Logvinovich O.S., the activity of ornithine decarboxylase in organs and tissues of mammals in hibernation and artificial hypobiosis. Fig.5 Melafen's influence on the delay phase of cellular response of leukocytes.

WAVE ALTERATIONS OF THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM UNDER ISCHEMIC CONDITIONS IN THE CARDIAC MUSCLE
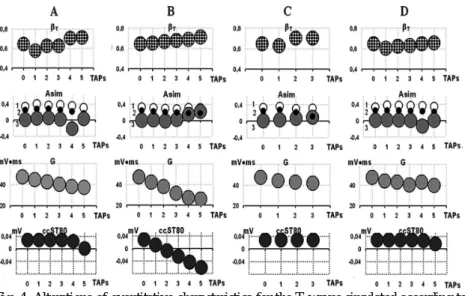
Computer experiments were performed using our system for 3D computer simulation of the electrical activity of the heart [3]. The initial (“normal”) duration of TAPs on the outer and inner surfaces of the left ventricle was 250 and 300 ms, respectively.
Perspective parameters are also a ratio of mean signal velocity on the left and right slopes of the T-wave (VmL/VmR) and a ratio of time intervals between the T-wave peak and points, where derivatives to the left and right of the peaks are maximal ( T1L/T1R). When targets in the organism are affected, microbial metabolites can amplify the negative effect of the inflammatory syndrome.
V. Boiko
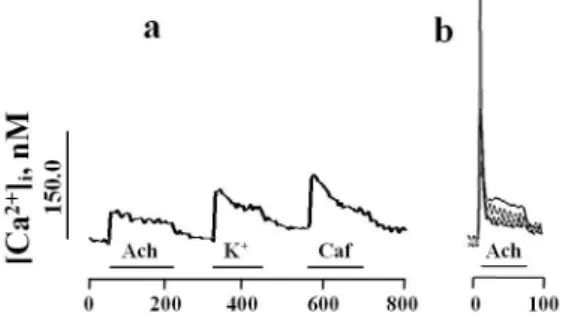
The nifedipine-insensitive component of the tonic response may be supplied by calcium from intracellular sources. Ryanodine (1 M), an agonist of ryanodine receptors at this concentration, caused an increase in the amplitude of the contractile response to carbachol by activating the release of stored Ca2+.
S. Bulat
Cys38 is located in the first strand of the five-stranded barrel in the SH3 subdomain. PHOSPHORYLATION OF THE N-TERMINAL ACTIN-BINDING DOMAIN OF THE MYOSIN LIGHT CHAIN KINASE IN CELLS AND IN VITRO.
S. Miroshnichenko 1
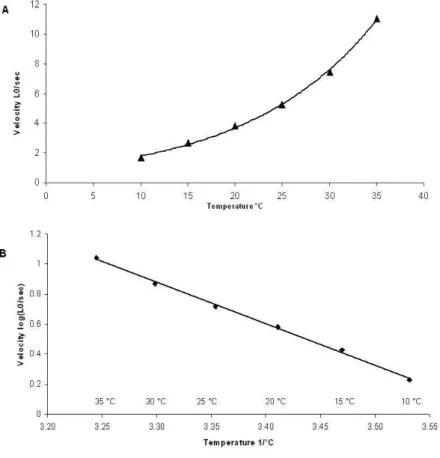
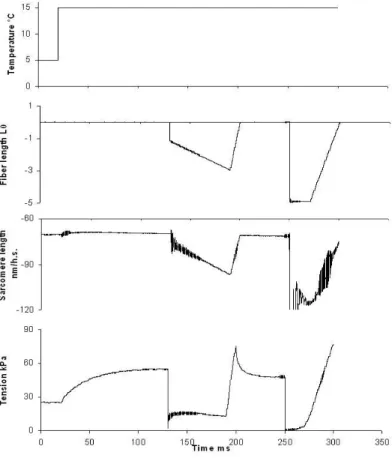
This was seen primarily as the inability of the muscles to maintain a consistent level of force response. With the increase in the frequency of stimulation to a new stable level (interval t4) after passing the pre-tetanus plateau (t3) the rate of force change. Our data on the temperature dependence of Vmax and Vopt of fast fibers are similar to those obtained in the in vitro motility assay in rabbit fast myosin [0], but differ from data obtained for intact fibers of fast mice [0].
Faulkner, Force-velocity relationship at high shortening velocities in rat soleus muscle, J Physiol. The expression of tropomyosin isoforms in the heart depends on the species and the age of the animal (1). For this we studied the dependence of the sliding speed of actin and actin-tropomyosin filaments in the in vitro motility assay on myosin and tropomyosin isoforms.
B.Belostotskaya 1,3
In this paper we studied the effects of ultra-low frequency (0.01-2.0 Hz) alternating magnetic field (AMF) on the contractile activity of myotubes of different maturity in primary culture of neonatal rat satellite cells. In our study we have shown that one of the mechanisms of Ca2+ influx in the cytoplasm of satellite cells localized in the muscle fiber is mediated by voltage-dependent L-type channels after activation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Voltage-gated L-type Ca2+ channels and nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in satellite cells are shown by us for the first time.
There is a view that voltage-dependent calcium channels appear only during differentiation of satellite cells at the stage of myoblast fusion and myotube formation (5, 6, 7). Here we propose for the conjugation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and voltage-gated calcium channel in satellite cells. The action of verapamil on satellite cells does not block Ca2+ entry into the cytoplasm.

D. Kreshchenko
Kubasov 1 and M.G.Dobretsov 2
These are ways of delivering stem cells to different parts of the brain. The application of stem cells was performed in the peripheral parts of both cranial nerves. It depends on the place of their injection into the peripheral parts of the cranial nerves.
Injection of cells in the vicinity of the olfactory nerve is associated with their movement and distribution in the rostral areas of the brain. Injection of stem cells into the trigeminal nervous system is associated with their migration to the caudal parts of the brain. Possible involvement of phosphatidylinositol kinases in the effect of oxidized glutathione and Glutoxime on intracellular Ca2+ concentration in macrophages.

G. Ladygin
However, the composition of the macular lipido-carotenoid globules has not been studied. Thus, it has been proved by us that only carotenes (without any xanthophylls) are available in the eyeballs. It is more important that we managed to show first: the composition of carotenes can change in the globules of the eyeball.
In all examined muscles, a shift of the myosin isoform composition towards an increase in the content of "slow" MHC was found during sleep. What is the physiological significance of the changes in myosin phenotype of chipmunk skeletal muscle during hibernation. Therefore, the decrease in the Ca2+ sensitivity of myosin can be considered an adaptation factor that prevents the unwanted activity of the myofibrillar apparatus of skeletal muscles of chipmunks during hibernation.

G. Lyabakh
At the same time, the influence of the EMF ELF on the ATPase activity of actomyosin in vitro isolated from rabbit skeletal muscle was estimated. One of the causes of such changes may be the synchronizing effect of EMF on the pacemaker activity of Cajal cells that play a key role in the spontaneous activity of smooth muscle in various organs. The effect of EMF ELF on the protein contractile elements of skeletal muscle, in particular on the ATPaase activity of actomyosin, was evaluated in the second part of the study.
The analysis of the effect of EMF ELF on the ATPase activity of actomyosin showed that this process is characterized by certain dynamics. In the present study, the effect of HU on the resting membrane potential (RMP), the electrogenic activity of the Na,K-ATPase 1 and 2 isoforms and their expression in the rat soleus muscle were investigated. Here we demonstrated that structural rearrangements of the tubulin cytoskeleton modulate the effect of glutoxime on Na + transport in frog skin.

A. Metalnikova
Introduction
Most studies report a positive inotropic effect of insulin in the cardiac ventricle of different mammalian species and in human myocardium. However, some investigators have described patterns of two-phase and even three-phase insulin action depending on species and age of animals under different pathologies and experimental conditions [1-4]. We have previously shown that the type of insulin-induced inotropic effect in ground squirrel heart tissue varies significantly over the annual cycle of animals [5].
In active animals in different seasonal periods and in aroused animals, insulin causes cardiostimulatory and cardiodepressive effects under the same conditions, depending on the time and concentration of the hormone used and the levels of arousal [5-7]. The main aim of the present study is to elucidate the possible reasons for the variability of insulin action in the myocardium of hibernators.
Methods
Results
The main aim of this study is to elucidate the possible reasons for the variation in insulin action in the myocardium of hibernators. application) positive effect (about 15-25%) comparable to the effects reported in isolated rat [3] and human [1, 2] hearts. In PM with the pronounced force-frequency relationship, the effect of insulin is significantly higher than in those that exhibit small frequency responses. It was suggested that ICaL might be involved in the insulin-induced negative inotropy in chipmunk hearts.
Nifedipine (1-1.5 hours pretreatment), a blocker of the L-type calcium channel, reduces the inhibitory effect of insulin in autumn and winter animals, and increases it in summer animals. It is known that alteration of protein phosphorylation in tyrosine residues is an important link in the mechanism of action of insulin [10]. In the group of summer animals, pretreatment of the papillary muscles with orthovanadate (100 mkM) does not alter the negative inotropic effect of insulin in a low range of stimulation frequencies, but almost completely abolishes this effect at stimulation frequencies above 0.3 Hz (n=4) . .
Discussion
At frequencies above 0.5-Hz stimulation, insulin of 10 nM concentration presumably induces a negative inotropic effect whose magnitude varies in different preparations (from 15 to 55%) and depends on the initial character of force-frequency relationship. This fact suggests that different mechanisms must be involved in insulin actions in animals of summer and winter periods.
Conclusion
Dehydration of the samples was carried out with ethanol in different concentrations and the acetone. In 2002, we discovered the ability of the muscle-X protein (a protein of the titin family) to form amyloids in vitro [1, 2] and later of other proteins of this family [3-9]. The comparison was performed in the upper and middle part of the left ventricle along a segment perpendicular to the epicardium.
Analysis of the hemolymph by an inverted optical microscope revealed the presence in the hemolymph of snails H. Schematic illustration of the cell compartments and Ca2+ uxes in the SR Ca2+ “clock” model. EFFECT OF CIRCADIC AND CIRCATIONAL RHYTHMS OF MONOMINERS ON THE PLASTICITY OF THE CENTRAL.
Thus, significant suppression of exploratory activity in animals with an increased level of serotonin in the brain occurs in autumn. The role of endogenous factors in the regulation of functional states of the central nervous system in hibernators.

S. Shenkman
In addition, in the case of symmetrical crowns, 4D configuration, the inclination of the helical paths differs from the experimental one, amounting to 71°. Contraction was simulated by unfolding myosin heads from the surface of the thick filament toward the surrounding thin filaments. It is worth noting that the actual diffraction patterns are dominated by the arrangement of the myosin heads within the bipolar hexagonal lattice of the sarcomere.
In the calculated Fourier spectra, the properties specific to the actual diffraction patterns of the relaxed muscles, i.e. the prominent meridional reflections at 3-d, 6-th, 9-th, etc. At the same time, Tm-Tn shifts around the filament axis are determined by a change in the arrangement of the actin monomers. Elongation of the actin filament (or microtubule) appears to be a universal mechanism for force generation in living cells.


![Fig. 2. The changes in (A), [Ca 2+ ] (B) and CsA-insensitive swelling of mitochondria (C) induced by 70 M Ca 2+ and 15 M Pal](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/pdfplayernet/435290.50447/34.629.87.545.364.538/fig-changes-csa-insensitive-swelling-mitochondria-induced-pal.webp)