RevBrasAnestesiol.2017;67(1):107---109
REVISTA
BRASILEIRA
DE
ANESTESIOLOGIA
PublicaçãoOficialdaSociedadeBrasileiradeAnestesiologiawww.sba.com.br
CLINICAL
INFORMATION
Quadratus
lumborum
block
in
chronic
pain
after
abdominal
hernia
repair:
case
report
Rita
Carvalho
∗,
Elena
Segura,
Maria
do
Céu
Loureiro,
José
Pedro
Assunc
¸ão
CentroHospitalarTondela-Viseu,Servic¸odeAnestesiologia,Viseu,Portugal
Received23July2014;accepted26August2014 Availableonline11November2016
KEYWORDS
Pain; Chronic; Neuropathic;
Quadratus lumborum; Ultrasonography
Abstract
Backgroundandobjectives: ThequadratuslumborumblockadewasdescribedbyR.Blancoin itstwoapproaches(IandII).Thelocalanestheticdepositioninthislocationcanprovideblockade
toT6-L1dermatomes.Weperformedthisfasciablockadeguidedbyultrasoundfortreatinga chronicneuropathicpainintheabdominalwall.
Casereport: Malepatient,61yearsold,83kg,withahistoryofthrombocytopeniadueto alco-holiccirrhosis,amongothers;hadchronicpainintheabdominalwallaftermultipleabdominal herniarepairsinthelastyearandahalf,withpoorresponsetotreatmentwith neuromodula-torsandopioids.Onclinicalexamination,herevealedaneuropathicpain,withprevalenceof allodyniatotouch,coveringtheentireanteriorabdominalwall,fromT7toT12dermatomes. WeoptedforaquadratuslumborumblocktypeII,guidedbyultrasound,withadministrationof
0.2%ropivacaine(25mL)anddepot(vial)methylprednisolone(20mg)oneachside.The proce-duregaveimmediatereliefofsymptomsand,aftersixmonths,thepatientstillhadasignificant reductioninallodyniawithoutcompromisingthequalityoflife.
Conclusions: WeconsiderthatperformingthequadratuslumborumblocktypeIIwasan
impor-tantanalgesicoptioninthetreatmentofapatientwithchronicpainafterabdominalhernia repair,emphasizingtheeffectsoflocalanestheticspreadtothethoracicparavertebralspace. Thetechniquehasproventobesafeandwelltolerated.Thepublicationofmoreclinicalcases reportingtheeffectivenessofthisblockadeforchronicpainisdesirable.
©2014SociedadeBrasileiradeAnestesiologia.Publishedby ElsevierEditoraLtda.Thisisan openaccessarticleundertheCCBY-NC-NDlicense( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
∗Correspondingauthor.
E-mail:ritasfcarvalho@hotmail.com(R.Carvalho).
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bjane.2014.08.010
0104-0014/©2014SociedadeBrasileiradeAnestesiologia.PublishedbyElsevierEditoraLtda.ThisisanopenaccessarticleundertheCC
108 R.Carvalhoetal.
PALAVRAS-CHAVE
Dor; Crônica; Neuropática;
Quadradolombar;
Ultrassonografia
Bloqueiodoquadradolombaremdorcrônicapós-hernioplastiaabdominal:relatode caso
Resumo
Justificativaeobjetivos: ObloqueiodafásciadomúsculoquadradolombarfoidescritoporR. Blanconassuasduasabordagens(IeII).Adeposic¸ãodeanestésicolocalnessalocalizac¸ãopode
conferirbloqueiodosdermátomosT6-L1.Osautoresfizeram essebloqueiodefáscia,guiado porultrassom,paratratamentodeumadorcrônicaneuropáticadaparedeabdominal.
Relatodecaso:Pacientedogêneromasculino,61anos,83kg,comantecedentesde tromboci-topeniaporhepatopatiaalcoólica,entreoutros,apresentavadorcrônicadaparedeabdominal apóshernioplastiasabdominaismúltiplashaviaumanoemeio,commárespostaaotratamento comneuromoduladoreseopioides.Noexameclínico,apresentavaumadorneuropática,com predomínio dealodiniaao toque, queabrangiatodaaparedeabdominal anterior,desdeos dermátomosT7aT12.Optou-se pelarealizac¸ãodeum bloqueiodoquadradolombartipoII
bilateral,guiadoporultrassom,comadministrac¸ãode25mLderopivacaína0,2%e20mgde metilprednisolonadepot(ampola)emcadaumdoslados.Oprocedimentoconferiualívio imedi-atodasintomatologiae,apósseismeses,opacientemantinhareduc¸ãosignificativadaalodinia, semcompromissodaqualidadedevida.
Conclusões:Os autores consideramque a realizac¸ão dobloqueio do quadrado lombartipo
II foiuma opc¸ão analgésicarelevante no tratamentode um paciente com dorcrônica
pós-hernioplastiaabdominalesalientaramosefeitosdadispersãodoanestésicolocalatéoespac¸o paravertebraltorácico.Atécnicamostrouserseguraebemtolerada.Édesejávelapublicac¸ão demaiscasosclínicosquereproduzamaeficáciadessebloqueionocontextodedorcrônica. ©2014SociedadeBrasileiradeAnestesiologia.PublicadoporElsevierEditoraLtda.Este ´eum artigoOpen Accesssobumalicenc¸aCCBY-NC-ND( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
Introduction
Describedby A. Blanco,1 the block of fasciaplane of the quadratus lumborum muscle provides unilateral blockade oftheabdominalwall,whichmayextendfromT6toL1.2,3 Quadratuslumborummuscleisinsertedintotheloweredge of the last rib and, by four tendons, into the apices of the transverse processes of the vertebrae L1 to L4. The local anesthetic deposited in this muscle fascia can be transportedalongituntiltheparavertebralspaceandalso throughthevascular-nervousrolls,2providingtheblockade
ofthereferreddermatomes.
WereportacaseofatypeIIbilateralblockofquadratus lumborumforthemanagementofapostoperativechronic pain.
Case
report
Malepatient,61 yearsold,83kg, referred tothe Chronic Pain Unit for chronic due to abdominalwall chronic pain aftermultipleabdominalhernioplasties.Hehadahistoryof diabetesmellitustype2,hypertension,duodenalulcer post-perforationstatus,alcoholicliverdisease,andconsequent thrombocytopenia(79.109/L).
Thepatienthadundergonefourabdominalwallsurgeries for abdominalwallrepair withesophagealstent.The last procedure wasmade a year anda half before. He devel-opedachronicneuropathicpainafterthethirdsurgery,with poorresponsetotreatment withopioid and neuromodula-tordrugs. The abnormalliverfunction andintolerance to
analgesicsconstitutedalimitationtotheincreasein thera-peuticdoses.
Thepatienthadaneuropathicpain,withprevalenceof allodyniatotouch,coveringtheentire anteriorabdominal wall fromT7toT12dermatomes,laterallylimitedby the anterioraxillary line. His scoreonthe visualanalog scale (VAS) was8/10 and9/10 in the specific questionnairefor neuropathic painscreening(DN4),withgreatinterference inqualityoflife.
Duetothepooranalgesicresponse,limitedbydrug toxic-ityandassociatedlivermorbidity,itwasdecidedtoperform a type II bilateral block of quadratus lumborum muscle guidedbyultrasound,afterobtainingthewritteninformed consentofthepatient.
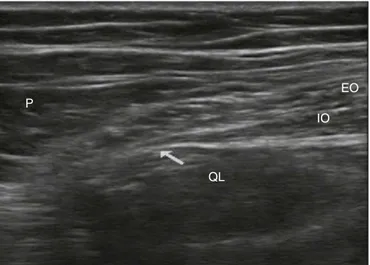
The technique was performed in the supine position, with elevation of the ipsilateral pelvis. Under aseptic conditions, a high frequency probe was used (5---10MHz), connected toan ultrasound unit in transverse orientation between the iliac crest and the costal margin, after the mid-clavicularline.Themuscleplaneswereidentified sub-sequentlyscanneduntilvisualizingthequadratuslumborum
muscle,at thesameplaneasthe psoasmajormuscleand theerectorspinae(Fig.1).
A100mmneurostimulation needlewasintroduced out-sidetheultrasoundplan,andsubcutaneousinfiltrationwas performed with2% lidocaine(3mL) guidedby ultrasound. Theneedletipwaspositionedbetweentherearfaceofthe
Quadratuslumborumblockinchronicpainafterabdominalherniarepair 109
P
QL
IO EO
Figure1 Ultrasoundofthelumbarsquareapproachtype II (describedbyR.Blanco).EO,externalobliquemuscle;IO, inter-nalobliquemuscle;QL,quadratuslumborummuscle;P,psoas majormuscle;arrow,injectionsite.
ropivacaine (25mL) and depot (vial) methylprednisolone (20mg)wereinjected,withvisualizationofthelocal anes-theticspreadintotheparavertebralspace.
The procedure was repeated in the other side with-outincidentorcomplications.Duringtheprocedure,verbal
contact was maintained with the patient, who never
expresseddiscomfort.
Sixty minutes after the procedure, the patient was asymptomatic,withoutallodyniathroughouttheabdominal wall,withaVASscoreof0/10forpainatrestandinmotion. He was dischargedfrom the hospital twohours after the procedureandreportedgreatsatisfactionwiththe manage-mentofhispain.
Evaluated five days after the procedure, the patient remainedasymptomatic,reportingonlyasenseofpressure ononesideoftheinjection,notperceivable.
At the first month of the procedure, the patient had theallodynia restrictedtoa limitedperiumbilical areaof approximately a quarter of the starting area and a VAS scoreof2/10atrestandof6/10inmotion.Becauseofthe underlyingthrombocytopenia,itwasdecidednottorepeat theblockadeandschedulealocaltreatmentwithcapsaicin 8%patch.
At the six months of the procedure and after a local treatmentwithcapsaicin8%patch,theallodyniaremained restricted tothe periumbilical area, with a VAS score of
3---4/10 at rest and in motion, and returned to his daily activitywithquality.
Conclusions
Tothebestofourknowledge,thisisthefirstpublishedcase ofaquadratuslumborummuscletypeIIblockadeguidedby ultrasoundforpostsurgicalchronicpain.
Weconsiderthatthequadratuslumborummuscletype IIblockadeisarelevantanalgesicoption inthetreatment ofpatientswithchronicpainafterabdominalherniarepair, refractorytoconventionaltreatment.
Thelocalanestheticandadjuvantanalgesicspreadtothe thoracic paravertebral space was essential for the symp-tomatic relief in this patient.1 The follow-up after the
procedureledtotheconclusionthatthisisasafeand well-toleratedtechniquewithirrelevantsideeffects.Itsclinical utilitywaslimited bythe hematologiccontingency of the patient to perform invasive therapeutic techniques. The authorssubsequentlyoptedforanothertherapeuticoption ofneuropathicpain,suchas8%capsaicin.4
We considernecessary thepublication ofmore clinical casesthatreproducetheanalgesicefficacyofthisblockade inthecontextofchronicpain.5,6
Conflicts
of
interest
Theauthorsdeclarenoconflictsofinterest.
References
1.BlancoR.Optimalpointofinjection:thequadratuslumborum
typeIandIIblocks.Anaesthesia.2014.
2.Visoiu M,Yakovleva N.Continuous postoperativeanalgesiavia
quadratuslumborumblock---analternativetotransversus abdo-minisplaneblock.PediatrAnesth.2013;23:959---61.
3.KadamVR. Ultrasound-guidedquadratuslumborum blockasa postoperativeanalgesictechniqueforlaparotomy.JAnaesthesiol ClinPharmacol.2013;29:550---2.
4.Dworkin R, O’Connor A, Audette J, et al. Recommendations for the pharmacological management of neuropathic pain: an overview and literature update. Mayo Clin Proc. 2010;85 Suppl.:S3---14.
5.CarneyJ, FinnertyO, RaufJ, etal. Studies onthespreadof localanaestheticsolutionintransversusabdominisplaneblocks. Anaesthesia.2011;66:1023---30.