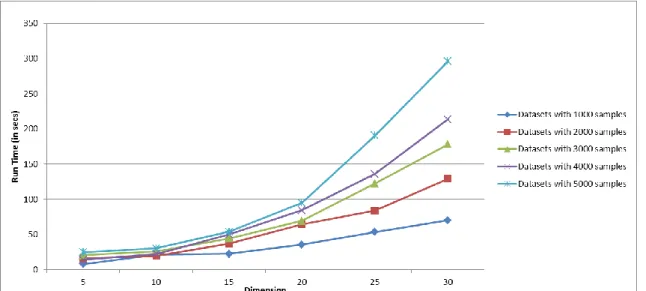
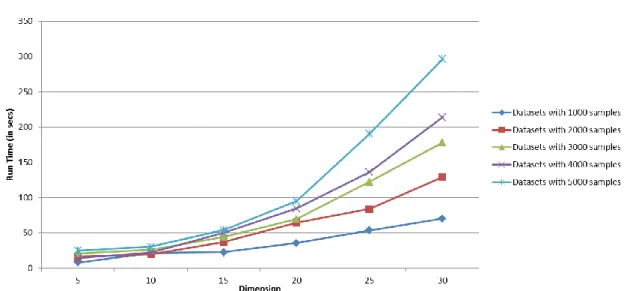
Artificial neural network models: data selection and online adaptation
Texto
Imagem

![Fig. 2.13. Bi-objective minimization problem. The shaded region presents dominated solutions and the solid curve illustrates non-dominated solutions [47]](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123dok_br/18054933.863322/71.892.300.587.103.351/objective-minimization-presents-dominated-solutions-illustrates-dominated-solutions.webp)
Documentos relacionados
The probability of attending school four our group of interest in this region increased by 6.5 percentage points after the expansion of the Bolsa Família program in 2007 and
of the progeny or replication to which they belonged; b) Stratified mass selection: the plants were divided into strata and each stratum was considered a replication. Thus, each
social assistance. The protection of jobs within some enterprises, cooperatives, forms of economical associations, constitute an efficient social policy, totally different from
Abstract - The multiobjective optimization method was applied in order to improve the droplet size distribution and stability of water-in-oil emulsions composed of sunflower
Baseadas na leitura de Leite e Tassoni (2002) e Almeida (1999), identificamos, conversando sobre a nossa prática, que a afetividade é fundamental no processo ensino aprendizagem,
To overcome this, an alternative method was presented by Laubach and Williams (2003) that applies the Kalman filter to jointly estimate the output gap, the trend growth
The DWT is applied for these images, trained with the neural network method and then proposed watermarking technique is applied to get the watermarked image as shown in
ABSTRACT – The aim of this study was to evaluate the method of neuroevolution of augmenting topologies (NEAT) to adjust the weights and the topology of artificial neural networks