Collisionless Dissipation of Radio-Frequeny Waves
in Axisymmetri Tokamak Plasmas
N.I. Grishanov 1
,C.A. de Azevedo 2
, and J.P.Neto 1;2
1
LaboratorioNaional deComputa~aoCienta, 25651-070Petropolis,Brazil
2
UniversidadedoEstadodoRiodeJaneiro,20550-013 Rio deJaneiro,Brazil
Reeivedon26June,2001
Contributionsoftrappedanduntrappedpartilestothetransverseandlongitudinaldieletri
per-mittivityelementsarepresentforradio-frequenywavesinatokamakwithirularross-setionsof
themagnetisurfaesand arbitraryaspetratio. Imaginarypartsofthelongitudinalpermittivity
elementsare important to estimatethe wave powerabsorbed by eletronLandaudamping (e.g.,
during the plasma heating and urrent drive generation) in the frequeny range of Alfven, fast
magnetosoni, and lowerhybridwaves. Whereas, imaginary parts of the transverse permittivity
elementsareneessarytoestimatetheylotron-resonantwavedissipationatthefundamental
y-lotronfrequenyofionsand/oreletrons. Thedissipatedwavepowerisexpressedbysummation
oftermsinludingtheseparateontributionsoftrappedanduntrappedpartilestotheimaginary
partsofboththe diagonal andnon-diagonalelementsofthedieletri permittivity. Theonrete
omputationsarearriedoutforatokamakplasmawiththemainTCABRparameters.
I Introdution
Tokamaks(boththelargeandsmall sizes)representa
promisingalternativeroutetomagnetithermonulear
fusion. To ahieve the fusion onditions in these
de-vies anadditionalplasma heatingmust beemployed.
One of the eetive heating shemes an be realized
viatheradio-frequenywaves. Topreditandanalyze
the powerabsorbed we should know the kineti wave
ondutivity (or dieletri) tensor. For large aspet
ratio tokamaks, solution of the Vlasov equation and
dieletri tensor evaluation are developed quite
om-pletely(see,e.g.,Refs. [1-4℄) byusing thesmallnessof
theinverseaspetratio: a=R<<1,whereaandRare
theminorand majorradiioftheplasmatorus. Inthis
paper,thetransverseandlongitudinaldieletritensor
elements are present for waves in a two-dimensional
axisymmetri tokamak withirularmagnetisurfaes
in theaseof arbitrary a=R<1. This model is
espe-iallysuitedtheTCABR tokamak(havingtheirular
plasma ross-setions)at the University ofS~aoPaulo,
as well as other tokamaks with small elongation and
triangularity.
II Plasma Model
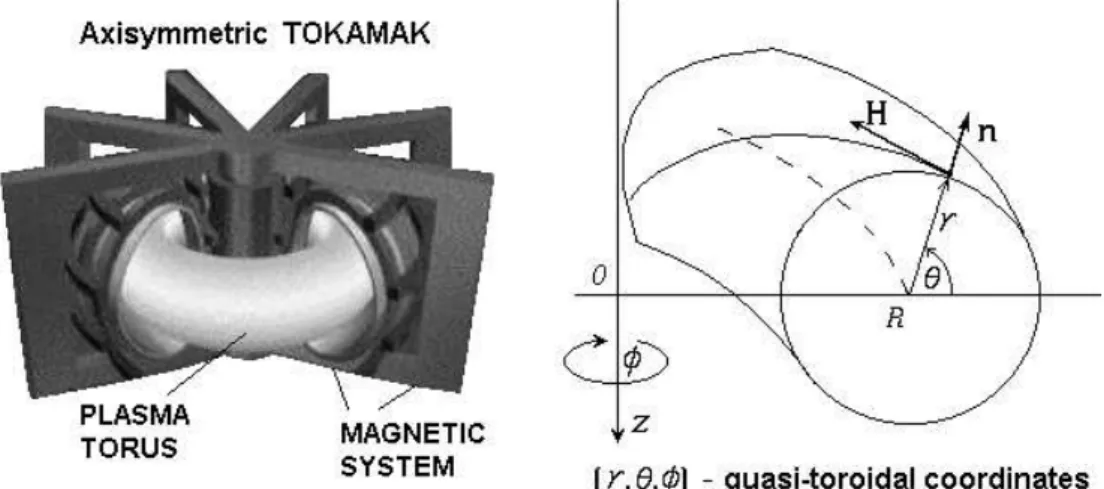
To desribe an axisymmetri tokamak with irular
(r;;), seeFig. 1,onnetedwith theartesian
oor-dinatesas
x=(R+ros)os;
y=(R+ros)sin;
z= rsin; (1)
where r and R are the minor and major radii of the
magnetisurfae,andarethepoloidalandtoroidal
angles, respetively. The poloidal, H
0
, and toroidal,
H
0
,projetionsofanequilibriummagnetieldH,in
thisplasmamodel,are,respetively,
H
0 (r;)=
H
0 (r)
1+os ;
H
0 (r;)=
H
0 (r)
1+os
= r
R
; (2)
satisfying the onditions: div H = 0 and (rotH)
r =
nH=0. Inthe(r;;) oordinates, themodulus of
anequilibrium magnetieldHisgivenas
H(r;)= q
H 2
0 +H
2
0
1+os
; (3)
where H
0
(r) and H
0
(r) orrespond to the toroidal
Figure1. Thequasi-toroidaloordinates(r;;)for anaxisymmetritokamakplasmawithirularmagnetisurfaes. nis
theunitvetornormaltothetoroidalmagnetisurfaesr=onst.
Detailedevaluationofthetransverseand
longitudi-nalpermittivityelementshasbeenreportedreentlyin
Refs. [5, 6℄. Inontrastto Ref. [7℄ related to it, the
Vlasovequationwassolvedseparatelyfortrappedand
untrappedpartilesusingi)thesetofoordinateswith
the"straight" magnetield lines, by introduingthe
newvariable 0
insteadofas
( 0
)=2artg "
r
1+
1
tg
0
2
#
; (4)
and ii) new time-like variables
u (
0
) and
t (
0
) [the
third kindellipti integrals,Eqs. (15, 16)℄ forthe
un-trappedandtrappedpartiles,respetively,todesribe
thebouneperiodimotionofeahpartilegroupalong
the magnetield line. As aresult ofthis proedure,
theexpressionsofthedieletritensorelementsbeome
simplerthanthosederivedinRefs. [7,8℄.
III Dieletri Tensor Elements
To evaluate the dieletri harateristis we use the
Fourierexpansionsoftheperturbedurrentdensityand
eletrieldin 0
:
j(r; 0
)
1 os 0
= 1
X
m j
m
(r)exp (im 0
);
E(r; 0
)
1 os 0
= 1
X
m 0
E m
0
(r)exp (im 0
0
): (5)
Note, the normal and binormal (to H) urrent
den-sityomponents, j
n and j
b
in our notation, are equal
to j
n = j
1 +j
1 and j
b = i(j
1 j
1
). The
ex-pressionsfor j
l j
l=1
areonvenientto analyzethe
y-lotronresonaneeets atthefundamental ylotron
frequeny of both the ions (if l = 1) and eletrons
(if l = 1) in the expliit form. Aordingly, to
esti-matethej
l
-omponentsweusetheleft(right)-hand
po-larizatedE
l
-projetionsonnetedwith E
n and E
b as
E
l = E
n ilE
b
. As a result, the whole spetrum of
E-eld(by P
m 0
)ispresentinagiven(bym)harmoni
oftheurrentdensity:
4i
! j
m
l (r)=
4i
!
j m
l;u (r)+j
m
l;t (r)
= 1
X
m 0
h
m;m
0
l;u
(r)+ m;m
0
l;t (r)
i
E m
0
l
(r); (6)
4i
! j
m
k (r)=
4i
! h
j m
k;u (r)+j
m
k;t (r)
i
= 1
X
m 0
h
m;m
0
k;u
(r)+ m;m
0
k;t (r)
i
E m
0
k
(r): (7)
Here m;m
0
l;u ;
m;m 0
l;t
and m;m
0
k;u ;
m;m 0
k;t
aretheontributionsofuntrapped(u)andtrapped(t)partilestothetransverse
andlongitudinaldieletripermittivityelements,respetively:
m;m
0
l;u =
0:5! 2
L r
p
1+
2:5
!h
v
T p
1
1
X Z
1
0
d
(
o +)
2 Z
+1
1 u
4
exp u 2
A m
p;l A
m 0
p;l du
(p+nq
t
lÆ lq)u U
l ()
m;m 0 l;t = 0:5! 2 L r p 1+ 2:5 !h v T p 1 1 X p Z 1 0 d (1+ o ) 2 Z +1 1 u 4 exp u 2 pu V l () B m p;l ^ B m 0 p;l du; (9) m;m 0 k;u = 2! 2 L r 2 p o (1+)
3 h 2 v 2 T (1 ) 1 X p Z 1 0 ( o ; 2 ;)C
m p C m 0 p
(p+nq
t ) 2 ( o +) 1:5
1+2u 2 p +2i p u 3 p W(u p ) d (10) m;m 0 k;t = 4! 2 L r 2 p o (1+)
3 h 2 v 2 T (1 ) 1 X p=1 Z 1 0 ( o ; 2 ;)D m p D m 0 p p 2 (1+ o ) 1:5
1+2v 2 p +2i p v 3 p W(v p ) d: (11)
Herewehaveusedthefollowingdenitions
A m
p;l
(u;)= Z
0 os
(m+nq
t
lÆ) lg() (p+nq
t lÆ lg) u (;) u (;) l r p 2( o +) h uv T p
(1+) F 2 ; K() u (;) u (;) ) s 1+ o sin 2 2
1 sin 2 2 d; (12) ^ B m p;l
(u;)= Z t 0 os (
(m+nq
t
lÆ) lg() p t (;) 2 t (; t ) l r p 2(1+ o ) h uv T p
(1+) " F arsin r 1 sin 2 ! ; ! K() t (;) t (; t ) #) s 1+ o sin 2 2 sin 2 2 d; (13) B m p;l
(u;)= ^
B m
p;l
(u;)+( 1) p
^
B m
p;l
( u;); W(z)=e z 2 1+ 2i p Z z 0 e t 2 dt ; (14) u (;)= Z 2 0 d (1+ o sin 2 ) p
1 sin 2 = o ; 2 ; ; o = 2 1 ; (15) t (;)= o ;arsin 1 p sin 2 ; ; t
()=2arsin p ; (16) C m p ()= Z 0 os
(m+nq
t
) (p+nq
t ) u (;) u (;) d; = e q H 2 0 +H 2 0 M ; (17) D m p ()= Z t 0 os
(m+nq
t ) p
t (;) 2 t (; t ) d+ +( 1) p 1 Z t 0 os
(m+nq
t )+p
t (;) 2 t (; t ) d; (18) U l ()= r p 2( o +) h v T p
(1+)
[!(1+)
u
(;)+l
K()℄; h
= H 0 q H 2 0 +H 2 0 ; (19) V l ()= 2r p 2(1+ o ) h v T p
(1+)
[!(1+)
t (;
t )+l
K()℄; h
= H 0 q H 2 0 +H 2 0 ; (20) u p ()= !r p
2(1+)(
o +)
jp+nq
t jh v T p u
(;); F(;)=
Z
0
d
p
1 sin 2 ; (21) v p ()= 2!r p
2(1+)(1+
o )
p h
v T p t (; t
); K()=F 2 ; ; v T = r 2T M ; (22) ! 2 L = 4Ne 2 M ; q t = h h 1 p 1 2
; Æ=
1:5h
p
1
2
; g=
Note, m;m
0
l;u ;
m;m 0
l;t ;
m;m 0
k;u ;
m;m 0
k;t
desribethe
ontri-bution ofanykindofuntrappedandtrappedpartiles
to the dieletri tensor elements. The orresponding
expressions for plasma eletrons and ions an be
ob-tained by replaing T (temperature), N (density), M
(mass) , e (harge)bythe eletron T
e ;N
e ;m
e ;e
e and
ion T
i ;N
i ;M
i ;e
i
parameters, respetively. To obtain
the total expressions of the permittivity elements, as
usual, itis neessaryto arryoutthesummation over
allspeiesofplasmapartiles.
Sinethephase oeÆientsC m
p
()and D m
p
(), for
thelongitudinalpermittivityelements,areindependent
ofthewavefrequeny, !,andthepartileenergy,v,it
ispossibletheanalytialLandauintegrationofthe
per-turbeddistributionfuntions of boththetrapped and
untrappedpartilesinveloityspae. Asaresultofthis
proedure,inontrasttoRef. [7℄wherethe
orrespond-ingphaseoeÆientsdependonv, m;m
0
k;u
and m;m
0
k;t are
written by the summation of boune-resonant terms
inluding the well known plasma dispersion funtion
W(z), i.e, by the probability integral of the omplex
argument, Eq. (14). After this,the numerial
estima-tionsofboththerealandimaginarypartsofthe
longi-tudinalpermittivityelementsbeomesimpler,andtheir
dependeneonthewavefrequeny!isdenedonlyby
theargumentsu
p
(;!;:::)andv
p
(^;!;:::)oftheplasma
dispersionfuntions, W(u
p
) and W(v
p
). Introdution
oftheW(z)funtion,inthestandardintegralformEq.
(14),beamepossiblesinethenalequationsforf s
0;u
andf s
0;t
(seeRef. [6℄)havebeenreduedtotherst
or-derdierentialequationswithrespettoonevariable
u
or
t
,respetively,withtheonstantoeÆientsinthe
left-handside. Anotherform oftheoeÆientsC m
p ()
and D m
p
() hasbeendone in Appendix by theJaobi
ellipti funtions, whih also anbeonvenientin the
omputeralulations.
The boune resonane onditions of the eetive
wave-partileinterationsinatokamak plamsa,as
fol-lowsfromEqs. (4)and(5),arethesamethosederived
inRef. [8℄,andan berewrittenas
(p+nq
t
lÆ lg)u U
l
()=0;
l;p=0;1;2;:::
foruntrappedpartiles,where u=v=v
T ,and
pu V
l
(^)=0; l;p=0;1;2;:::
forthetrappedpartiles.
Sinethewholespetrumof theE-eld(by P
1
m 0
)
ispresentinagiven(bym)urrentdensityharmoni,
seeEqs. (6)and(7),itisneessarytotakeintoaount
thatthepoloidaleigenmodenumbersexitedina
toka-makplasmamaydierfromthebasimodenumber(s)
generated by the antenna system. Moreover, the
ex-itation/dissipation of E (m
0
)
k
-harmonis with m 0
6= m
anleadto theadditionalheating ofboththetrapped
and untrapped partiles and destabilize a wide lass
of the low-frequenydrift-Alfveneigenmodes near the
so-alled rational magneti surfaes, where the
longi-tudinal wave vetor omponent hanges its sign, i.e.,
where m+nq
t
(r)=0. This meansthat one-mode
ap-proximation(over)isnotvalidtosolvetheMaxwell's
equationsin thetokamaks,inthegeneralase.
Never-theless,thereissomeinteresttoomparethedieletri
harateristis of a toroidal plasma (obtained by a
two-dimensionalonsiderationoftheproblem)andthe
orresponding harateristis of a ylindrial plasma
model (one-dimensional onsideration), whih is well
developed and often used for the study of the
radio-frequeny plasma heating and urrent drive problems
in tokamaks in the frequeny range of Alfven, lower
hybridand ion-ylotronwaves.
IV Wave Dissipation
One of the main mehanisms of the radio-frequeny
plasma heating is the eletron Landau damping of
wavesduetotheCherenkovresonaneinterationofE
k
withuntrappedandtrappedeletrons. TheCherenkov
resonaneonditionsaredierentfortrappedand
un-trappedpartilesintokamakgeometryandhave
noth-inggeneralwiththewave-partileresonaneondition,
! =(h
=r)(m+nq
t )v
k
, in the ylindrialmagnetized
plasmas. As a result, after averagingin t and 0
and
aountingfor Eq. (7), thewavepower dissipated by
the eletronLandaudamping, P
k
=Re(E
k j
k
), anbe
estimatedas
P
k =P
k;u +P
k;t =
!
8 1
X
m 1
X
m 0
Im m;m
0
k;u
+Im m;m
0
k;t h
ReE m
k ReE
m 0
k
+ImE m
k ImE
m 0
k i
(24)
where,asfollowsfromEqs. (10)and (11),
Im m;m
0
k;u =
4! 2
L r
2 p
o (1+)
2:5
h 2
v
2
T (1 )
1
X
1
(p+nq
t )
2 Z
1
0 (
o ;
2 ;)
(
o +)
1:5 u
3
p
exp( u 2
p )C
m
p C
m 0
p
Im m;m
0
k;t =
8! 2
L r
2 p
o (1+)
2:5
h 2
v
2
T (1 )
1
X
p=1 1
p 2
Z
1
0 (
o ;
2 ;)
(1+
o )
1:5 v
3
p
exp( v 2
p )D
m
p ()D
m 0
p
()d; (26)
d
are the ontribution of untrapped, Im m;m
0
k;u
, and
trapped, Im m;m
0
k;t
, partiles to the imaginary partof
the longitudinal permittivity elements: Im m;m
0
k =
Im m;m
0
k;u
+Im m;m
0
k;t
. Thus, for the given !, m, n, r
and E-eld amplitudes, the parts P
k;u and P
k;t dier
bythedierentontributionsofuntrappedandtrapped
eletronstoIm m;m
0
k
elements.
Thereis anotherimportantplasmaheating
meha-nismdue to the ylotron wavedampingin therange
ofion/eletronylotronfrequenies,whentheplasma
partilesinterateetivelywiththetransverseeletri
eld omponents, E
l
. Under the ylotron resonane
heating(onthefundamentalharmonis)thepower
ab-sorbed,P
l
=Re(E
l j
l
),anbeexpressedas
P
l =P
l;u +P
l;t =
!
8 1
X
m 1
X
m 0
Im m;m
0
l;u
+Im m;m
0
l;t h
ReE m
l ReE
m 0
k
+ImE m
l Im E
m 0
l i
: (27)
d
As was noted above, l = 1 orresponds to the
wave power absorbed under the ion-ylotron
reso-nane heating when !
;i
; whereas l = 1 should
be used under the eletron-ylotron plasma heating
when ! j
;e
j. Theontributions ofuntrappedand
trappedpartiles to theimaginaryparts of the
trans-versepermittivityanbereadilyderivedfromEqs. (8)
and (9) by using the well known residue (or Landau
rule)method.
V Numerial Results
Now, we alulate numerially the ontribution of
trappedanduntrappedeletronstoIm m;m
0
k
. Tohave
someanalogywith theone-mode(ylindrial)
approx-imation of the wave dissipation by eletron Landau
damping, let us estimate the diagonal (m = m 0
)
ele-ments Im m;m
k;u
and Im m;m
k;t
. The orresponding loal
ylindrialapproximation,Im m;m
k;
, hasthenextform
Im m;m
k; =
2 p
r 3
! 2
po !
h 3
jm+nq
t j
3
v 3
T exp
! 2
r 2
h 2
(m+nq
t )
2
v 2
T
: (28)
d
TheestimationsofIm m;m
k;u ,Im
m;m
k;t
andIm m;m
k; are
arried out for waves with mode numbersn = 4and
m=1inaplasmawiththemainTCABR-parameters:
R = 0:61 m, a = 0:18 m, H
0
= 1 T, q
t (r) =
1:1=(1 0:7r 2
=a 2
),N(r)=310 19
(1 0:95r 2
=a 2
)m 3
,
T(r) = 1000(1 0:99r 2
=a 2
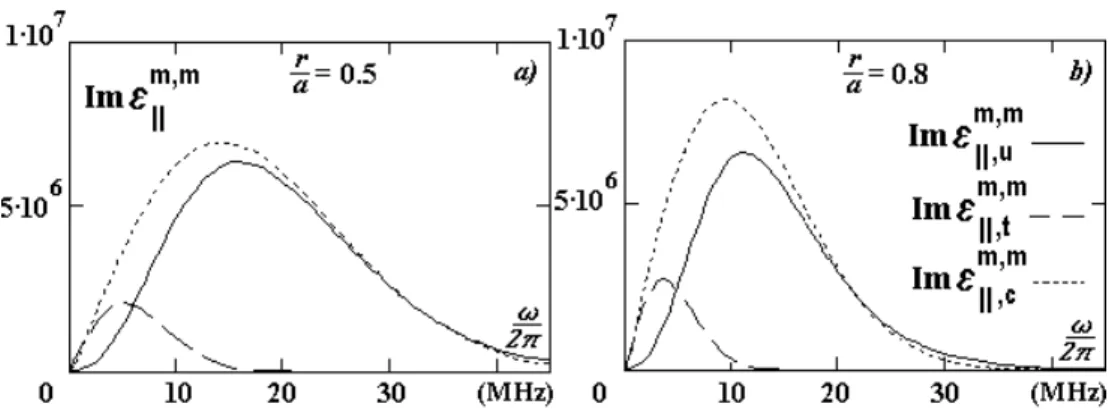
) eV. As shown in Fig. 2,
the ontributions of untrapped and trapped eletrons
to Im m;m
k
depend substantiallyon and !. By
om-paring Im m;m
k;u
and Im m;m
k;t
, we see that the Landau
damping of waves with a high phase veloity, v
ph =
!r=[h
(m+nq
t )℄ > v
T
(e.g., lower hybrid waves), is
duetothebouneresonantinterationwithuntrapped
eletrons. Itmeansthat,undertheLower-Hybrid
Res-onaneHeating,thefavorableonditionsanbereated
totransformthewavemomentumintothemomentum
Figure2. Theontributionof untrapped(solid lines), Im m;m
k;u
, and trapped(long-dashed lines),Im m;m
k;t
, eletronsto the
imaginarypartofthelongitudinalpermittivityinatokamakplasmaasafuntionofwavefrequeny,!,fordierentmagneti
surfaes: a)r=a=0:5; b)r=a=0:8.
Note, for both the toroidal and ylindrialplasma
models,Im m;m
k;u
andIm m;m
k;
areexponentiallysmallfor
thefastwaveswithv
ph >>v
T
. However,thewave
dis-sipationbyuntrappedeletronsanbelargerthanthe
orrespondingylindrialapproximationsatthe
exter-nalmagnetisurfaes,wherev
ph =v
T
23.
Another feature of wave-partile interation in a
toroidalplasmaistheroleoftrappedpartilesbeomes
substantialfor the slow waves with v
ph << v
T under
the ondition when ! is omparable with the boune
frequenyofthethermaleletrons.Moreover,thewaves
(usually,low-frequenywaves)interateetivelywith
the trapped eletrons at the external magneti
sur-faes, wherethefration oftrapped partilesinreases
as p
2=(1+). Theeetiveheating of trapped
ele-trons(Fig. 3) ispossibleintokamaksusingtheAlfven
waves,whentheloalAlfvenresonaneonditionis
re-alized near the plasma boundary (or in the region of
moderateradii).
Figure3. Theradial strutureofIm m;m
k;u
(solidlines),Im m;m
k;t
(long-dashed lines),andIm m;m
k;
(short-dashed lines)inthe
TCABRtokamakplasmafordierentlevelsofwave(generator)frequeny: a)!=2=4MHz;b)!=2=5:5MHz.
VI Conlusion
The kineti transverse (8, 9) and longitudinal (10,
11)permittivity elementshavebeenderived for
radio-frequenywavesbysolvingVlasovequationfortrapped
and untrapped partiles in an axisymmetri toroidal
plasma with irular magneti surfaes and arbitrary
aspetratio. Thesedieletritensoromponentsare
ex-pressedbysummationofboune-resonantterms,whih
inlude the double integration in veloity spae, the
resonantdenominators,thephaseoeÆients,the
stan-dardelementaryandelliptifuntions. Itisshownthat
plasmadispersionfuntion, ortheprobabilityintegral
of theomplexargument)ispossibleonly forthe
lon-gitudinalpermittivity.
Imaginarypartsofthelongitudinalpermittivity
ele-mentsareimportanttoestimatethepowerabsorbedby
eletronLandaudamping(e.g.,duringtheplasma
heat-ingandurrentdrivegeneration)inthefrequenyrange
of Alfven, fastmagnetosoni,and lowerhybridwaves.
Whereas,imaginarypartsofthetransversepermittivity
elementsare neessarytoestimate the ylotron
reso-nantwavedissipationatthefundamentalylotron
oftermsinludingtheseparateontributionsoftrapped
anduntrappedpartilestotheimaginarypartsofboth
thediagonalandnon-diagonalelementsofthedieletri
permittivity.
Thedieletritensor omponents, Eqs. (8-11), an
beused forboththe Large(<<1) and Low (<1)
Aspet Ratio Tokamaks to analyze the nite- eets
in the frequeny range of Alfven, Fast Magnetosoni,
LowerHybrid,and Ion/EletronCylotronWaves.
Appendix:
Phase CoeÆients by the Jaobi Ellipti F
un-tions
ThephaseoeÆientsin Eqs. (8-11) anbe
alu-latedbyintroduingtheJaobielliptifuntions,whih
areasthestandardfuntions for advaned versions of
suh mathematial programs as Mathad,
Mathemat-ia, Maple. In partiular, forthe longitudinal
(paral-lel) dieletri permittivity the oeÆients C m
p
() and
D m
p
()anberepresentedas
C m
p ()=
Z
K()
K() os
"
2(m+nq
t
)am(;w) (p+nq
t )
^
(
o ;w)
^
(k
o ;K())
#
dn(;w)dw (29)
D m
p ()=
p
Z
2K()
2K() os
2(m+nq
t )arsin
p
sn(;w)
p 0:5
^
(
o ;w)
^
(
o
;K()) #
n(;w)dw (30)
Here theorrespondingJaobielliptifuntions are
sn(;w)= 2
p
K() 1
X
l=0 ^ q
l+1=2
()
1 q^ 2l+1
() sin
(2l+1)w
2K() ;
n(;w)= 2
p
K() 1
X
l=0 ^ q
l+1=2
()
1+q^ 2l+1
() os
(2l+1)w
2K() ;
dn (;w)=
2K() +
2
K() 1
X
l=1 ^ q
l
()
1+q^ 2l
() os
lw
K() ;
am(;w)= u
2K() +
1
X
l=1 2^q
l
()
l(1+q^ 2l
()) sin
lw
K() ;
d
where theparameterq^isequalto
^
q()=exp
K(1 )
K()
;
and theelliptiintegralof thethird kindinthe (;w)
variableshasbeendoneas
^
(
o ;w)=
Z
w
0
du
1+
o sn
2
(;u) :
ThephaseoeÆientsA m
p;l
(u;) and B m
p;l
(u;), for
thetransversepermittivityelements,mayberewritten
newwvariable, insteadoftheanglevariable 0
:
w( 0
)= Z
0
=2
0
d
p
1 sin 2
foruntrappedpartiles,and
w( 0
)= Z
arsin 1
p
sin
0
2
0
d
p
1 sin 2
Referenes
[1℄ V.N. Belikov, Ya.I. Kolesnihenko, A.B. Mikhailovskii
andV.A.Yavorskii,Sov.J.PlasmaPhys.3,146(1977).
[2℄ F.M.Nekrasov, Sov.J.PlasmaPhys.18,520(1992).
[3℄ F. Porelli, R. Stanieviz, W. Kernerand H.L. Berk,
Phys.Plasmas1,470(1994).
[4℄ S.V.Kasilov, A.I. Pyatak and K.N. Stepanov, Plasma
Phys.Reports24,465(1998).
[5℄ N.I.Grishanov, C.A.deAzevedoandJ.P.Neto,X Int.
Congress onPlasma Phys. & 42nd Annual APS-DPP
Meeting, Quebe,Canada,2000, Vol.I,p.13(2001).
[6℄ N.I.Grishanov,C.A.deAzevedoandJ.P.Neto, Plasma
Phys.ControlledFusion43,1003(2001).
[7℄ F.M.Nekrasov,A.G.Elmov,C.A.deAzevedo,A.S.de
Assis and J.P.Neto, Plasma Phys.Controlled Fusion
43,727(2001).
[8℄ N.I. Grishanov and F.M. Nekrasov, Sov. J. Plasma