Prioritized aesthetic attributes of product:
A fuzzy-AHP approach
H.C.Yadav1, Rajeev Jain2, Sandarbh Shukla3 and P.K.Mishra4 1
H.C.Yadav*_ Research Scholar MED, MNNIT Allahabad, India
2
Rajeev Jain_ Head MED Kalaniketan Polytechnic College Jabalpur, India 3
Sandarbh Shukla_ Research Scholar MED, MNNIT Allahabad, India 4
P.K.Mishra_ Professor MED, MNNIT Allahabad, India * corresponding author E-mail: harishivri@gmail.com
Abstract:
In the competitive environment success of a product depends upon inclusion of the aesthetic attributes which is desired by the customers. AHP allows decision makers to model a complex problem in a hierarchical structure but a questionnaire and interview based approach has been adopted for present methodology to identify the aesthetic attributes of car profile and their relative importance but it is found that data collected through questionnaire and interviews are some time very much vague or ambiguous and insufficient to interpret the results. To overcome these limitations the fuzzy based approach has been appropriate methodology to convert the customer emotion into usable design data. The present methodology deals with the application of Fuzzy Analytical hierarchy process (FAHP) to evolve the prioritized aesthetic attributes of car profile. This study presents an integrative design approach to obtain the prioritized aesthetic attributes of car profile. The proposed method has been illustrated using customers survey data.
Keywords: Product design, Aesthetic, Fuzzy AHP, Customer satisfaction. 1. Introduction:
Inclusion of aesthetic aspects in product design process can create good potential of the product in the market. Consumers’ decision to purchase a particular product is motivated by not only it’s technical competence and fit for use, but also by the emotional response induced by its physical appearance. The role of physical appearance has dramatically increased in the 21st century as the society and market has become more aware and choosy towards the aesthetic quality of the products. The physical appearance of a product plays a vital role in the consumers’ preference and choice of the product (Chuang et al., 2001).
Kansei Engineering establishes a framework for quantifying the relationship between design characteristics and emotional responses. (Nagamachi, 1989, 1995; Demirats et al., 2009). Shieh and Yang (2008) have reported that the relative importance of the form features can also be identified by a feature selection method. Hsiao and Liu (2002) have used a shape morphing and image prediction method to develop a three-dimensional (3-D) model to help the product designers to obtain the product form of a computer monitor. Researchers (Lavie and Tractinsky, 2004; Liu, 2003, Rashid et al., 2004; Schenkman and Jonsson, 2000) have used a one dimensional construct (e.g., a semantic index “beautiful verse ugly” or a single aesthetic measure with Likert scale rating) to explain how users perceived subjective quality.
2. Research framework: 2.1. Fuzzy AHP approach
In conventional AHP, the pair wise comparisons for each level with respect to aesthetic criteria are conducted using a nine-point scale. Each pair wise comparison indicates an estimate of the priorities of the compared aesthetic criteria. The pair wise comparison ratios are in crisp real numbers. Even though the discrete scale of 1-9 has the advantages of simplicity and easiness for use but it does not take into account its inability to adequately handle the inherent uncertainty and impression associated with the mapping of the decision-makers perception to exact numbers (Deng, 1999). Importance of different aesthetic criteria of car profile always contains ambiguity and multiplicity of the meaning. These descriptions are usually linguistic and vague. It may also be recognized that human assessment on qualitative attributes is always subjective and thus imprecise. Chan et al (2007) has reported that most decision-makers tend to give assessments based on their knowledge, past experience and subjective judgment. Therefore conventional AHP seems to be inadequate for this work to generate importance weights for the aesthetic criteria of car profile.
In order to model this kind of uncertainty in human preference, fuzzy sets can be incorporated with the pair wise comparison as an extension of AHP. Since fuzziness and vagueness are common characteristics in many decision-making problems, the fuzzy AHP approach allows a more accurate description of the decision-making process (Ayag and Ozdemir, 2006). The fuzzy AHP method in decision-making process can be applied in many different areas due to its accuracy. Kahraman et al. (2003) used fuzzy AHP to select the best supplier firm providing the most satisfaction for the attribute determined. The use of fuzzy methodology allows the decision maker to incorporate both qualitative and quantitative data into the decision model. For this reason, decision makers usually feel more confident to give interval judgment rather than fixed value judgments. The fuzzy theory also allows use of mathematical operators and computer in the fuzzy domains.
2.2. Fuzzy set theory
The fuzzy set theory allows the membership functions to operate over the range of real numbers [0, 1]. A fuzzy set is defined by a membership function and all the information about a fuzzy set is described by its membership function. The membership function maps elements (crisp inputs) in the universe of discourse (interval that contains all the possible input values) to elements degrees of membership within a certain interval, which is usually [0, 1]. Then, the degree of membership specifies the extent to which a given element belongs to a set or is related to a concept. The most commonly range used for expressing degree of membership is the unit interval [0, 1]. If the value assigned is 0, the element does not belong to the set (it has no membership). If the value assigned is 1, the element belongs completely to the set (it has no membership). Finally, if the value lies within the interval [0, 1], the element has a certain degree of membership (it belongs partially to the fuzzy set). A fuzzy set, then, contains elements that have different degrees of membership in it. The main characteristic of fuzziness is the grouping of individuals into classes that do not have sharply defined boundaries. A fuzzy number is a special fuzzy set F = {(x, µF(x)) , x R}, where x takes it values on the real line, R : −∞< x < +∞ and μ (x )is a
continuous mapping from R to the closed interval [0, 1].A triangular fuzzy number denoted as M = (a, b, c), where a ≤b ≤c has the following triangular type membership function;
Alternatively, by defining the interval of confidence level α, the triangular fuzzy number can be characterized as:
M , , ∀ ∈ ,
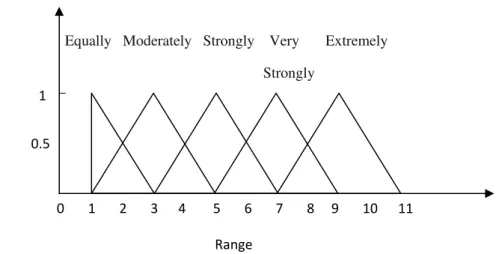
In this study, triangular fuzzy numbers, to , have been used to represent subjective pair wise comparisons of aesthetic criteria of car profile. A tilde “~” is placed above a symbol if the symbol represents a fuzzy set. In order to take the imprecision of human qualitative assessments into consideration; the five triangular fuzzy numbers are defined with the corresponding membership function as shown in Figure 1 and Table 1.
Table 1. Definition and Membership Function of Fuzzy Numbers
Intensity of Importance
Fuzzy number Definition Membership function
1 Equally important/preferred (1, 1, 3)
3 Moderately more important/preferred (1, 3, 5)
5 Strongly more important/preferred (3, 5, 7)
7 Very strongly more important/preferred (5, 7, 9)
9 Extremely more important/preferred (7, 9, 11)
The α – cut values and index of optimism incorporated into fuzzy AHP matrix take care of the accuracy of the measurement. α − cut is known to incorporate the experts or decision maker(s) confidence over his/her preference or the judgments. It will yield an interval set of values from a fuzzy number. For example, α = 0.5 will yield a set α . = (2, 3, 4). The operation is presented by Figure 2.
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
Range
µM
(x)
1
0.5
Figure 1. Membership functions of triangular fuzzy numbers of
Equally Moderately Strongly Very Extremely
Strongly
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Range
µM
(x)
1
0.5
Some main operations for positive fuzzy numbers are described by the interval of confidence as given below:
∀ , , , ∈ ,M , ,
N , , ∈ ,
M N ,
M N ,
M N ,
,
where M and N are crisp values of interval of confidence.
According to classical AHP (Saaty, 1980) hierarchical analysis, a decision-maker can obtain the ratios aij (i, j
=1,… , n) by pair-wise comparison of factors A1,…,Am under some specific criteria. However, the aij is an
estimator and depends on the decision-makers’ subjective perception or experience of the relative significance of factors Ai and Aj. Therefore, it exits vagueness from Saaty’s original method between scales 1 to 9 on
decision-makers judgment. Human judgment cannot determine the relative significant weights with any certainty when doing pair-wise comparison. Such a person can describe them linguistically, and can attach a degree of importance that corresponds to the attribute, with the weights thus coming from the linguistic variables. The present study uses the word “importance” to represent the measurement scales on the linguistic variables. This research also uses intuitional response approach to deal with the ambiguity of the judgment process, and reduces the uncertainty of linguistic expression by triangular fuzzy numbers. In the AHP analytic process, the triangular fuzzy numbers replaced the crisp ratios to present the weights, and to distinguish the relative significance of eight aesthetic criteria.
The fuzzy judgment matrices for seven aesthetic criteria can be obtained from quantified decision-makers’ cognition by linguistic variables and it’s the corresponding triangular fuzzy numbers. After individual paired comparison ratio judgments have been gathered, it is necessary to calculate the geometric mean. Finally, the weight of five aesthetic criteria is obtained by using the eigenvector method, and by utilizing eigen-value to test the consistency of the decision process.
2.3. Computational procedure of fuzzy AHP
The AHP method is also known as an eigenvector method. It indicates that the eigenvector corresponding to the largest eigen value of the pair wise comparisons matrix provides the relative priorities of the criteria. A vector of weights obtained from the pair wise comparisons matrix reflects the relative performance of the various criteria. The procedure of this the approach is as follows:
Step 1:Constructing the fuzzy comparison matrix: By using triangular fuzzy numbers, via pair wise
comparison, the fuzzy judgment matrix A (a ij ) is constructed as equation 4;
Where
,
, , ,
, ,
, ,
Step 2:Estimating the degree of optimism for A
Degree of satisfaction for the judgment matrix is estimated by the index of optimism . The larger value of the indicates the higher degree of optimism. The index of optimism is a linear convex combination defined as:
, ∀ ∈ ,
While α is fixed, following crisp judgment matrix can be obtained after setting the index of optimism, , in order to estimate the degree of satisfaction
… … ⋱ ̂ ̂
Step 3: Solving fuzzy eigen value.
A fuzzy eigen value, is a fuzzy number solution to
A x λ x
where is A n × n fuzzy matrix containing fuzzy numbers a and x is a non-zero n x 1, fuzzy vector containing fuzzy number x i .To perform fuzzy multiplications and additions by using the interval arithmetic and α− cut,
the equation 12 becomes equivalent to
a x , a x … . a x , a x λx , λx
Where
A a ] , x (x 1,…….., x n)
a a , a , x x , x , λ λ , λ
For 0 < α≤ 1 and all i, j, where i=1, 2,…..,n and j=1,2,…..,n
Step 4: Determining the weights of attributes
The Eigen value method is used for calculating the eigenvector or weighting vector for each pair-wise matrix.
The eigenvector is calculated by fixing the value and identifying the maximal Eigen value (Saaty, 1980).
max is calculated then Normalization of both the matrix of paired comparisons and evolution of priority weights (approximate attribute weights). In order to control the results of the method, the consistency ratio for each of the matrices and overall inconsistency for the hierarchy are calculated. The deviations from consistency are expressed by the following equation:
max
Where: CI is consistency index.
The consistency ratio (CR) is used to estimate directly the consistency of pair wise comparisons
RI
Where: RI is selected from Table 2 according to the rank of the matrix.
Table 2. Average Index for Randomly Generated Weights
Matrix Rank 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
RI 0.00 0.58 0.90 1.12 1.24 1.35 1.41 1.45 1.49
The comparisons are acceptable if CR< 0.1. If the consistency test is not passed, the original values in the pair wise comparison matrix must be revised by the decision maker.
3. Methodology:
4. Aesthetic attributes of car profile:
The principal medium of aesthetic communication to customer is the shape of an object, but the color, texture, material and other visual properties also play an important role. These object properties in combination make impression on customers and exert emotions. These facts makes task complicated. To ease the complication all dimensions of aesthetics of objects has to be addressed individually.
In this study shape of a car profile has been chosen as a aesthetic quality for customer satisfaction. Aesthetic quality for customer satisfaction involves multiple parameters. It is important to identify the important and representative aesthetic parameters to ensure satisfaction. A set of criteria parameters for aesthetic satisfaction
Yes
No
Ranking the criteria Is the consistency index< 0.10?
Use sensitivity analysis to determine the source of variance Constructing the fuzzy comparison matrix
by using fuzzy number
Transformation with degree of optimism
Solving Eigen vector Problem Recognition
Select a group of subject matter experts
Define scope and boundaries of the AHP
Decompose the problem in to hierarchy
Define membership function with and make a scale
Perform pair-wise comparison at each level using scale responses on the questionnaire
were evolved through literature reviews (Liu, 2003; Rashid et al., 2004; Schenkman and Jonsson, 2000; Pham, 1999; Talia and Noam, 2004). Seven aesthetic parameters were identified based on the discussions with the professional product designers. They are originality, elegant, family-feeling, modern, masculine, youthful and dynamic.
5. Weight of aesthetic attribute:
A fuzzy AHP technique to evaluate the aesthetic attributes of car profile has been presented in this study. About twenty-five professionals working at responsible positions in the field of product design were interviewed to evaluate the aesthetic attributes of the car profile in the hierarchy model. The aim of interaction was to understand their opinions on three aspects:
(i) Weight judgments of aesthetic attributes of the car profile. (ii) Their attitude toward the FAHP approach used by this study and (iii) their suggestions in general.
All aesthetic attributes of car profile have been listed and after that the decision-makers were requested to express the preference ( , , , , by pair-wise comparison of the relative importance of each aesthetic attribute using triangular fuzzy numbers by separate questionnaire to estimate their relative importance in relation to the element at the immediate proceeding level.
After finalizing the assessment of relative importance of aesthetic attributes of car profile, the fuzzy comparison matrixes for the aesthetic attributes are prepared as shown in Table 3.
Table 3. Fuzzy comparison matrix of aesthetic attributes of car profile
Attributes Originality Elegant
Family-feeling Modern Masculine Youthful Dynamic Originality 1
Elegant 1
Family-feeling 1
Modern 1
Masculine 1
Youthful 1
Dynamic 1
After finalizing the assessment of relative importance by these experts for the aesthetic attributes of car profile, the triangular membership function and α-cuts were used to convert the subjective judgments of experts to become fuzzy judgments. After that, a degree of optimism for the experts was estimated by the index of optimism . All initial individual fuzzy comparison matrices based on triangular membership function and α-cut were were formulated. The lower limit and upper limit of the fuzzy numbers with respect to α are defined using equation 2.
, , ,
, ,
, ,
, , ,
The α-cut values and index of optimism incorporated into fuzzy AHP matrix take care of accuracy of the service quality measurement. The values α=0.5 and =0.5 are used in this study. By putting α=0.5 in the above expression and then putting the value of fuzzy numbers in the Table 5 fuzzy comparison matrix is obtained for the aesthetic attributes. Fuzzy comparison matrix (FCM) for the determinants (α=0.5, =0.5) of aesthetic attributes is given below:
.
, , , , , ,
, , , , , ,
, , , , , ,
, , , , , ,
, , , , , ,
, , , , , ,
, , , , , ,
5.1 Estimating the degree of optimization:
Degree of satisfaction for the judgment matrices is estimated by the index of optimism . The larger value of the index indicates the higher degree of optimism. The index of optimism is a linear convex combination defined by equation 10. The following crisp judgment matrix can be obtained after setting the index of optimism , in order to estimate the degree of satisfaction. Here =0.5 are used to transform fuzzy group comparison matrices into group crisp comparison matrices, from which the importance weights were obtained. For example, group crisp comparison matrix (GCCM) is obtained as shown below after using =0.5 (in equation 5).
. .
. .
. . . .
. . . . .
. . . .
.
. . .
5.2 Eigen value and eigen vector:
Let . . = A. Eigen value of the matrix A can be obtained by solving the characteristic equation of A, i.e. det ..
. , . . , . . , . . ,
. . , . . , . .
As the value of is the largest, the corresponding eigenvectors of A can be calculated as by substituting the in the equation 7:
. , . , . , . , . , . , .
After normalization, the importance weights of the aesthetic attributes can be determined as:
5.3 Check the consistency ratio:
If the consistency ratio ( ) is less than 0.1, then comparison are acceptable, otherwise not. If the consistency test is not passed, the original values in the pair wise comparison matrix must be revised by the decision maker. Here CR of the matrix A can be calculated as:
CR and CI –
For . , in matrix A then .
– 0.126883
For RI=1.35 (from Table 2) the value of .
. .
For matrix A as, CR<0.1 so this comparison is acceptable.
Table: 4 Weight of aesthetic attributes
Aesthetic Attributes Weight
Originality 0.3875 Elegant 0.1617 Family-feeling 0.0296 Modern 0.04 Masculine 0.0603 Youthful 0.2298 Dynamic 0.0912
6. Result and discussion:
Based on literature review, views of experts from areas product design and academics, and users of car, seven aesthetic attributes were selected. The analysis shows that aesthetic attribute originality, youthful and elegant are of prime importance (Table 4). The results of a survey on “Aesthetic attributes of car profile” clearly shows the importance of integration of fuzzy approach with AHP; in prioritizing of customer requirements.
7. Conclusion:
The Fuzzy AHP approach is very useful methodology to convert user’s emotions into usable design data. The selection of the aesthetic attributes was made based on the review of the literature, discussion with the experts in the area of product design and survey data received from the users. It was found from the pair wise comparison of the aesthetic attributes that originality, youthful and elegant are of prime importance.
References: Journal:
[1] Ayag, Z. and Ozdemir, R.G. A fuzzy AHP approach to evaluating machine tool alternatives. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 17, 2006, 179-190.
[2] Baron, L., Achiche, S. and Balazinski, M. Fuzzy decision support system knowledge base generation using a genetic algorithm. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning, 28, 2001, 125–148.
[3] Buckley, J. J. Fuzzy hierarchical analysis. Fuzzy sets systems, 17, 1985, 233-247.
[4] Chuang, M.C., Chang, C.C. and Hsu, S.H. Perceptual factors underlying user preferences toward product form of mobile phones. International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, 27, 2001, 247-258.
[5] Chang, Y.H. and Yeh, C.H. A new airline safety index. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 38 (4), 2004, 369–383. [6] Chan, F.T.S., Kumar, N., Tiwari, M.K., Lau, H.C.W. and Choy, K.L. Global supplier selection: A fuzzy-AHP approach. International
Journal of Production Research, 46, 2007, 3825-3857.
[7] Deng, H. Multi-criteria analysis with fuzzy pair wise comparison. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning, 21, 1999, 215-231. [8] Demirtas, E.A., Anagun, A.S. and Koksal, G. Determination of optimal product styles by ordinal logistic regression versus conjoint
analysis for kitchen faucets. International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, 39, 2009, 866-875.
[9] Hsiao, S.W. and Liu, M.C.A morphing method for shape generation and image prediction in product design. Design Studies, 23, 2002.
[10] Khurana, M.K., Mishra, P.K. and Singh, A.R. Barriers to information sharing in supply chain of manufacturing industries. International Journal of Manufacturing System, 1 (1), 2011, 9-29.
[11] Kahraman, C., Cebeci, U. and Ulukan, Z. Multi- criteria supplier selection using fuzzy AHP. Logistics Information Management, 16, 2003, 382-394.
[12] Lavie, T. and Tractinsky, N. Assesing dimensions of perceived visual aesthetics of web sites. International Journal of Human-Computer studies, 60, 2004, 269-298.
[13] Liu, Y. Engineering aesthetics and aesthetics ergonomics: Theoretical foundation and dual process methodology. Ergonomics , 46 (11/14), 2003, 1273-1292.
[14] Nagamachi, M. Kansei Engineering: A new ergonomic consumer oriented technology for product development. International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, 15 (1), 1995, 3-11.
[15] Rashid, A., Mac Donald, B.J. and Hashmi, M.S.J. Evaluation of aesthetics of products and integrating of the finding in a proposed design system. Journal of Material Processing Technology, 153-154, 2004, 380-385.
[16] Schenkman, B.N. and Jonsson, F.U. Aesthetics and preferences of web pages. Behavior and Information Technology, 19 (5), 2000, 367–377.
[17] Shieh, M.D. and Yang, C.C. Multiclass SVM-RFE for product form feature selection. Expert Systems with Applications, 35(1–2), 2008, 531–541.
[18] Talia, L. and Noam, T. Assessing dimensions of perceived visual aesthetics of web sites. International Journal of Human–Computer Studies, 60, 2004, 269–298.
[19] Yeh, C.H., Deng, H. and Chang, Y.H. Fuzzy multicriteria analysis for performance evaluation of bus companies. European Journal of Operational Research, 126, 2000, 459–473.
Books:
Nagamachi, M. Kansei Engineering. Kaibundo Publishing Company, Tokyo, 1989. Saaty T.L. The Analytic Hierarchy Process, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1980. Proceedings: