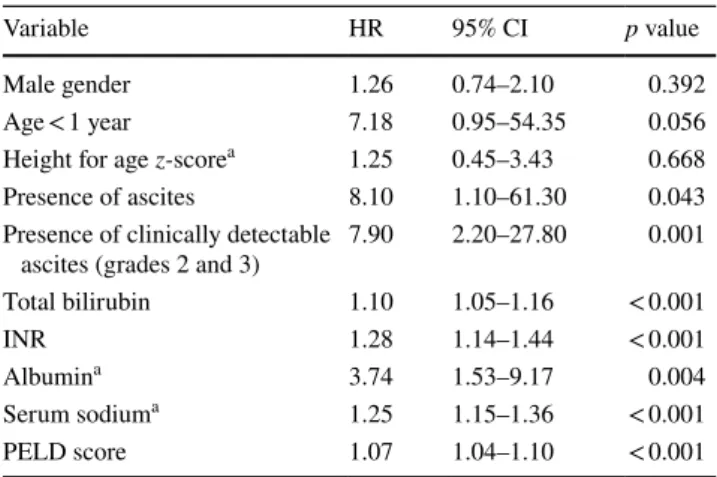
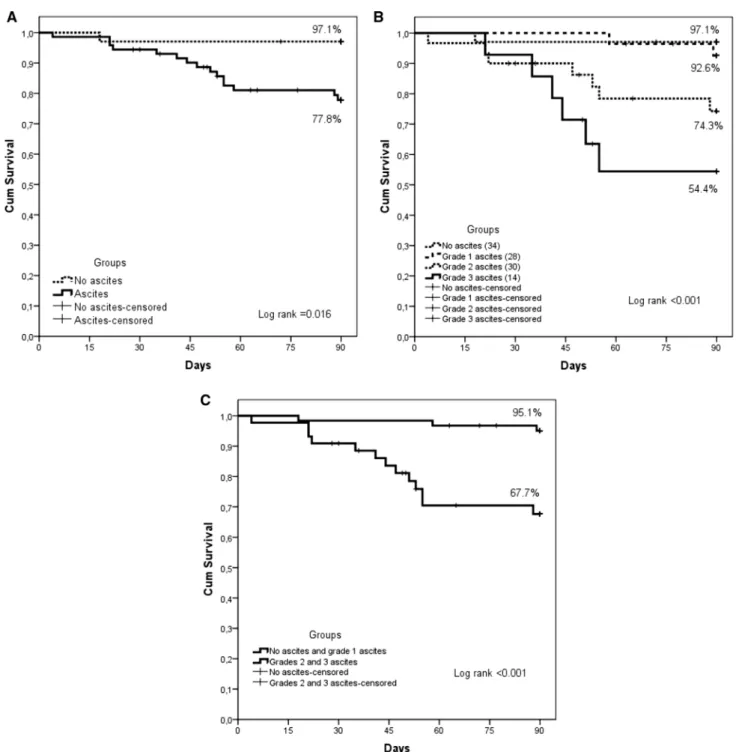
Severity of Ascites Is Associated with Increased Mortality in Patients with Cirrhosis Secondary to Biliary Atresia
Texto
Imagem
Documentos relacionados
Corrupção, baixo desempenho e conflito de interesses são assuntos estampados diariamente nos jornais locais. Para a análise destes problemas, discute- se a importância de
Objective: To evaluate the association between acute kidney injury through the pediatric Risk, Injury, Failure, Loss and End Stage Renal Disease score and mortality in a
In a study by Hoste, the associa- tion of old age and a high score of disease severity with the occurrence of AKI did not apply to groups of patients with AKI, classified by
Four variables were independently associated with the stage of chronic kidney disease two years after liver transplantation: (i) age (at liver transplantation), (ii) male gender,
In order to compare the variables between different groups, the sample was stratiied by age (<6, ≥ 6 and <12, ≥ 12 months), sex, nutritional status (BMI
Comparison of the sequential organ failure assessment score with the King’s College Hospital criteria and the model for end-stage liver disease score for the prognosis
Separating the patients by type of heart disease is observed that there are differences between the groups in the variables: age at time of surgery, size of homograft, Z- score value
The presence of hepatopulmonary syndrome was significantly associated with severity of liver disease assessed by the MELD (Model for End-Stage Liver Disease) score, but not with