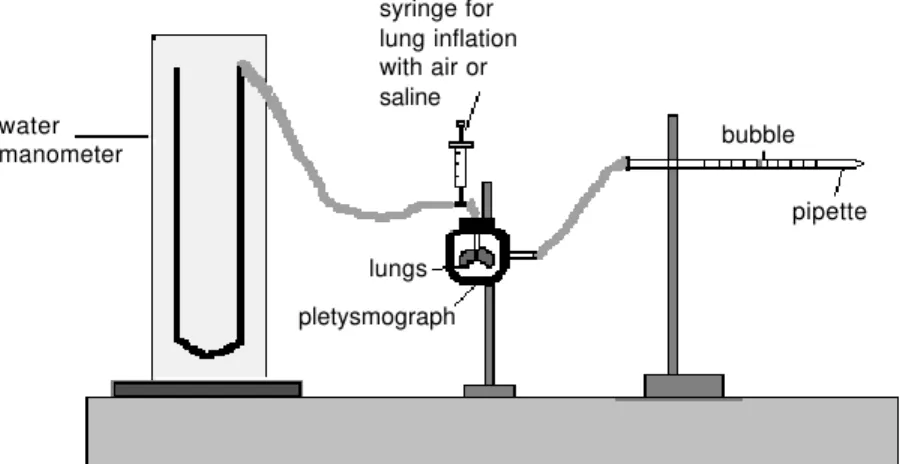
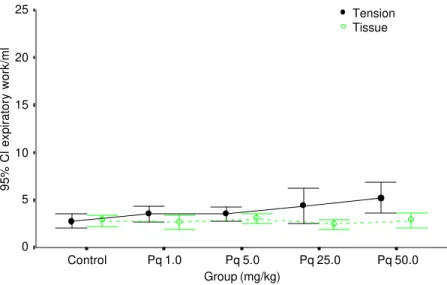
Paraquat poisoning: an experimental model of dose-dependent acute lung injury due to surfactant dysfunction
Texto
Imagem

Documentos relacionados
Our objective in the present study was to establish the first experimental model of hemolysis-induced acute pancreatitis and to assess the factors that trigger acute pancre- atitis
Chart 1 - Experimental studies on the efects of hypercapnic acidosis in acute pulmonary injury and ventilator-induced lung injury.. Animal
According to the present findings, the adverse effects of corticoids seem to follow a dose–dependent relationship, given that although treating the animals with a dose of 0.6
Objective: To evaluate the stability of hemodynamic, respiratory and gas exchange variables in an animal model of oleic acid-induced acute lung injury.. Methods: This was
Objective: To evaluate the stability of hemodynamic, respiratory and gas exchange variables in an animal model of oleic acid-induced acute lung injury.. Methods: This was
Integrated risk assessment of the evolution and emergence of antibiotic resistance in the environment addresses two main issues: first, the potential of subinhibitory
The results showed a possible dose-dependent analgesic effect of vigabatrin (gamma-vinyl- GABA) on experimental neuropathic pain, as shown by the significant (p<0.05)
In the present study, in order to de- termine hematological alterations caused by ranitidine, we administered the drug in concentrations of 100 mg/kg (single dose) and of 50