www.ecmjournal.org MJ Stoddart et al. Editorial
i
European Cells and Materials Vol. 24 2012 (pages i-ii) DOI: 10.22203/eCM.v024a00 ISSN 1473-2262
*Corresponding Author: Martin J. Stoddart
Musculoskeletal Regeneration Program, AO Research Institute,
Clavadelerstrasse 8, 7270 Davos Platz, Switzerland
Tel: 0041-81-414-2448 Fax: 0041-84-414-2288 Email: martin.stoddart@aofoundation.org
There are various strategies that can be adopted when performing in vitro experiments with primary cells such as mesenchymal stem cells. It is generally accepted that multiple donors need to be investigated to take into account donor to donor variability; this is especially critical when investigating primary human cells. However, increasingly it is being seen that studies are pooling the cells from multiple donors prior to performing the experiment. This has obvious advantages but also many disadvantages, the greatest being loss of statistical power.
Pooling donors reduces variability within, and between, experiments. In some cases, such as the allogenic transplantation of primary cells, the pooling of cells may be a necessity due to the low numbers of harvested cells.
To overcome the loss of statistical power, multiple experiments using various donor pools can be performed. When the experiment is of long duration, as is often the case in tissue engineering studies, pooling the cells offers the opportunity to perform a large experiment with multiple replicates.
Statistically speaking, each independent experiment is an n = 1 and the replicates are an indication of measurement variation. While it is sometimes argued that three independent experiments using the same pool of cells is therefore an n = 3, this is incorrect as any variation measured would be due to subtle changes in methodology introduced during each experiment. Ultimately, one pool of cells is considered to be a single sample and any repeat experiments using the same sample will only determine slight variation between experimental procedures. It is also undeniable that valuable information is lost when taking this approach. The most obvious being, how reproducible is a phenomenon within a population? Do all donors respond to the same extent or is there a variation in the magnitude of the response? More critically as we move towards autologous cell based therapies, how many donors respond to a particular treatment and how many do not? For novel cell based therapies to be translated into a clinical setting, it is critical to know what per cent of the population are likely to respond. If it is determined that a
IN VITRO
EXPERIMENTS WITH PRIMARY MAMMALIAN CELLS:
TO POOL OR NOT TO POOL?
EDITORIAL
Martin J. Stoddart*, R. Geoff Richards and Mauro Alini
AO Research Institute Davos, Clavadelerstrasse 8, Davos Platz, Switzerland
www.ecmjournal.org MJ Stoddart et al. Editorial
reduced per cent are responders, it may then be possible to identify the sub-group of patients which will respond to treatment, thereby increasing the potential for clinical success.
By pooling cells and then performing the experimental
protocol there is the risk that the inal measured outcome
is an average of three very different populations, resulting in the description of a population which did not exist in any of the three donors. The variance measured in such an experiment is not variance between donors, it is variance caused due to subtle differences during the execution of the experiment. This can be seen in a recent paper where one of the 5 donors had a very similar pattern of response but was several orders of magnitude higher (Schätti et al., 2011). It is possible this was due to the fact that donor was very young compared to the others (17 vs. 55, 70,
45 and 66 years). While this is still to be clariied by
further experimentation, if the donors had been pooled prior to the experiment being performed it would never have been known that the variance was there. Similarly, it was recently shown that human adipose derived stromal cells increase endogenous expression of Nell-1 but the magnitude of increase is donor dependent (James et al., 2012). This information would have been lost if the cells were pooled in advance.
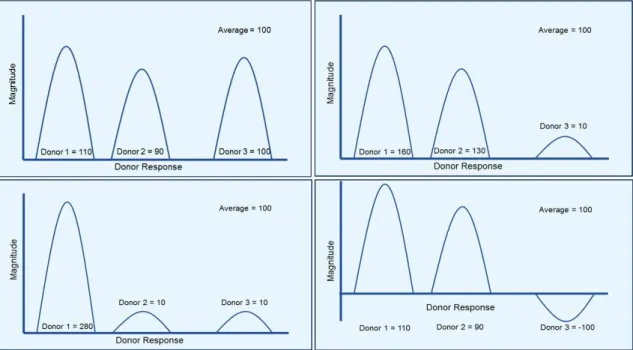
If the four donor pools proposed in figure 1 are compared they would all result in an average response of
100 but the actual frequency and amplitude of the response is unknown, and would not be detected by the using standard deviation calculations. Thus, even when presented in exactly the same way, the data from triplicates from three donors used separately in individual experiments are very different from those from triplicates with three repeated experiments from the same donor pool.
For this reason we would strongly suggest that for clarity and maximal statistical power, experiments should be performed with cells from a single donor and then repeated using a minimum of three donors.
Reference List
James AW, Pang S, Askarinam A, Corselli M, Zara JN, Goyal R, Chang L, Pan A, Shen J, Yuan W, Stoker D, Zhang X, Adams JS, Ting K, Soo C (2012) Additive effects of sonic hedgehog and nell-1 signaling in osteogenic versus adipogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stromal cells. Stem Cells Dev 21: 2170-2178.
Schätti O, Grad S, Goldhan J, Salzmann GM, Li Z, Alini M, Stoddart MJ (2011) A combination of shear and dynamic compression leads to mechanically induced chondrogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells. Eur Cell Mater 22: 214-225.