effective procedure in all cases.6 Attempts todefine some parametersthatcouldbeusedtoguidethetypeofprocedure tobeperformedarenowbeingmade.6Fromstudying cadav-ers,Itoietal.7concludedthatbonedefectsoftheglenoidcavity greaterthan21%providetheconditionsfortheforceneeded forshoulderdislocationtobeconsiderablylower.Application ofabonegrafttosuchdefectsincreasesthestabilityofthe joint.7
Balg and Boileau6 created an instability score (ISIS) for determiningthepreoperativeriskfactorsamongpatientswith recurrentinstability, with the aimof assistingsurgeons in indicatingarthroscopic oropensurgery.According tothese authors,forpatientswithhighriskofrecurrentdislocation, transpositionofthecoracoidprocesstotheanteroinferior bor-deroftheglenoidcavityisaneffectiveoption.6Thisprocedure wasfirst describedbyLatarjet8 in1954and byHelfet9 (the authorwhonamedthetechniquetheBristowprocedure)in
1958.In1982,PatteandDebeyre10addedfurtherstabilityto theoriginaltechniquethroughusingthecoracoacromial lig-ament,whichoverlapsthejointcapsuleafterfixationofthe bonegraft.
ThefirstBrazilianauthorstopublishtheirexperienceof treating recurrent anterior shoulder dislocation using the techniqueofbonegraftingfromthecoracoidinassociation withligamentstabilizationwereGodinhoandMonteiro,11in 1993.Theseauthorsdidnothaveanycasesofrecurrenceof thedislocation,and90%ofthepatientsreturnedtotheir previ-oussportsactivities.Bessièreetal.12conductedaretrospective studyon186patientswhopresentedrecurrentpost-traumatic anterior instability. They comparedthe patients treatedby means ofBankart’sarthroscopic repairofthe injuryversus Latarjet’s operation,8 with a mean follow-up of six years, andconcludedthatthesecondgrouppresentedbetterRowe scores3andlowerratesofrecurrentinstability.12
The objective ofthis study was to evaluate the results from patients with recurrent anterior shoulder dislocation whoweretreatedusingtheLatarjettechnique,8highlighttheir complicationsandattempttocorrelatethesewiththeir pos-siblecauses.
Sample
and
methods
SurgeryGroupofourservice.Outofthistotal,51patients(52 shoulders)wereanalyzedretrospectively.
Theinclusioncriteriathatweusedwerethatthepatients neededtohaveneverundergoneanysurgerypreviouslyand tohavebeenfolloweduppostoperativelyforaminimumof oneyear.Patientswhohadundergonesomeprevious shoul-dersurgerywereexcluded,alongwiththosewhoseoutpatient follow-uphadlastedforlessthanoneyearaftertheoperation. Themeanlengthoffollow-upwas22months,witharange from12to66.Withregardtosex,42(82.4%)weremaleandnine (17.6%)werefemale.Theagerangewasfrom15to59years, withameanof31.Thedominantsidewasaffectedin29cases (55.8%).Regardingetiology,48(92.3%)reportedthattherehad beensometypeoftraumaandinfourcases,thefirstepisode hadoccurredafteraconditionofconvulsion(7.6%).
Inrelationtothesurgicalindication,43shoulders(82.7%) underwenttheprocedurebecauseofthepresenceofbone ero-sion,five(9.6%)becausethesepatientsplayedcontactsports andfour(7.7%)becausethesepatientssufferedfrom convul-sions.Inthislastgroup,threecases(5.8%)alsopresentedbone erosion.Amongthe51patientsevaluated,38(74.4%)practiced physicalactivities.Ofthese,eight(15.6%)wereprofessional sportplayers. Themean lengthoftimebetweenthe initial dislocationandthesurgerywassixyears,witharangefrom fourmonthsto40years.Thenumberofepisodesofdislocation beforethesurgeryrangedfromtwotomorethan100,witha medianof15.
All the patients underwent simple radiography of the shoulderandtheradiographicviewsusedinthepreoperative evaluationwere:frontal,correctedtoneutralrotation; apical-oblique13;axillarylateral;andWestPoint.14Axialcomputed tomography and/ormagneticresonance imaging were also performed.
Inrelationtothesurgicaltechniqueused,allthepatients underwenttheiroperationsinthedeckchairpositionandthe accessrouteusedwasabovethecoracoidprocess,extending tothedeltopectoralspacebyaround5cm.Thecoracoid pro-cesswasosteotomized1.5–2cmfromitstip,attheoriginofthe conjoinedtendon.Agraftwaspreparedsuchthatitsconvexity wasplaneddownandbloodiedforadaptationtotheglenoid border.Thiswasthentransferredbymeansofthesubscapular muscle(openedlongitudinallybetweenitsuppertwothirds andthelowerthird)andthejointcapsule(openedvertically). Inthismanner,thegraftwassupportedalongitsmajoraxis, attheanteroinferiorborderoftheglenoid,whichwas previ-ouslypreparedthroughresectionofthelabrum(orwhatwas leftofit)anddecorticationoftheglenoid borderandneck. Thegraftwasfixedusingtwoscrewsthatwereparalleltothe
jointsurfaceandanchoredintheposteriorcorticalboneof thescapularneck,thuspromotingcompressionbetweenthe fragments.15Thecoracoacromialligamentwaspreservedat thecoracoidandwassuturedatthemedialbandofthejoint capsule.10Asuctiondrainwasleftinplacefor48hafterthe operation.Regardingthetypeofimplantused,thegraftwas fixedusingsmall-fragmentscrews.
Afterthesurgery,thepatientswereimmobilizedbymeans ofacushionedslinginordertokeepthelimbinapositionof neutralrotationforsixweeksoruntilboneconsolidationhad beenverified.Duringthisperiod,thepatientswereinstructed toperformpassivelateralrotationexercises,whichbeganon thefirstpostoperativeday.
The patients underwent postoperative evaluations by means ofsimple radiographs produced one, three and six weeksaftertheoperation.Iftherewereanydoubtsregarding the consolidation or the position of the graft, computed tomographywasperformed.
Shoulder range of motion was measured bilaterally in accordance with the criteria ofthe American Academyof OrthopedicSurgeons (AAOS).16 The functionalresults were evaluatedclinicallybymeansofRowe’scriteria3andthe mod-ifiedversionofthescoringsystemproposedbytheUniversity ofCaliforniaatLosAngeles(UCLA).17Thepatientswereasked abouttheirreturntosports,inthecaseofpractitioners.
Thedatawereorganizedanddescriptiveanalysiswas per-formedbymeansofconstructingfrequencytablesandgraphs andcalculatingcentraltrendandvariabilitymeasurements.
Inthestatisticalanalysis,weused95%confidenceintervals andthesignificancelevelof0.05(p<0.05).Whennecessary,we usedStudent’sttestforpaireddata(totestthedifferencesin measurementsbetweentheoperatedandcontralateralsides) andthenonparametricMann–Whitneytest(tocomparethe meanresultsbetweenthegroupswithgoodandpoorresults). Totestwhethertherewasindependencebetweenpairsof vari-ables,Fisher’sexacttestwasused.
Thisstudywasapprovedbythehospital’sethicscommittee underCAAEnumber22949213.3.0000.5479.
Results
Inrelationtoshouldermobility,weobservedthatthemean activeelevation, lateralrotationand medialrotationofthe operatedlimbwerelessthanthoseofthecontralaterallimb (whichhadnotbeenoperated)andthatthereductioninrange ofmotionwasstatisticallysignificantinallplanes.These val-uescanbeseeninTable1.
Table1–Rangeofmotionoftheoperatedandcontralateralshoulders.
Movement Mean Standarddeviation Minimum Maximum Significance(p)
A B A B A B A B
Elevation 146 151 18.91 11.95 60 110 180 180 0.019
Medialrotation 8 7 2.41 1.83 Gluteus T12 T5 T5 0.001
Lateralrotation 59 63 18.49 10.49 0 30 85 85 0.048
Source:thehospital’smedicalandstatisticalfiles.
Table2–ResultsfromRoweandUCLAscores.
Rowe n UCLA n Result
Excellent 78.8% 41 75% 39 Satisfactory
Good 3.8% 2 7.7% 4
Fair 11.5% 6 7.7% 4 Unsatisfactory
Poor 5.8% 3 9.6% 5
Source:thehospital’smedicalandstatisticalfiles.
n,absolutenumberofshoulders.
Table3–Detailingofthefindingsfrompatientswith poorresults.
Findingfromphysicalor radiographicexamination
Percentage(%) n
Limitationonlateralrotation 7.69 4
Pain 17.31 9
Positiveapprehensiontest 11.54 6
Pseudarthrosis 11.54 6
Recurrence 3.85 2
Total 21.15 11
Source:thehospital’smedicalandstatisticalfiles.
n,absolutenumberofshouldersthatpresentedcomplications.
ThemeanpostoperativescoresfromtheRowe3andUCLA17 functional evaluations were 90.6 (range: 30–100) and 31.4 (range:8–35),respectively.BoththroughtheUCLAscore17and throughtheRowescore,3nineshoulders(17.3%)were classi-fiedaspresentingunsatisfactoryresults(fairand poor)and 43(82.7%) assatisfactory(good and excellent). However,in comparingthefourpossibleoutcomes(excellent, good,fair andpoor)usingthesetwomethods,therewasvariationinthe numberofshouldersclassifiedintheexcellentandgood sub-groups,andlikewiseinthefairandpoorsubgroups(Table2).
Amongthepatientspresentingconvulsions,therewasa statisticallysignificant correlation between convulsion and poorresults/complications(p=0.026).
Wedidnotfindanystatisticallysignificantcorrelationfor thevarianceinthetimethatelapsedbetweenthefirstepisode
of dislocation and the surgery in relation to poor results (p=0.729),orforthenumberofepisodesofdislocationin rela-tiontopoorresults(p=0.663).Thepatientswhoweresports participantswhoseresultsweresatisfactoryand unsatisfac-torydidnotshowanycorrelationwiththepatientswhodid notpracticesports(p=0.180).Sex,ageanddominancedidnot showanycorrelationwiththeoutcomesfromthecases.
Amongthe38patientswhopracticedsports(73.1%ofthe total), six did not return to their previous sports practice, amongwhomonewasaprofessionalsportsplayer.
Eleven shoulders(21.2%)presented poorresults.Among these,seven(13.4%)remainedunstable:two(3.8%)hadnew episodes of dislocation and five (9.6%) presented positive apprehensiontests,amongwhomthreeevolvedwith associ-atedpseudarthrosisofthecoracoidprocess.Therewerefour casesofcomplications(7.7%):threepresenting pseudarthro-sis without instability (5.8%) and onewith early loosening ofthesynthesismaterial(1.9%),15daysaftertheoperation (Tables3and4).
Discussion
In our sample, limitation ofthe range ofmotionoccurred inall:5◦ ofelevation,4◦oflateralrotationandonevertebra
ofmedialrotation.Despitepresentingstatisticalsignificance, thedecreaseinmobilitywasveryslight.Ikemotoetal.18 evalu-ated26patientswithameanlengthoffollow-upof38months and also observedthat there waslimitation of mobilityin theoperatedshoulderinallplanes,butmoremarkedlysoin
Table4–Correlationbetweentheclinicalandradiographicfindingsfromthepatientswithpoorresults.
Case Clinicalfindings Radiographicfindings
Pain LimitationonLR Apprehension+ Recurrence Pseudarthrosis Graftposition Screw
1 X X C S+L
2 X X X M S
3 X X C C
4 X X X X I C
5 X X M S+L
6 X X X M S+L
7 X M+I C
8 X X X X I S+B
9 X X X C C
10 X X C C
11 X C B
Source:thehospital’smedicalandstatisticalfiles.
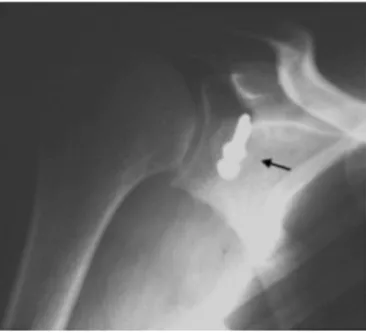
Fig.1–Radiographofashoulderinlateralscapularview showingbreakageofsynthesismaterial(arrow).
relation to movements of lateral rotation. Godinho and Monteiro11hadalargernumberofpatientswithlossofmedial rotation(13outof40),whilelateralrotationwaslimitedinonly 11patients,withameanof14.1◦.Ontheotherhand,Hovelius
etal.19 observedinaprospectivestudyon112patientsthat therewasalossoflateralrotationoverafollow-upperiodof twotofiveyears,withlossesof19◦ inadductionand21◦ in
abduction.19
Schroder etal.20 reported good andexcellent functional and stability results from their retrospective study on the Latarjetprocedure8basedontheRowescore.3Themeanwas 81.8among52patients,amongwhom36wereconsideredto beexcellent,fivefairand11poor,20i.e.30.7%oftheresults wereunsatisfactory.Inourstudy,wefoundthatninepatients (17.3%) had results that were considered tobe unsatisfac-tory(fair/poor),basedontheRowescore3andUCLAscore17 (Table2).
Wefollowedupfourpatientswithepilepsy(7.7%ofthetotal numberofshoulders)inourstudyandobservedthattherewas astatisticallysignificantcorrelationbetweenpresenceof con-vulsionsandpoorresults/complications(p=0.026).Theonly patientwhoseconvulsiveconditionwaswellcontrolledhad anexcellentresult.Therewasonecaseofsurgicalrevision, ninemonthsaftertheoperation,inapatient whosuffered fracturingofthegraftandbreakageofthesynthesismaterial (Fig.1),afteranewconvulsiveepisode.Thesedataareinline withwhatwefoundintheliterature.Raissetal.21publisheda studyinwhich14shouldersin12patientswithepilepsywho hadundergonetheLatarjetprocedure8 wereretrospectively evaluated.Theyobservedthatdislocationrecurredin43%of
Fig.2–Anteroposteriorradiographofarightshoulder showingmedializedgraft(arrow).
the cases,asdidChecchiaetal.,22 whofoundarecurrence rateof42%whenstudyingtechniquesfortreatingrecurrent anterior shoulderdislocation inepileptic patients. The lat-terauthorsattributedthepoorresulttopoorclinicalcontrol overtheconvulsivecrises.Raissetal.21consideredthatonly patientspresentinggoodcontrolfromaneurologicalpointof viewwhosufferrecurrentdislocationduringday-to-day activ-itiesshould undergothe Latarjetprocedure,8 andweagree withthisview.
Wefoundarecurrencerateforepisodesofdislocationof 3.8%(twocases).Oneofthesecasesinvolvedapatientwith poorlycontrolledepilepsywhohadnineepisodesof disloca-tionandtheotherwasapatientwhosufferedacaraccident (rollover)inthefourthmonthafterthesurgeryandevolved withaconditionofinstabilityaftertheincident.
Inasystematicreviewon1904shoulders,Griesseretal.23 foundarecurrencerateof2.9%.23Lädermannetal.24reported a recurrent dislocationrate of1.7%in theirsample of117 shouldersandfoundthat3.4%persistedwithapositive appre-hensiontest.24Inourstudy,fivepatients(9.6%)evolvedwith a positive apprehension test. In one of these cases, there were no objective findings that would explain this result and webelievethatthis wasacasemotivatedtoward sec-ondarygains(timeoffworkorfinancialbenefits).Anothercase involvedapatientwithseverepsychiatricproblemsand dif-ficultsubjectiveinterpretationoftheclinicalexamination.In theotherthreepatients,thepositiveapprehensiontestswere associatedwithpseudarthrosis,andtheresultswere unsatis-factory.Weattributedthesefailurestopoorgraftpositioning (Figs.2–4),sincethegraftswerebelowtheiridealposition.In twopatientsandinthethirdcase,thegraftwasmedialized andthescrewswerenotreachingbothcorticallayersofthe glenoidbone.Thesepatientsunderwentsurgicalrevision.
Fig.3–Radiographofashoulderinaxillaryviewduring theimmediatepostoperativeperiod,showingscrewsthat didnotreachthesecondcorticallayer(arrow).
Thetotal pseudarthrosisrate observedamongthe cases evaluated in our study was 11.5%, corresponding to six shoulders.Threeofthesecasesalsopresentedpositive appre-hension test and were discussed earlier.Among the other threepatientswithpseudarthrosis(5.8%),therewasonecase inwhichalthoughnon-consolidationofthegraftwasevident, thisdidnotinfluencethepatient’sdailyactivities.Thispatient refusedtoundergothe revisionprocedure.Hisresultsfrom theUCLA17andRowe3functionalevaluationswere24and80, respectively.Theothertwocaseswereduetotechnicalfailure: oneevolvedwith UCLA17 and Rowe3 of 12and 65, respec-tively,withmajorlimitationsondailyactivities.Onreviewing
Fig.4–Radiographofashoulderinaxillaryviewshowing pseudarthrosisofthegraft(arrow).
thispatient’sradiographicexaminations,weobserved medi-alization ofthegraft and screwsonlypassingthroughone ofthe corticalbone layers.Oneofthese screwsbroke and theother becameloose28 monthsaftertheoperation,and this patientunderwentsurgicalrevision.Theother patient, whodidnotpresentanyepisodesofrecurrentshoulder dis-location,wasnotreviewedbecausehediedduetoexternal causes.
In a retrospective study, Walch and Boileau15 found a pseudarthrosisrateof2.4%andcorrelatedthecauseofthis complication to the positioning of the screws, which only passed through one cortical layer. However, they did not findthatthiscomplicationinfluencedthefinalevaluation.In thissamestudy,inwhichthetechniquewasdescribed,the
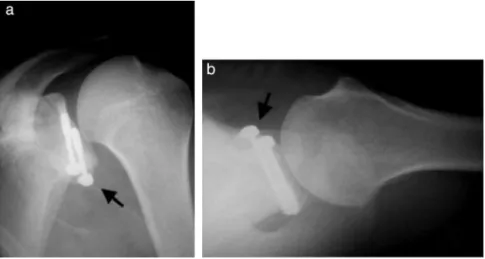
Fig.6–Radiographsofaleftshoulderin(a)anteroposteriorviewand(b)axillaryview,showinggoodpositioningofthegraft (arrows).
authorsrecommendedthatthescrewsshouldpassthrough bothcorticallayersandthatthegraft shouldbepositioned very cautiously, with the limb rotated internally so as to acceptslightlymedialpositioningofamaximumofafew mil-limeters andavoidthe lateral border ofthe glenoid.These authorsstatedthatdrillingshouldbeperformedinaplane parallel to the joint surface.15 We agree that this is the best position for the graft and screws (Figs. 5 and 6) and highlight that the glenoid cavity presents anteversion of around 30–40◦ and that the graft should notadvance into
thejointbut,rather,shouldformacontinuationofthejoint surface.
Oneofthecasesevolvedwithearlylooseningofthe syn-thesismaterialduringthefirsttwoweeksaftertheoperation, andthispatientunderwentanewsurgicalprocedureinorder tofixthecoracoidagain.Thehypothesisofaninfectious pro-cesswasruledout.Fromanalysisontheradiographicimages, weconcludedthattherehadbeenatechnicalfailure,sincethe grafthadremainedinalowandmedializedposition,which wastheprobablecauseofthisloosening.
Griesseretal.23reportedacomplicationrateof30%,caused by recurrences, neurovascular lesions, hematomas, infec-tions,pseudarthrosisofthegraftandmovementlimitations.23 Wedidnothaveanycasesofneurovascularlesion,hematoma orinfection.
Thisstudyhassomelimitationssuchasitsretrospective natureand itsminimum follow-upofonlyoneyear. Alter-ations like arthrosis (which has been described as one of the complications of the Latarjet procedure)8 need longer postoperativeperiodsforthemtobecomevisibleon radio-graphs. Inorder toreach a conclusionofgreater precision regardingtheevolutionofepilepticpatients,webelievethat alargersamplewouldbeneeded,despitetheverysuggestive resultsobtainedregardingtherelationshipbetween convul-sionsandpoorresults.Ontheotherhand,thepositivepoints of our study are that its sample was very suitable, with enoughpatientswithveryuniformepidemiological character-isticswhounderwentoperationsinexactlythesamemanner, thereby eliminating variables that could have altered our results.
Conclusions
TheLatarjetprocedureforcorrectingrecurrentanterior shoul-derdislocationledtogoodandexcellentresultsin82.7%ofthe cases.Thecomplicationsobservedwererelatedtotechnical errors.
Conflicts
of
interest
Theauthorsdeclarenoconflictsofinterest.
r
e
f
e
r
e
n
c
e
s
1.EmamiMJ,SolookiS,MeshksariZ,VosoughiAR.Theeffectof openBristow–Latarjetprocedureforanteriorshoulder instability:a10-yearstudy.MusculoskeletSurg. 2011;95(3):231–5.
2.BankartAS.Thepathologyandtreatmentofrecurrent dislocationoftheshoulderjoint.BrJSurg.1938;26:23–9. 3.RoweCR,PatelD,SouthmaydWW.TheBankartprocedure:a
long-termend-resultstudy.JBoneJointSurgAm. 1978;60(1):1–16.
4.NeerCS,FosterCR.Inferiorcapsularshiftforinvoluntary inferiorandmultidirectionalinstabilityoftheshoulder:a preliminaryreport.JBoneJointSurgAm.1980;62(6):897–908. 5.BiglianiLU.Anteriorandposteriorcapsularshiftfor
multidirectionalinstability.TechOrthop.1989;3:36–45. 6.BalgF,BoileauP.Theinstabilityseverityindexscore.Asimple
pre-operativescoretoselectpatientsforarthroscopicoropen shoulderstabilization.JBoneJointSurgBr.2007;89(11):1470–7. 7.ItoiE,LeeSB,BerglundLJ,BergeLL,AnKN.Theeffectofa
glenoiddefectonanteroinferiorstabilityoftheshoulderafter Bankartrepair:acadavericstudy.JBoneJointSurgAm. 2000;82(1):35–46.
8.LatarjetM.Treatmentofrecurrentdislocationofthe shoulder.LyonChir.1954;49(8):994–7.
9.HelfetAJ.Coracoidtransplantationforrecurringdislocation oftheshoulder.JBoneJointSurgBr.1958;40(2):198–202. 10.PatteD,DebeyreJ.Luxationsrecivatesdel’épaule.EneyelMed
11.GodinhoGG,MonteiroPC.Tratamentocirúrgicoda
instabilidadeanteriordoombropelatécnicadeDidier-Patte. RevBrasOrtop.1993;28(9):640–4.
12.BessièreC,TrojaniC,CarlesM,MehtaSS,BoileauP.Theopen Latarjetprocedureismorereliableintermsofshoulder stabilitythanarthroscopicBankartrepair.ClinOrthopRelat Res.2014;472(8):2345–51.
13.GarthWP,SlappeyCE,OchsCW.Roentgenographic demonstrationofinstabilityoftheshoulder:theapical obliqueprojection.JBoneJointSurgAm.1984;66(9):1450–3. 14.RokousJR,FeaginJA,AbbottHG.Modifiedaxillary
roentgenogram.ClinOrthop.1972;82:84–6.
15.WalchG,BoileauP.Latarjet–Bristowprocedureforrecurrent anteriorinstabilitytechniques.TechShoulderElbowSurg. 2000;1(4):256–61.
16.HawkinsRJ,BokosDJ.Clinicalevaluationofshoulder problems.In:RockwoodCAJr,MatsenFA3rd,HirakiA, editors.Theshoulder.2nded.Philadelphia:Saunders;1998.p. 175–80.
17.EllmanH,KaySP.Arthroscopicsubacromialdecompression forchronicimpingement.Two-tofive-yearresults.JBone JointSurgBr.1991;73(3):395–8.
18.IkemotoRY,MurachoviskyJ,NascimentoLP,BuenoRS, AlmeidaLO,StroseE,etal.ResultadosdacirurgiadeLatarjet notratamentodainstabilidadeanteriortraumáticadoombro associadaàerosãoósseadacavidadeglenoidal–Seguimento mínimodeumano.RevBrasOrtop.2011;46(5):553–60. 19.HoveliusL,AkermarkC,AlbrektssonB,BergE,KörnerL,
LundbergB,etal.Bristow–Latarjetprocedureforrecurrent
anteriordislocationoftheshoulder.A2-5yearfollow-up studyontheresultsof112cases.ActaOrthopScand. 1983;54(2):284–90.
20.SchroderDT,ProvencherMT,MologneTS,MuldoonMP,Cox JS.ThemodifiedBristowprocedureforanteriorshoulder instability:26-yearoutcomesinNavalAcademymidshipmen. AmJSportsMed.2006;34(5):778–86.
21.RaissP,LinA,MizunoN,MelisB,WalchG.Resultsofthe Latarjetprocedureforrecurrentanteriordislocationofthe shoulderinpatientswithepilepsy.JBoneJointSurgBr. 2012;94(9):1260–4.
22.ChecchiaSL,DoneuxPS,MiyazakiAN,LeiteAFM,Simmer FilhoJ,MenezesMVC.Tratamentociru´rgicodaluxac¸a˜o recidivanteanteriordoombroempacientesconvulsivos.Rev BrasOrtop.2000;35(9):340–6.
23.GriesserMJ,HarrisJD,McCoyBW,HussainWM,JonesMH, BishopJY,etal.Complicationsandre-operationsafter Bristow–Latarjetshoulderstabilization:asystematicreview.J ShoulderElbowSurg.2013;22(2):286–92.
24.LädermannA,LubbekeA,SternR,CunninghamG,BellottiV, GaziellyDF.Riskfactorsfordislocationarthropathyafter Latarjetprocedure:along-termstudy.IntOrthop. 2013;37(6):1093–8.