Toxic and Metabolic Myelopathies
Texto
Imagem

Documentos relacionados
MRI Sagital T2WI, Axial T1WI and Sagital T1WI postcontrast (Gd-DTPA): Multiple cystic lesions in intradural- extramedullary situation leading to spinal cord compression..
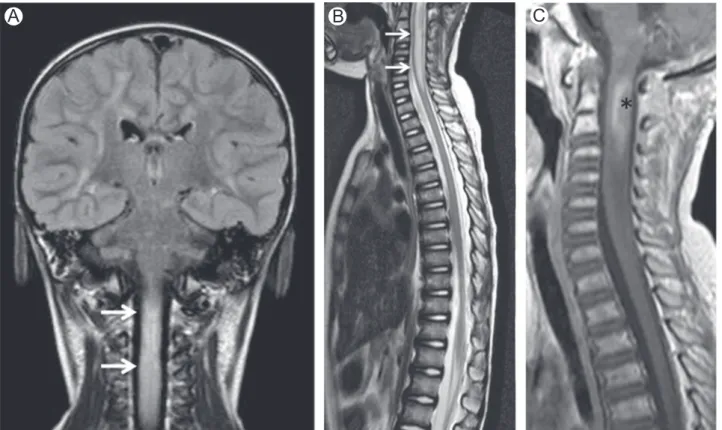
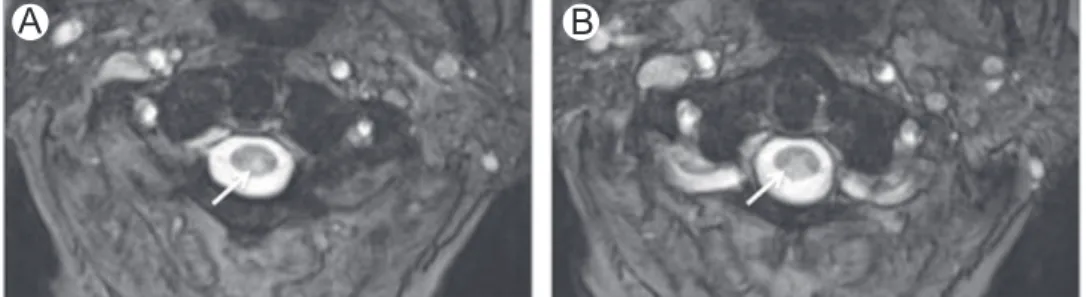
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain (Fig 1A) and spinal cord (Fig 1B) showed areas of high signal intensity on T2 weighted and luid attenuation inversion recovery (FLAIR)
Brain MRI re- vealed right frontal and bilateral thalamic lesions with increased signal in T2-weighted and lair images (Figs A, B, C, D).. Cerebrospinal luid analysis showed mild
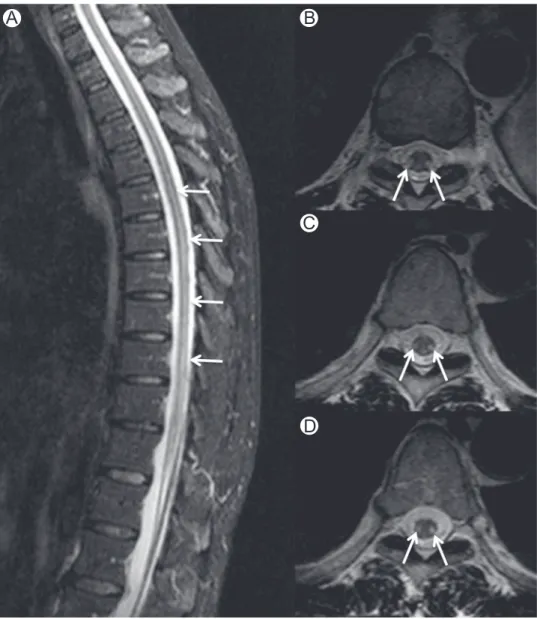
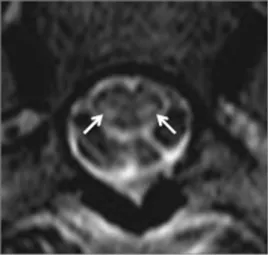
Spinal cord MRI: (A) extensive swelling of spinal cord, caused by vacuolization of myelin; (B) subtle contrast enhancement of posterior column; (C) cross-section images of
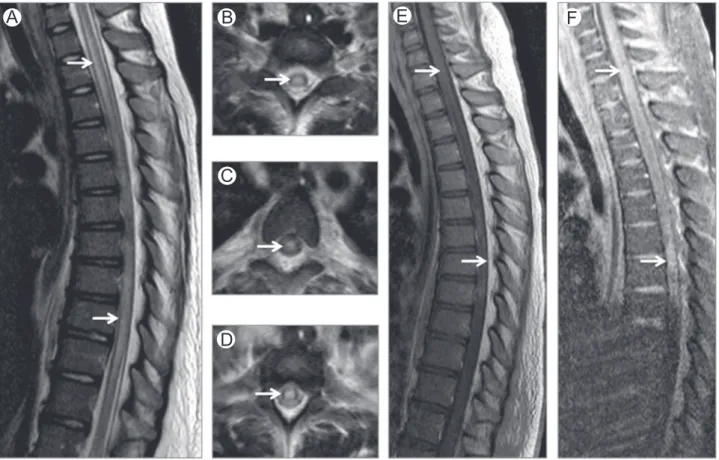
Diagnosis of SMR is usually presumptive, relying on a positive epidemiology and pertinent neurological picture (spinal cord and/or nerve root involvement, most often the lower
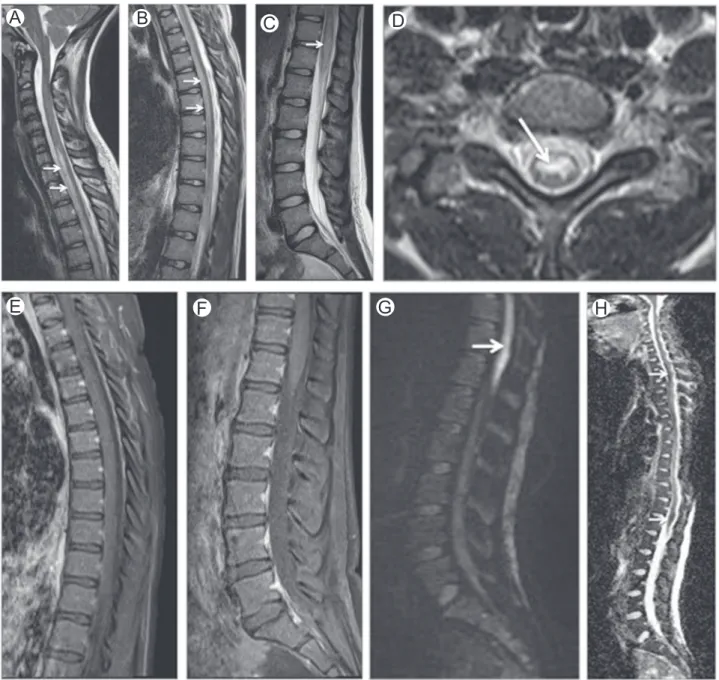
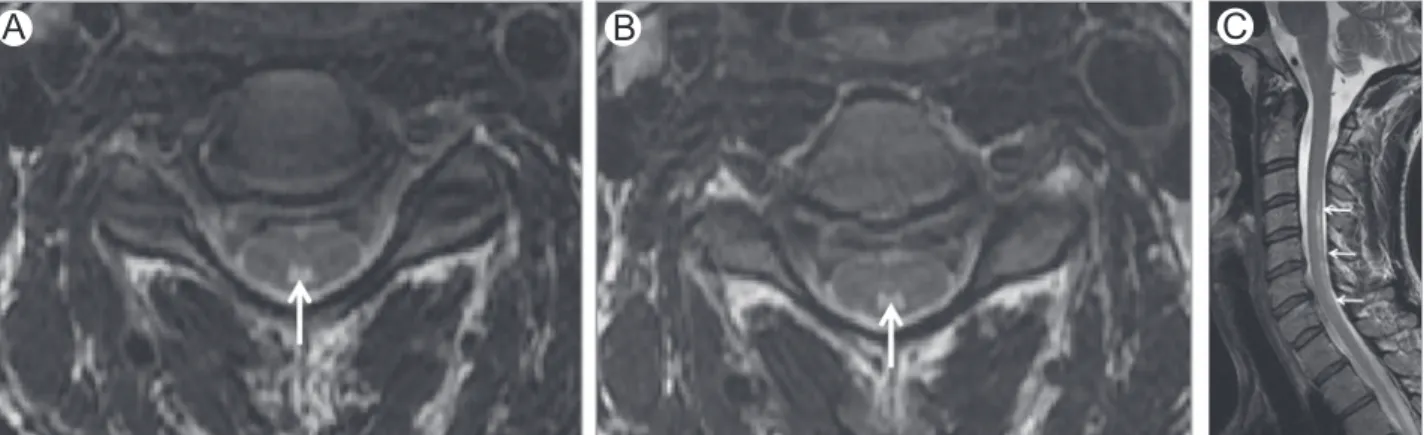
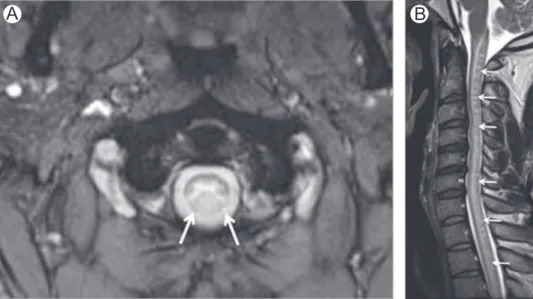
Brain and spinal cord magnetic resonance imaging studies showed: (A) infratentorial and upper cervical spinal cord atrophy (especially in medulla oblongata) with symmetrical areas
(A) CT, bilateral posterior parietal and frontal cortico and subcortical hypo- dense lesions; (B) MRI, FLAIR, bilateral temporo-occipital hyperintense lesions; (C-D) MRI,
DTI correlates of cognition in conventional MRI of normal-appearing brain in patients with clinical features of subacute combined degeneration and biochemically proven vitamin