There is no association between microRNA gene polymorphisms and risk of triple negative breast cancer in a Chinese Han population.
Texto
Imagem

Documentos relacionados
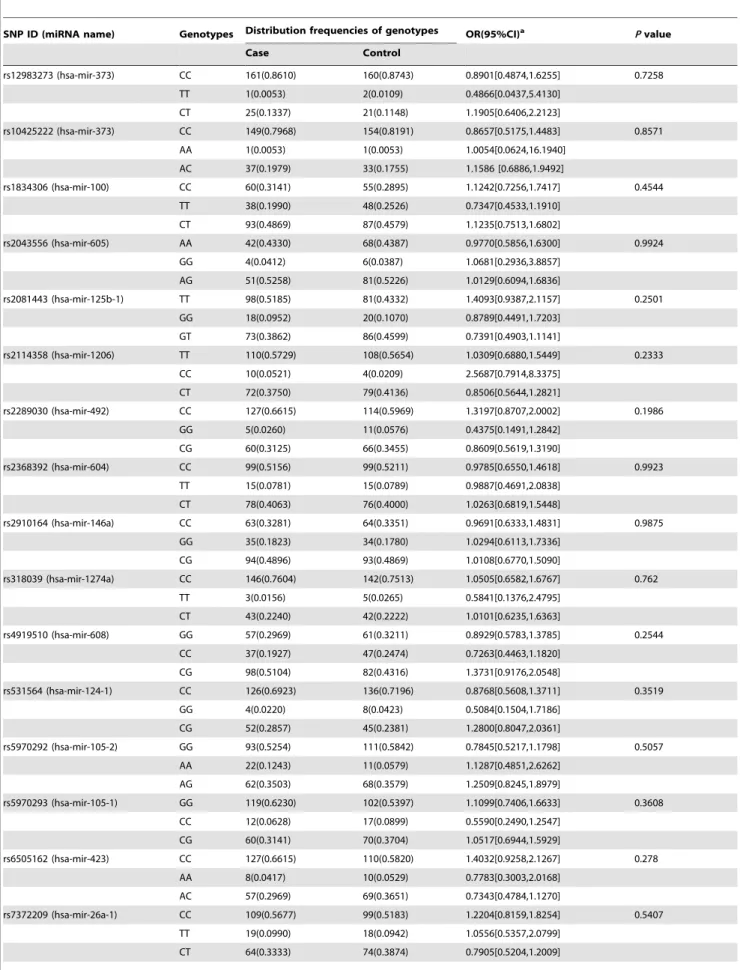
By using multiple logistic regression analysis, each of the 8 SNP associations was tested using 3 different genetic models (Dom- inant, Recessive and Additive model), in 4 types
MiRNA related single nucleotide polymorphisms (miR-SNPs), defined as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in miRNA genes, miRNA binding site and miRNA processing machinery,
Although all SNPs lacked an overall association with breast cancer, rs6788895 was found to be associated with ER-positive breast cancer and was previously reported to be associated
To explore potential interactions between the tagSNPs and smoking status, we performed multiple tests to assess result consistency, including analyses of specific
However, previous studies mainly focused on limited polymorphisms, thus we carried out a case-control study in the Han Chinese population to systemically investigate the
Due to the complex functions of the CD40 pathway in the prognosis of cancer, polymorphisms of the CD40 gene that have crucial roles in the translational efficiency of the CD40
Given the association between polymorphisms in the CD28 gene region and cervical cancer risk in different populations, as well as the potential role of costimulatory molecules
Although genetic variation of two new SNPs, rs1419881 in the TCF19 gene and rs652888 in the EHMT2 gene, were not associated with the outcome of HBV infection in the Thai population,