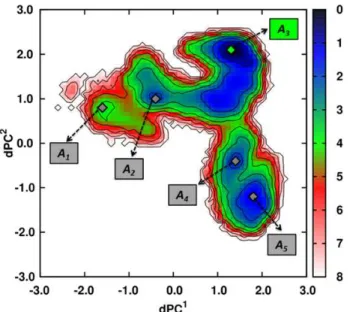
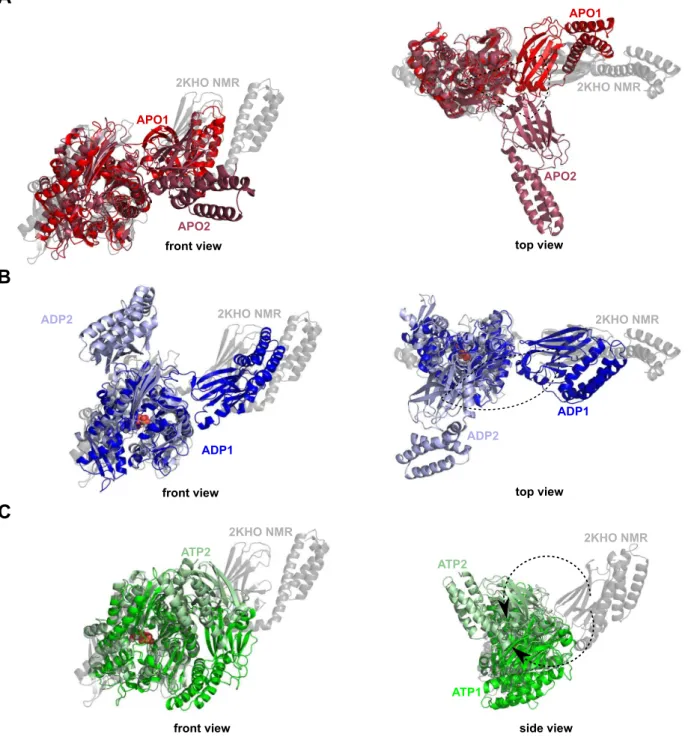
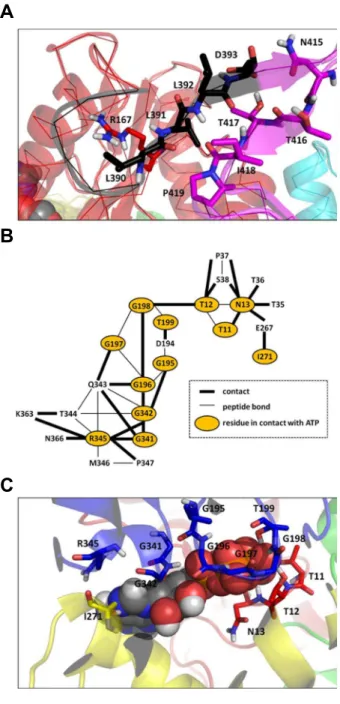
Decipher the mechanisms of protein conformational changes induced by nucleotide binding through free-energy landscape analysis: ATP binding to Hsp70.
Texto
Imagem


Documentos relacionados
Here we evaluate the K18A mutation on ShK, and calculate the change in binding free energy associated with this mutation using the path-independent free energy perturbation
The data show that the shift from 9- O - to 4- O -Ac-Sia receptor usage primarily entailed a change in ligand binding topology and, surprisingly, only modest changes in
The induced proteins were guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit beta-like protein (ACS1), phosphoglycerate mutase (GPM1), peroxisomal catalase (CTA1) and
demonstrate by DXMS and antibody binding studies that cleavage of the mucin domain and glycan cap and incubation at low pH are insufficient to trigger the conformational changes of
Some studies pointed to the influence of ions on the AChE activity by binding to peripheral sites promoting conformational modifications or changing the
noncatalytic sites showed lowered ATPase activity, indicating that the nucleotide binding to the noncatalytic sites has a substantial role for recovery from MgADP inhibition in BF
All inhibitors were subsequently docked into the binding site obtained from the receptor and conformation of the inhibitors with the lowest binding free energy was used to
was performed to corroborate the experimental results, by predicting the binding mode, relative binding energy of the complex formed between β -carboline derivatives with DNA and