Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Sympathectomy for Palmar Hyperhidrosis: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.
Texto
Imagem
Documentos relacionados
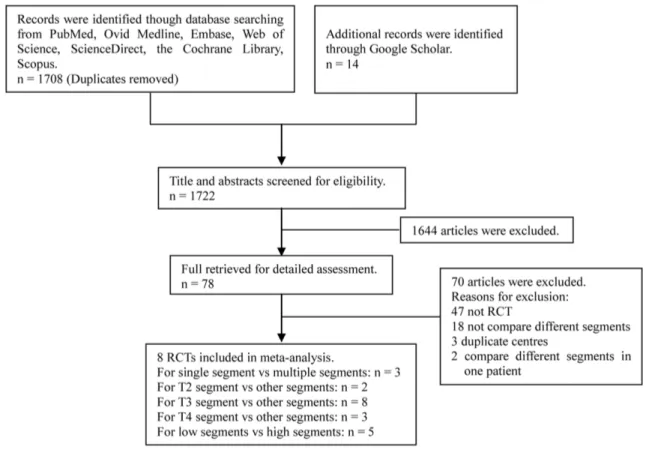
Studies included in the meta-analysis satisfied the following criteria: (i) randomized controlled trials were limited to human subjects; (ii) patients were individuals undergoing
These studies included exclusively double- blinded randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of adult patients with established type 1 diabetes who received a long-acting insulin
The most recent published meta-analysis examined randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comprising a total of 8,961 patients and showed that off-pump coronary artery bypass
The review included randomized controlled trials with patients during the immediate postoperative period of cardiac surgery, which compared the use of noninvasive ventilation,
Med database, using the following Mesh and Entry terms : (((Randomized controlled trial[pt] OR controlled clinical trial[pt] OR randomized controlled trials[mh] OR
Only randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that compared the effects of strength training to no exercise in terms of reducing pain among PFPS sufferers were included..
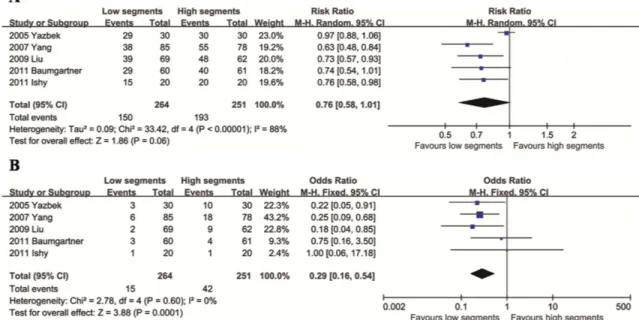
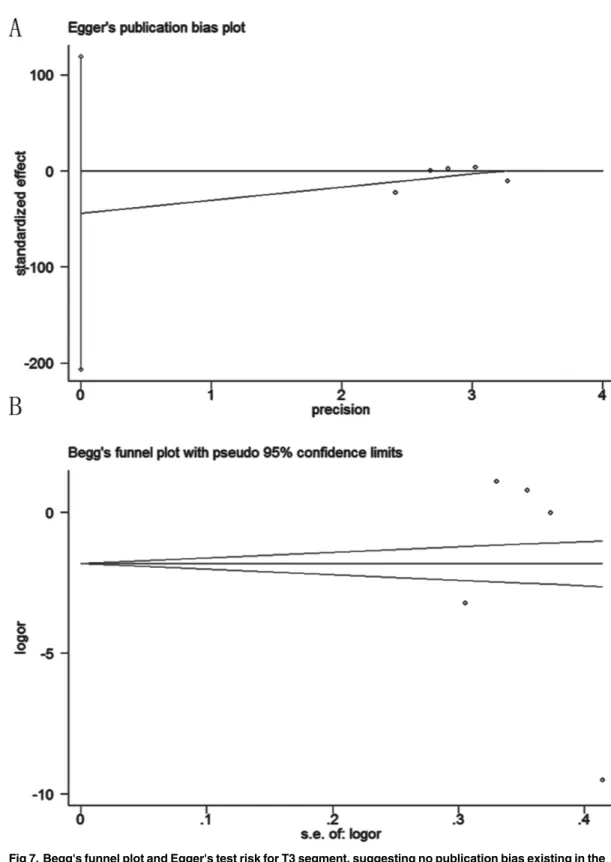
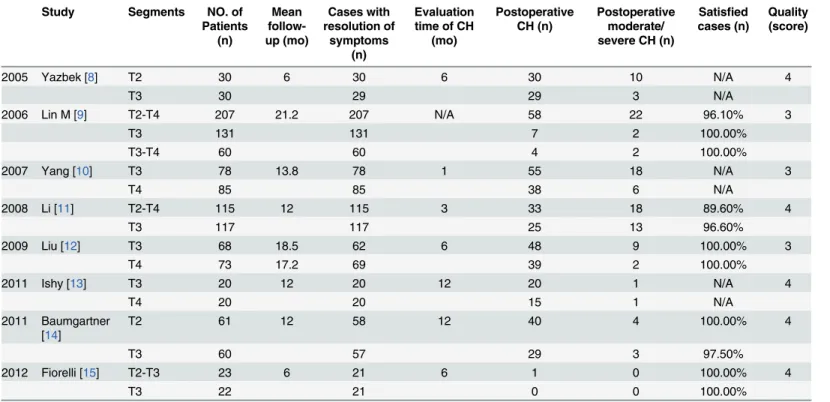
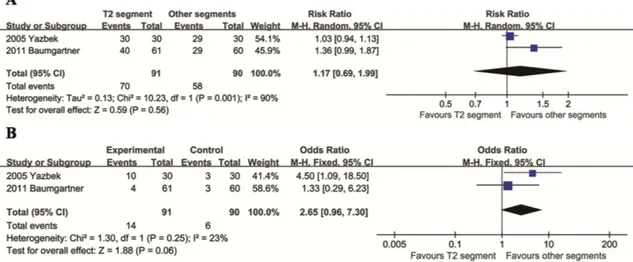
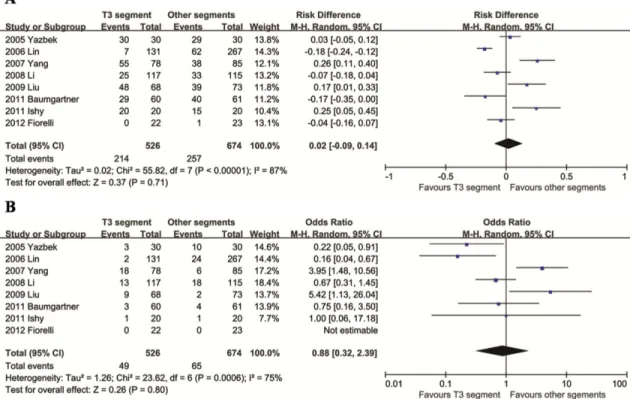
CONCLUSION: Patients with palmar hyperhidrosis and plantar hyperhidrosis who underwent video-assisted thoracic sympathectomy to treat their palmar hyperhidrosis exhibited good
Abbreviation: n/a: not available; MA: meta-analysis; ADR: adverse reaction; randomized placebo-controlled trials; RPCTs: randomized placebo-controlled trials; RCCTs: randomized