Published online September 24th, 2010 © http://www.ijav.org
Case Report
International Journal of Anatomical Variations (2010) 3: 149–150
Introduction
The caroticoclinoid foramen is an inconstant structure which is located in the anterior cranial fossa, composed by the ossification of a fibrous ligament [1] that begins on the anterior clinoid process and binds to the middle clinoid process [2]. Caroticoclinoid foramen, allows the passage of one of six segments of the internal carotid artery, the clinoidal segment [3].
The fibrous ossification of ligaments is considered a normal physiological process that occurs with aging, however this process is an exception when one considers the formation of the caroticoclinoid foramen [4]. Study by Hochstetter [5] revealed the presence of this foramen in fetuses and children skulls.
The aim of this study was to evaluate the characteristics of caroticoclinoid foramen in a Brazilian dry human skull and the clinical influences that this structure may generate, covering an area where neurosurgical operations are common.
Case Report
This work reports about caroticoclinoid foramen, on both sides, encountered in a dry adult human skull, female, belonging to the anatomy laboratory of the Department of Basic Sciences, Faculty of Dentistry of Araçatuba, Paulista State University. The anterior clinoid process was intact and there was complete ossification of the fibrous ligament between anterior and middle clinoid processes. This foramen was located in the middle cranial Alexandre Rodrigues FREIRE [1]
Ana Cláudia Rossi [1]
Felippe Bevilacqua PRADO [1]
Paulo Henrique Ferreira CARIA [1]
Paulo Roberto BOTACIN [2]
Department of Morphology, State University of Campinas - UNICAMP, Piracicaba [1], Department of Basic Sciences, Paulista State University - UNESP, Araçatuba [2], SP, BRAZIL.
Mr. Alexandre Rodrigues Freire Postgraduate Student Department of Morphology State University of Campinas UNICAMP, Piracicaba, SP, BRAZIL.
+55 19 21065200 alefreire@fop.unicamp.br
Received February 8th, 2010; accepted August 4th, 2010
ABSTRACT
Numerous structures of the skull are well defined in literature. But there are some inconstant structures, which when present may be located in the sphenoid bone by the junction of the anterior and middle clinoid processes. The aim of this study was to evaluate the characteristics of caroticoclinoid foramen in Brazilian human skull. This case report shows a female dry human skull with 2 caroticoclinoid foramina. The largest diameter of this structure was found 5.5 mm on the right side and 5.4 mm on the left. Although being an uncommon foramen, the knowledge is important because it is located in the sphenoid bone, an important region for neurosurgery. ©
IJAV. 2010; 3: 149–150.
Key words [caroticoclinoid foramen] [human skull] [neurosurgery]
eISSN 1308-4038
The caroticoclinoid foramen formation in the human skull and its clinical correlations
fossa, and related medial to the anterior clinoid process and lateral to the tuberculum of sella turcica. It was also located posterior to the optic canal and anterior to the pituitary fossa, as was observed in this case (Figure 1). The morphometry of each foramen was performed using a manual caliper. The larger transverse diameter was measured, from the edge formed by the ossified ligament until the edge formed by the anterior clinoid process. To avoid errors in measurement, it was performed three times by the same examiner being regarded as the repeated values. The diameter of the foramen was 5.5 mm on the right side and 5.4 mm on the left.
Discussion
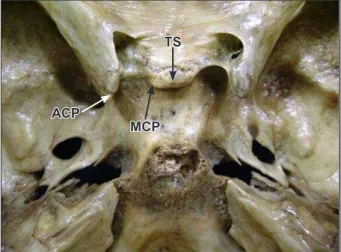
Caroticoclinoid foramen is formed after the ossification of the fibrous ligament that connects the anterior and middle clinoid processes. When there is no ossification of the fibrous ligament in the dry skull only a space between the anterior and middle clinoid processes is observed (Figure 2).
150 Freire et al.
found an average diameter of 5.24 mm on the right side and 5.25 mm on the left, diameters were larger than the caroticoclinoid foramen.
The formation of this foramen may cause compression and narrowing of the internal carotid artery, located medially to the anterior clinoid process [4]. Changes in internal carotid artery may cause compression of the cavernous sinus because of its medial position [7,8]. The study by Das et al. [9] shows that the presence of the caroticoclinoid foramen causes morphological changes in the internal carotid artery in almost all cases. These variations occur due to the presence of foramen, which cause difficulty in performing a neurosurgical technique in the region [7].
References
[1] Standring S. Overview of the Development of the Head and Neck Head: Skull and Mandible. In: Standring S, ed. Gray’s Anatomy: the Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. 39th Ed., New York, Elsevier. 2005; 462–467.
[2] Sicher H, Du Brul EL. Oral Anatomy. 6th Ed., Saint Louis, The C.V. Mosby Company. 1975; 12. [3] Williams PL, Warwick R, Dyson M, Bannister L. Gray’s Anatomy. 37th Ed., Edinburgh, Churchill
Livingstone. 1989; 373–377.
[4] Ozdogmus O, Saka E, Tulay C, Gurdal E, Uzun I, Cavdar S. The anatomy of the carotico-clinoid foramen and its relation with the internal carotid artery. Surg Radiol Anat. 2003; 25: 241–246. [5] Hochstetter F. Über die Taenia interclinoidea, die Commissura alicochlearis und die Cartilago
supracochlearis des menschlichen Primordialkraniums. Gegenbaurs Morph Jahrb. 1940; 84: 220–243. (German)
[6] Erturk M, Kayalioglu G, Govsa F. Anatomy of the clinoidal region with special emphasis on the caroticoclinoid foramen and interclinoid osseous bridge in a recent Turkish population. Neurosurg Rev. 2004; 27: 22–26.
[7] Inoue T, Rhoton AL Jr, Theele D, Barry ME. Surgical approaches to the cavernous sinus: a microsurgical study. Neurosurgery. 1990; 26: 903–932.
[8] Seoane E, Rhoton AL Jr, de Oliveira E. Microsurgical anatomy of the dural collar (carotid collar) and rings around the clinoid segment of the internal carotid artery. Neurosurgery. 1998; 42: 869–886. [9] Das S, Suri R, Kapur V. Ossification of caroticoclinoid ligament and its clinical importance in skull-based
surgery. Sao Paulo Med J. 2007; 125: 351–353.
[10] Narolewski R. Significance of anatomic variants of bony surroundings of the internal carotid artery and their significance for lateral surgical approaches to the cavernous sinus. Ann Acad Med Stetin. 2003; 49: 205–229. (Polish)
[11] Sekhar LN, Burgess J, Akin O. Anatomical study of the cavernous sinus emphasizing operative approaches and related vascular and neural reconstruction. Neurosurgery. 1987; 21: 806–816. Figure 1. Internal view of skull with the caroticoclinoid foramen and
adjacent structures. (CCF: caroticoclinoid foramen; ACP: anterior clinoid process; OL: ossified ligament; MCP: middle clinoid process; OC: optic canal; TS: tuberculum sellae; PF: pituitary fossa)
In clinical practice, when occurs a paraclinoid aneurysm, the anterior clinoid process is removed as a treatment [8]. In this treatment there is more difficulty when the caroticoclinoid foramen is present, causing higher possibility of serious bleeding in this region [10]. Due to the great caliber of internal carotid artery in this region, the possibility of headache due to compression by the foramen is high [4]. This feature is crucial for the choice of surgical removal of the anterior clinoid process. After the removal of the anterior clinoid process, a space
is observed: the clinoid space, which has triangular shape and small size [7]. Sekhar and Akin [11] affirmed that this space varies according the dimensions of anterior clinoid process and the internal carotid artery [11]. Furthermore, their work showed the position of the caroticoclinoid foramen in an area close to the one occupied by the cavernous sinus. The formation of the caroticoclinoid foramen may change the dimensions of this area [11], considered by some authors as intracavernous [8]. Other authors consider it as an area outside the cavernous sinus [2,3].
The formation of the caroticoclinoid foramen may cause changes in the internal carotid artery, especially in clinoid segment, when comparing the transverse diameter of these structures. Thus, it is concluded that the presence of this foramen has important clinical implications, and its knowledge is required for better planning of surgical treatments that involve this region.
Figure 2. Internal view of skull with absence of the ossified ligament between anterior and middle clinoid processes. (TS: tuberculum sellae; ACP: anterior clinoid process; MCP: middle clinoid process)
MCP ACP
TS OC
ACP
OL MCP