FORAGING BEHAVIOR OF BEE POLLINATORS ON THE TROPICAL WEED Triumfetta semitriloba: FLIGHT DISTANCE AND DIRECTIONALITY
Texto
Imagem
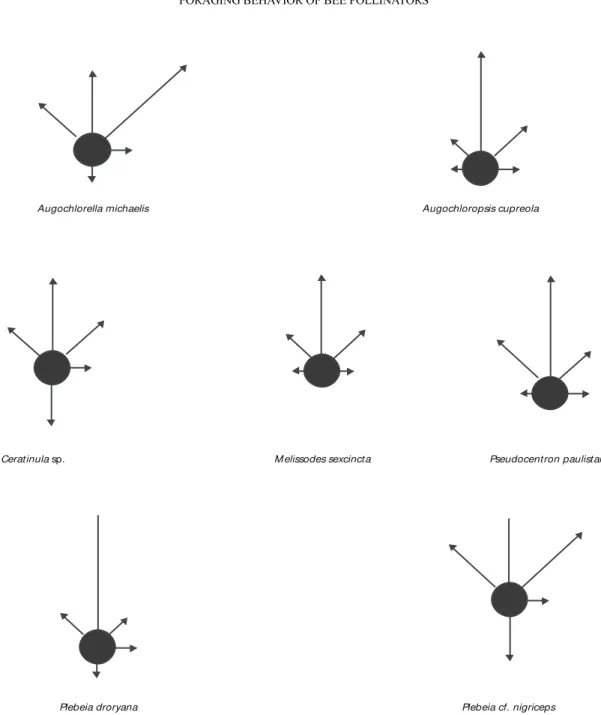
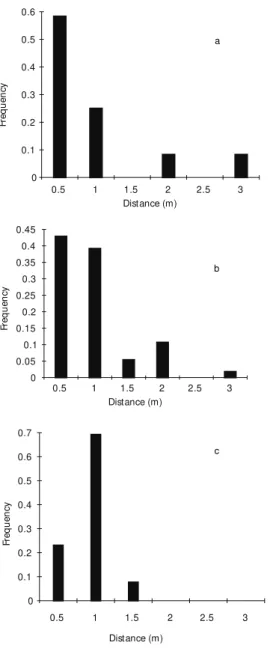

Documentos relacionados
social media definida pela Konica Minolta, porque concluiu que os principais tipos de social media utilizados pelas organizações na Europa são as redes sociais públicas como.. o
Especificamente, pretendeu-se a avaliar se existem diferenças nos parâmetros das comunidades riqueza e equidade entre matas-de-galeria relativamente próximas entre si e pertencentes
Além disso, deve-se anotar, voltando à primeira estatística apresentada neste trabalho, que a síndrome da unanimidade pela qual passam os tribunais, muito mais que justificar
The intercanine distance, the distance between the second lateral incisors at their distal sur- faces, and the distance between the adjacent surfaces of the canine and second
Analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) results testing the influence of fish size, group size, distance of shelter and substrate on Flight Initiation Distance of Acanthurus
As análises das curvas de tendência representativas do comportamento da degradação das fachadas permitem interpretar a evolução progressiva dos danos e estabelecer relação com
Comparing multivariate statistics: The estimates of Mahalanobis' distance (D 2 ), mean Euclidean distance of standardized data (de) and the estimated mean Euclidean distance of
Since restoration intervention has increased vegetation complexity (for example, De la O-Toris et al. 2012), this may lead to decreased predation risk perception, and therefore,