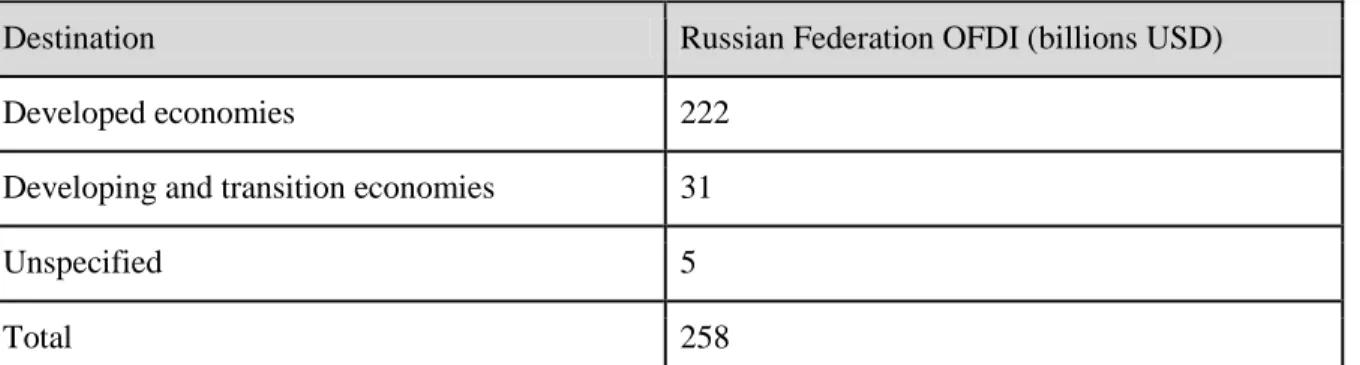
Master's thesis title Institutional determinants behind Russian direct foreign investments in the Graduate School of Management of the Latin American Faculty. The purpose of this article is to investigate how the institutional distance between Russia and Latin America affects the amount of Russian foreign direct investment in Latin America.
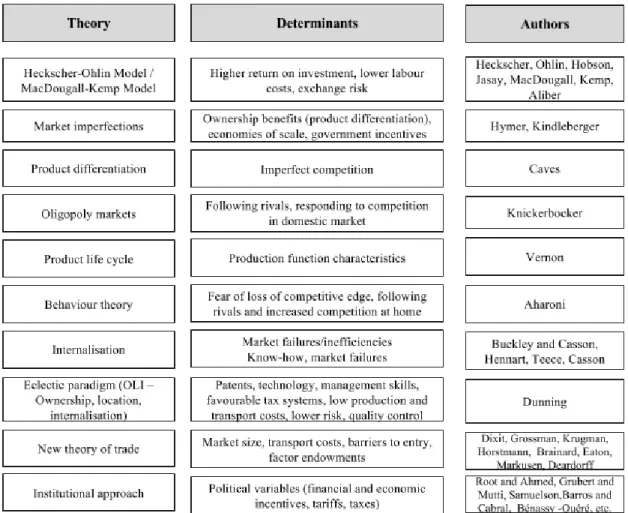
FDI determinants theoretical background and examples
Overview of institutional determinants of FDI
So we can conclude that all the variables mentioned above are institutional determinants of FDI. Some authors claim that institutional determinants affect not only the volume of FDI but also the probability of FDI (Cezar and Escobar, 2015).
FDI determinants in emerging economies
Many researches prove that there is a strong impact of the protection of intellectual property rights on FDI. Following the existing literature, increasing the quality of property rights protection in developing countries, where the initial level of property rights protection is low, leads to increased FDI inflows.
Institutional determinants of FDI in context of Russian FDI in Latin America
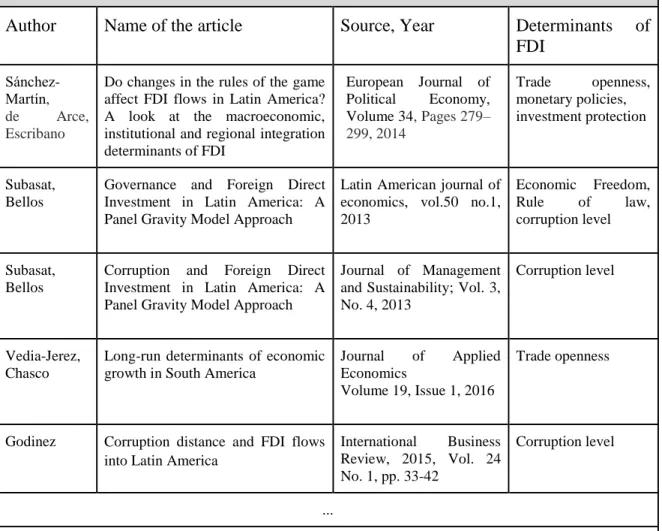
Overview of recent studies devoted to institutional determinants of foreign direct investment in Latin America and institutional determinants of Russian foreign direct investment. Literature on the subject of institutional determinants of inward FDI in Latin America Author Article name Source, Year Determinants of. See the full table in Appendix 5: Literature on the topic of institutional determinants of inward foreign direct investment in Latin America.
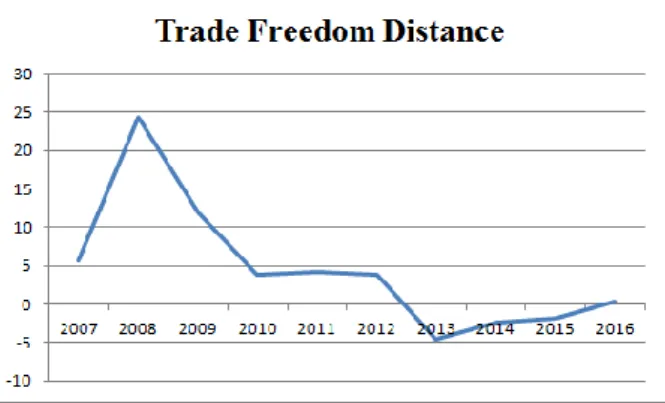
Other institutional determinants of foreign direct investment in Latin America are less discussed in the existing literature, which prevents us from deriving a reasonable hypothesis about them. Thus, the quality of investment institutions in Latin America is likely to influence Russian foreign direct investment in Latin America. Trade Freedom, like Investment Freedom, characterizes market openness and has a significant impact on the amount of inward foreign direct investment in Latin America.
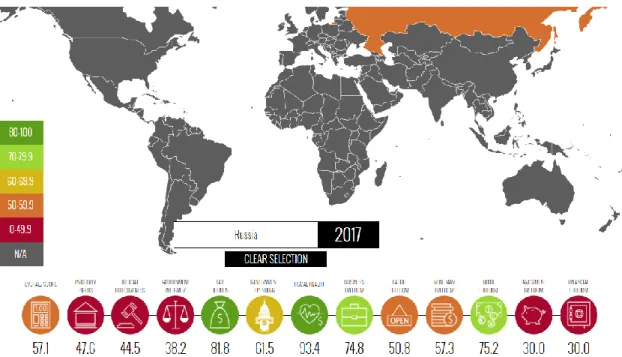
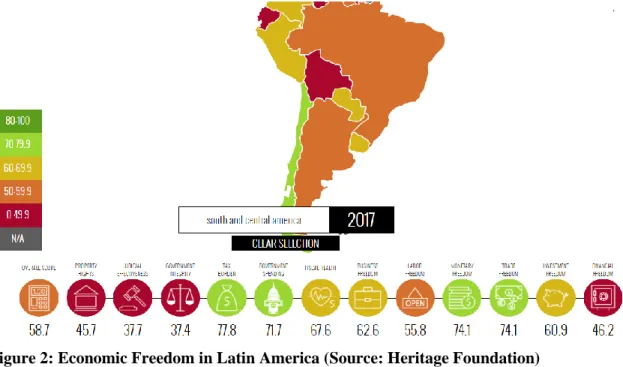
According to recent studies, trade openness in Latin America is a powerful predictor of FDI inflows (Shah and Qayyum, 2015; Sánchez-Martín, de Arce and Escribano, 2014). Figure 2 and Figure 3 show a current situation regarding economic freedom in Latin America and Russia.
Research design
Summarizing of hypothesis
Methodology
For independent variables, as stated at the beginning of this study, we will take institutional distances between Russia and Latin American countries. For a more complete and detailed analysis, it is reasonable to include all variables based on distance from the study (not necessarily simultaneously). This will help to check hypotheses and furthermore identify possible significant predictors of bilateral FDI, which were less discussed in the existing literature and not predicted from literature review. Including so many complex institutional variables in the model forces us to check many assumptions and the entire logic of the model.
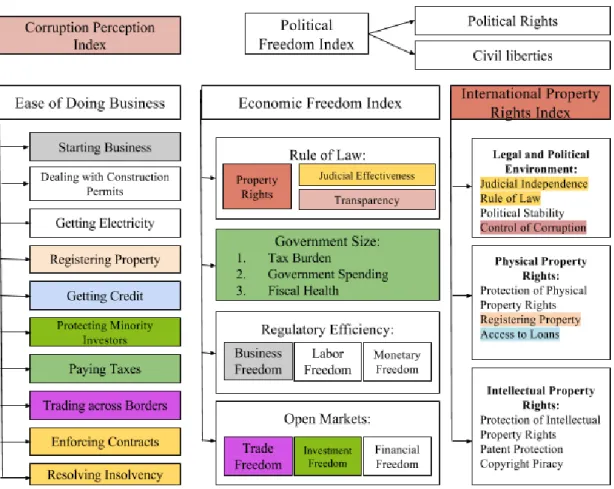
The main obstacle to consider here is that all these institutional variables are composed of different subcategories, more specific indicators, which can significantly correlate with each other and only evaluate the development of the same institutions. As we can see from the figure above, some institutional indexes contain overlapping categories, which can cause correlation problems. So it is reasonable to eliminate some components to prevent this. The best option is panel regression analysis, which allows us to identify predictors of foreign direct investment based on several years of information.
While choosing the model for the research, we should consider the cross-country heterogeneity which is stable and which correlates with independent variables (institutional distances), which means that there are some specific non-random characteristics of countries in the data set. We should also take into account that we take for analysis all available data for almost all Latin American countries where Russian companies find FDI, which means that our sample is non-random.
Data gathering
42 In addition to the Central Bank statistics, we can collect data on foreign direct investment from the aforementioned ZEPHYR and Thomson Reuters, which can help interpret the results. This chapter provided the justification for the choice of data and methodology that will be used for hypothesis testing. The data collection process and limitations of the data are described in this chapter.
Finally, we have one dependent variable (FDI) and twelve independent variables (institutional distance) for analysis; we have enough observations to proceed further with the panel regression model.
Data analysis and findings
Hypothesis testing
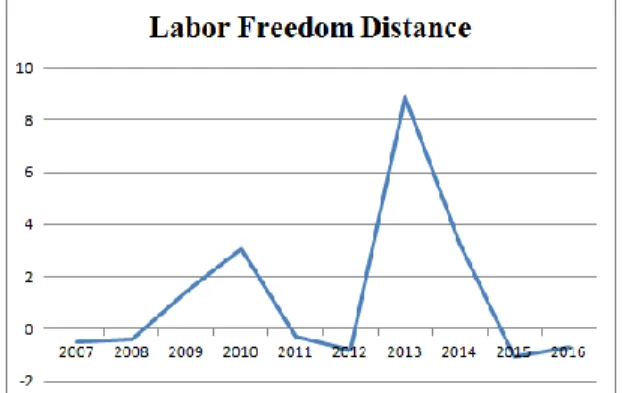
Trade Freedom distance (95% confidence level), Investment Freedom distance (90% confidence level) and Labor Freedom distance (90% confidence level). This model does not include Financial Freedom distance, Political Freedom distance and International Property Rights Index distance due to correlation problem. The same can be said for other positive institutional distances: general economic freedom distance, political freedom distance and corruption perception distance.
The positive impact of Labor Freedom distance also proves the shift towards the efficiency search strategy of Russian companies in Latin America. The distance of positive investment freedom also has a positive impact on Russian FDI in Latin America, which means that one of the main decision-making factors for Russian investors is investment protection regulations. To summarize, the positive effect of the positive distance of economic freedom on Russian FDI in Latin America indicates the intention of Russian companies to operate in a more developed institutional environment, which results in increased effectiveness and competitiveness in the international arena.
This analysis showed no significant influence of distance to corruption perception and distance to political freedom on foreign direct investments. The lack of a proven relationship between foreign direct investment and distance to contract enforcement can thus be partly explained by the absence of a significant effect of distance to corruption perception and distance to political freedom.
Theoretical and practical contribution
Conclusions and discussion
Kalotay, K Outward Foreign Direct Investment from Russia in a Global Context", Journal of East-West Business, Vol. Kolstad, I., Villanger, E How does social development affect foreign direct investment and domestic investment?", Chr. Michelsen Institute, Social Development Papers, Paper No. 2012), "What determines Chinese FDI?", Journal of World Business, Vol. 1999), "Transnational transfer of strategic organizational practices: a contextual perspective", Academy of Management Review, Vol. 1999), “Organizational Legitimacy Under Conditions of. complexity: the case of multinational enterprise”, Academy of Management Review, Vol. 2011), “Outward FDI from Russia and its policy context, update 2011”, Columbia FDI Profiles, available at: www.vcc.columbia.edu. Mohamed, S.E; Sidiropoulos, M.G Another look at the determinants of foreign direct investment in MENA countries: an empirical study", Journal of Economic Development, Vol. 2010), "Institutional, industry and power effects on integration in cross-border acquisitions", Organization Studies, Vol .
The Ambiguity of the Evidence and Why it Matters”, European Journal of Development Research Vol. 1990), “Institutions, Institutional Change and Economic Performance”, New York, Cambridge University Press, Douglass C. Quazi, R.M Foreign Direct Investment in Latin America: A Panel Regression Study”, The International Journal of Business and Finance Research, Vol. Stoian, C Extending Dunning's Investment Development Path: The role of home country institutional determinants in explaining outward buitelandse direkte investering”, International Business Review, Vol.22, pp.
Subasat, T., Bellos, S Corruption and Foreign Direct Investment in Latin America: A Panel Gravity Model Approach”, Journal of Management and Sustainability;. Zubkovskaya, A., Michailova, S The development of Russian multinationals from the 1990s to the present", Organizations and Markets in Emerging Economies, Vol.5 No.2, pp.
Russian MNEs’ investment projects in Latin America
The creation of a large hydropower plant "Argentina - Patagonia" in the south of Argentina is also planned with Russian participation. In Mexico, the Russian JSC "Power Machines" company participated in the construction of a number of Mexican hydropower plants. In the same year several projects in the development of agriculture, energy and machinery production were started in Nicaragua.
The main purpose of this project is the installation and use of GLONASS measuring stations in the Federal Republic of Brazil. In Ecuador, JSC "Russian Railways" and the Ministry of Coordination of Strategic Sectors of the Republic of Ecuador signed a protocol of intent in the implementation of railway projects. For example, in Brazil, JSC "Russian Railways" and JSC "Uralvagonzavod" are planning the possible purchase of the Brazilian oil and telecommunications company TIM.6 There is a possibility of cooperation of Russian companies in the creation of a large transport hub based on the modernization of the Mariel seaport and the construction in the area of a modern international airport with cargo terminals.
34;Inter RAO - Export" has won the international tender and will now participate in the construction of the hydroelectric power plant "Chihuido I" in the province of Neuquen, Argentina. The renewal of credit cooperation with Cuba will allow our companies to participate in the construction of a thermal power plant and the modernization of the Jose Marti metallurgical plant in Cuba.
Institutions in Latin America
On the other hand, all these new institutions further complicate the institutional environment in Latin America and require more horizontal and vertical coordination. The effectiveness of Latin America's banking system has declined over the past decade. 9 International Monetary Fund 2016 report “Financial Integration in Latin America”, https://www.imf.org/external/np/pp/eng pdf.
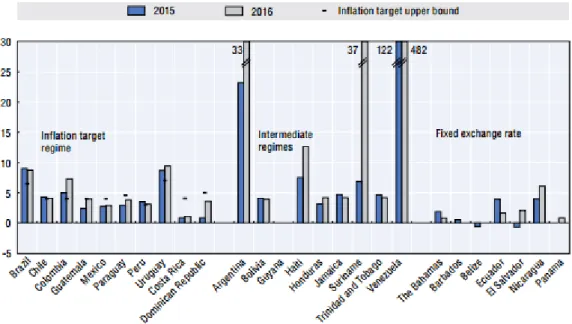
10 Cluster Report – Trade Integration in Latin America and the Caribbean, IMF Country Report No. 17/66, March 2017. As shown in Figure 10, labor institutions in Latin America have deteriorated over the past decade, which is a good signal for investors. Latin America performs quite well, showing the high level of efficiency and transparency when dealing with construction permits and starting a business.
According to the World Bank, the enforcement of contracts in Latin America varies around 50 on the 100-point scale, which indicates low development of judicial institutions (for comparison, this index is higher than 70 in the Russian Federation). But the situation in Latin America can be compared to the situation in Russia and other emerging economies with low IPRI.
MITs and BITs
At the moment, the Russian Federation has bilateral agreements with Argentina, Cuba, Ecuador, Guatemala, Nicaragua and Venezuela. The document commits each party to ensure fair and equitable treatment of the other party's investments in accordance with local laws. According to this agreement, each side can list the sectors and areas of activity in which it has excluded or restricted the operation of foreign investors.
According to this document, all disputes must be resolved through negotiation or, if that is impossible, through arbitration in the country on whose territory the investments are made. The last option to resolve international disputes is the "ad hoc" arbitration in accordance with the arbitration rules, United Nations Commission on International Trade Law. The BIT with Argentina was signed later, in 1998; it implies a quite similar condition for bilateral cooperation between the countries.
In the BIT with Argentina, there is also a paragraph dedicated to entry permits for non-citizens. In accordance with the document, investors and personnel, who are citizens of one country, can enter and stay in the territory of another country to carry out investment-related activities.
List of developing and emerging countries
Literature on the topic of institutional determinants of FDI in Latin America
19 Hossain Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and Corruption: Are they a major obstacle to encourage inward FDI.
Literature on the topic of institutional determinants of Russian FDI decisions
Indexes and FDI flows
Conventional notations
Correlation table