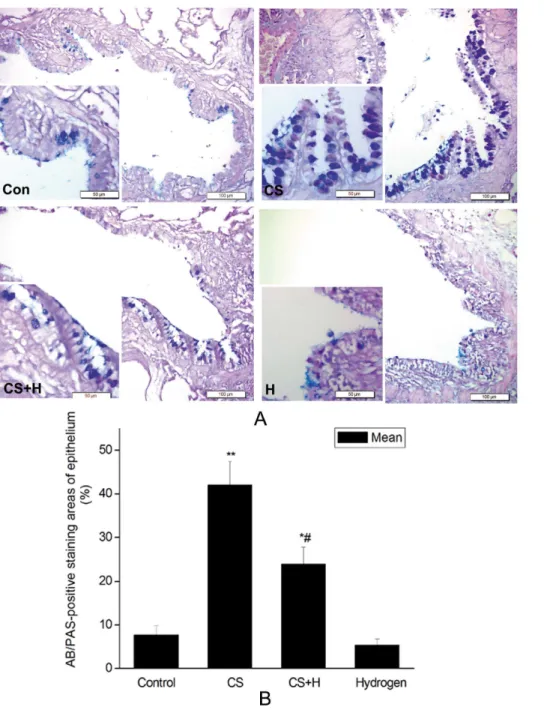
Attenuation of cigarette smoke-induced airway mucus production by hydrogen-rich saline in rats.
Texto
Imagem



Documentos relacionados
Our results demonstrated no statistical significant differences in the mean absolute amplitudes of alpha and theta spectra induced by intracisternal infusion of uro- guanylin
(50) studied the effects of hydrogen- rich saline treatment in a mouse model of haploidentical allogenic bone marrow transplantation and found that the hydrogen-rich saline group
Results Pretreatment with simvastatin prevented alen- dronate-induced macroscopic gastric damage and reduced the levels of MDA and GSH, TNF-a and IL-1b, MPO activity, and mucus
posadasii (C.p.) extract on the cell influx in acute and chronic zymosan-induced arthritis (ZYA) in rats and mice.. extract or saline (-)
The discussion includes properties of combustive hydrogen, abnormal combustion in hydrogen engine, engine components, thermal efficiency, emission production, power output, emissions
Intrinsic resistance refers to an innate characteristic of a given species, frequently encoded in the chromosome, and that is common to most (or all) strains of
Este relatório relata as vivências experimentadas durante o estágio curricular, realizado na Farmácia S.Miguel, bem como todas as atividades/formações realizadas
leprae induced low levels of apoptosis and reduced cell proliferation in this human SC