KI NETIC PA RAM E TERS STUDY BASED ON BURN-UP
FOR IM PROV ING THE PER FOR MANCE OF RE SEARCH
RE AC TOR EQUI LIB RIUM CORE
byAtta MU HAM MAD, Masood IQBAL*, and Tayyab MAHMOOD
Nu clear En gi neer ing Di vi sion, Pa ki stan In sti tute of Nu clear Sci ence and Tech nol ogy, Nilore, Islamabad, Pa ki stan
Sci en tific pa per DOI: 10.2298/NTRP1404253M
In this study ki netic pa ram e ters, ef fec tive de layed neu tron frac tion and prompt neu tron gen er a tion time have been in ves ti gated at dif fer ent burnup stages for re search re ac tor's equi lib -rium core uti liz ing low en riched ura nium high den sity fuel (U3Si2-Al fuel with 4.8 g/cm3 of ura nium). Re sults have been com pared with ref er ence op er at ing core of Pa ki stan re search Re -ac tor-1. It was ob served that by in creas ing fuel burn-up, ef fec tive de layed neu tron fr-ac tion is de creased while prompt neu tron gen er a tion time is in creased. How ever, over all ra tio beff/L is de creased with in creas ing burn-up. Prompt neu tron gen er a tion time L in the un der study core is lower than ref er ence op er at ing core of re ac tor at all burn-up steps due to hard spec trum. It is ob served that beff is larger in the un der study core than ref er ence op er at ing core of due to smaller size. Cal cu la tions were per formed with the help of com puter codes WIMSD/4 and CI TA TION.
Key words: de layed neu tron frac tion, prompt neu tron gen er a tion time, research re ac tor, WIMSD/4, CI TA TION
IN TRO DUC TION
Ki netic pa ram e ters play im por tant role in pre -dict ing con trol and safety per for mance of any re ac tor sys tem. Ki netic pa ram e ters are a func tion of core pa -ram e ters like fuel en rich ments, fuel den sity, neu tron spec trum, core size and ge om e try, mod er a tor type and fuel com po si tion, etc. Re ac tor tran sient re sponse strongly de pends upon the ki netic pa ram e ters ra tio
beff/L [1, 2]. Val ues of ef fec tive de layed neu tron frac tion and prompt neu tron gen er a tion time vary with in creas ing fuel burnup. Changes in the ki netic pa ram e -ters de pend upon the burn-up limit and must be con sid ered in tran sient anal y sis [3, 4]. Fuel den sity vari a tion re sults in al ter ation of fuel to mod er a tor ra tio, which causes the change in neu tron en ergy spec -trum. By uti liz ing high den sity fuel, neu tron spec trum be comes hard [5] and in the hard spec trum, fast fis sion fac tor is in creased. Vari a tion in fast fis sion fac tor changes the de layed neu tron frac tion and av er age in -verse ve loc ity of neu trons which causes a change in the prompt neu tron gen er a tion time. Ef fec tive de layed neu tron frac tion beff strongly de pends on the core size [6] there fore it must be eval u ated if core size is
changed. An other fac tor that af fects the ki netic pa ram -e t-ers is th-e pos i tiv-e in s-er tion of r-e ac tiv ity du-e to which re ac tor power jumps to a higher level. Due to heat ing of fuel and cool ant, the neu tron spec trum be comes hard and vari a tions in ki netic pa ram e ters oc cur for a short time but the ef fect of this short time is neg li gi ble [7].
On im proved per for mance base, equi lib rium re search re ac tor core was pro posed uti liz ing low en -riched ura nium (LEU) high den sity fuel (U3Si2-Al) [8]. The pro posed core with high den sity fuel (uranium den sity 4.8 g/cm3) with out any changes in the stan dard
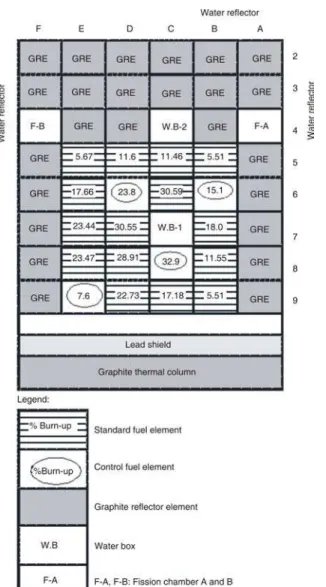
and con trol fuel el e ments of Pa ki stan Re search Re ac -tor- 1 (PARR-1) com prises 15 stan dards and 4 con trol fuel el e ments. Pro posed core is shown in fig. 1 with wa ter boxes at C7 and C4 po si tions. This is com pact and highly un der mod er ated core with 235U en rich
-ment of 19.99% [8]. From three sides it is re flected by graph ite blocks while on one side there is graph ite ther mal col umn to min i mize the neu tron leak age and flat ting the flux pro file. De ple tion anal y sis of core re -veals that it can be op er ated for 41 full power days at 9 MW con tin u ously [8]. There fore ev ery stan dard fuel el e ment will be ir ra di ated for 205 full power days while ev ery con trol fuel el e ment will be for 164 full power days [8].
Flow of ki netic pa ram e ters in a typ i cal swim -ming pool type re search re ac tor was in ves ti gated in [9] while ki netic pa ram e ters of ma te rial test re ac tor with higher den sity silicide dis per sion fuel for a 10 MW IAEA bench mark re ac tor was stud ied in [10]. Cal cu la -tion and mea sure ment of ki netic pa ram e ters of PARR-1 ref er ence op er at ing core was stud ied in [11].
In the cur rent anal y sis, burn-up de pend ency of ef fec tive de layed neu tron frac tion and prompt neu tron gen er a tion time has been stud ied for the above men -tioned equi lib rium core [8] for fur ther in ves ti ga tion of the tran sient anal y sis.
CAL CU LA TION OF beff/L
Re ac tor ki netic pa ram e ters (ef fec tive de layed neu tron frac tion and prompt neu tron gen er a tion time) have been cal cu lated for pro posed equi lib rium core uti liz ing higher ura nium den sity of 4.8 g/cm3. Burn-up
(% age of 235U) for pro posed core at be gin ning of equi -lib rium core (BOEC) and end of equi -lib rium core
(EOEC) is shown in fig. 2 and fig. 3, re spec tively. Ten en ergy groups' mi cro scopic crosssec tions were ob -tained through the use of MTR_PC26 pack age. The en ergy group struc ture used is given in tab. 1 [4, 9, 11]. All cross-sec tions were cal cu lated at 40 °C. Unit cell shown in fig. 4 [12] was se lected for gen er a tion of cross-sec tions and num ber den si ties of fuel part of stan dard and con trol fuel el e ment. Num ber den si ties and cross-sec tions gen er ated by WIMSD/4 [13] and BORGES [14] from MTR_PC26 pack age were uti -lized in CI TA TION [15] for 2-D anal y ses of the core. Ax ial buck ling of the core was em ployed in third di -men sion. All cal cu la tions were per formed with xe non in equi lib rium con di tion. Av er age val ues of ther mal and fast flux of the core were eval u ated through CI TA -TION. Fast and ther mal flux dis tri bu tions in the core con fig u ra tion are shown in fig. 5. It is clear from fig. 5 that ther mal flux is sig nif i cantly higher at C4 and C7, the wa ter boxes for sam ple ir ra di a tion. How ever, among these two lo ca tions, max i mum ther mal neu tron flux has been ob served at cen tral ir ra di a tion fa cil ity
C7. How ever, fast flux is higher in the cen tral fuel re gion of the core and de creases due to leak age at pe riph -er ies shown in fig. 5. For both th-er mal and fast fis sion, val ues of six group de layed neu tron yields vdj(th) and
vdj(fast) for 235U, 238U, 239Pu, and 240Pu were taken
from [16] given in tab. 2. Weighted flux av er age of
these neu tron yields for each de layed neu tron group of the men tioned iso topes was taken by us ing the fol low -ing re la tion
vdj vdj th th vdj fast fast th fast
= +
+
( )f ( )f
f f (1)
where vdj is the to tal de layed neu tron yield of jth group,
vdj (th) – the de layed neu tron yield of jth group due to ther mal fis sion, vdj (fast) – the de layed neu tron yield of
jth group due to fast fis sion, fth – the ther mal neu tron
flux and ffast – the fast neu tron flux. These flux
weighted av er age val ues of de layed neu tron yields for the above men tioned iso topes were uti lized at the in put of CI TA TION. Through the use of per tur ba tion cal cu la tions op tion in CI TA TION, ef fec tive de layed neu -tron frac tion was ob tained ac cord ing to re la tion
b
c f b s f
eff =
åV å ¢ j g å N å
V i
i g i g b b j b in f n b i i n
i i
( , ) *, , , , , , ,
å åc( )g f*i g, ånå , f,
g n f n i n
(2)
where Vi rep re sent the vol ume of re gion i, c'(j, g) – the de layed neu tron dis tri bu tion func tion, bb, j – the de -Fig ure 3. Burn-up (% age of 235U) of pro posed core
at EOEC
Ta ble 1. Ten en ergy group struc ture for mi cro scopic cross-sections
En ergy group [eV]
Up per en ergy
WIMSD4 en ergy group
Av er age en ergy
[eV] Re marks
1 10×106 1-5 2.87×106 Above thresh old fis sion of 238U and no de layed pro duc tion
2 0.821×106 6-7 4.98×105 Av er age en ergy of 2 to 6 de layed neu tron group pro duced
3 3.025×105 8 2.353×105 Av er age pro duced en ergy of first de layed neu tron group
4 0.183×106 9-20 8.2×103 Fourth and fifth groups are of equal leth argy in ter vals in WIMSD groups from 9-33
5 367.262 21-33 20.551
6 1.15 34-40 1.057 Group cov ers the res o nance of 240Pu i. e. at 1 eV
7 0.972 41-45 0.78 The group 7 sep a rates the en ergy bound aries of group 6 and 8
8 0.625 46-55 0.296 This group cov ers the res o nance of 239Pu i. e. at 0.3 eV
9 0.14 56-60 0.0837 Ninth group is based on the max i mum ther mal neu tron cut-off en ergy,
0.14 eV (5 kT)
10 0.050 61-69 2.2×10–4 Re main ing ther mal groups
layed neu tron frac tion of de layed fam ily j at lo ca tion i
for nu clide b and Nb,i – the num ber den sity of nu clide b
at lo ca tion i, f – the neu tron flux, f* – the adjoint flux,
c – the dis tri bu tion func tion, and v – the av er age num ber of neu tron per fis sion. For prompt neu tron gen er a -tion time, the CI TA TION code cal cu lates the prompt neu tron life time (l) and mul ti pli ca tion fac tor (k) can then be cal cu lated by re la tion L = l/k s. For es ti ma tion of prompt neu tron life time through CI TA TION, the code re quires as its in put the flux weighted, av er age in verse ve loc ity, for each en ergy group ac cord ing to re la tion
1 1 0 0 u u f f æ è ç ö ø ÷ =
ò
ò
( ) ( ) ( )E E E
E E
d
d 4
4 (3)
where u(E) is the en ergy de pend ent neu tron ve loc ity. The value of (1/u) is cal cu lated by in tro duc ing small
s s u f f a a E v
E E E
E E ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) , =
ò
ò
0 0 0 0 4 d d 4 (4) 1 1 0 0 0 u s s u f f æ è ç ö ø ÷ = =ò
ò
a a E vE E E
E E
( ) ( ) ( )d
( )d
0
4
4 (5)
where sa,0 = 1.0 b (1 b = 10–28 m2) in WIMSD/4 [18] li
-brary at most prob a ble ve loc ity i. e. u0 = 2200 m/s at
most prob a ble en ergy, i. e. 0.0253 eV.
By in tro duc ing (1/u) ab sorber in WIMSD/4 in -put and keep ing the neu tron ve loc ity at most prob a ble en ergy u0 = 2200 m/s in BORGES in put, BORGES cal cu lates the av er age in verse ve loc ity of neu tron for each group and writes it in the mi cro scopic crosssec tion out put file in the CI TA TION in put for mat. Uti liz ing the av er age in verse ve loc i ties of neu tron, the CI -TA TION code com putes the prompt neu tron life time by the re la tion
l
V n
k V g
i n i n i
i
i g i g n i n f n =
å
å å å å
u f f
c f n f
( ) ( ) , * , , * , , 1 (6)
u(n) is the neu tron ve loc ity and Sf is the mac ro scopic
fis sion cross-sec tion.
RE SULTS AND DIS CUS SIONS
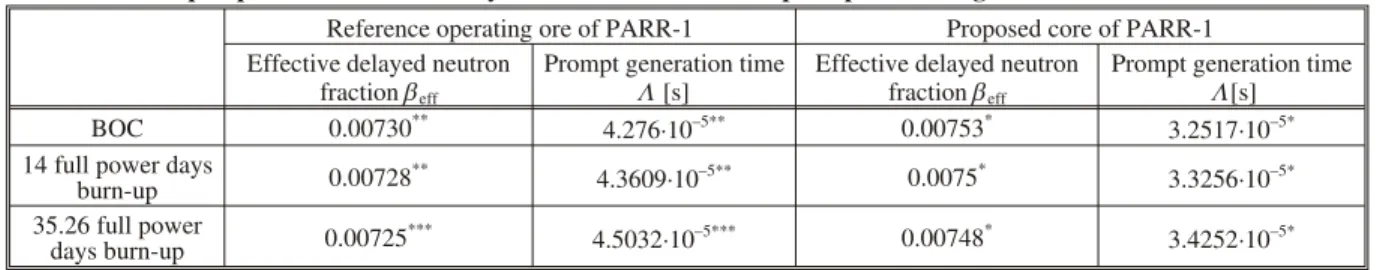
Ef fec tive de layed neu tron frac tions and prompt neu tron gen er a tion times were cal cu lated at dif fer ent steps of burn-up cy cle for the un der study pro posed core. Ta ble 3 in di cates that by in creas ing core burn-up, ef fec tive de layed neu tron frac tion is de creas ing while prompt neu tron gen er a tion time is in creas ing. With in -creas ing burn-up of fuel, ini tial load ing of 235U is de
-pleted; 239Pu and its higher iso topes are pro duced due
to in ter nal con ver sion of 238U. Plu to nium iso topes are Fig ure 5. Fast (up per value) and ther mal (lower val ues)
neu tron flux (´1013 cm–2s–1) in the pro posed core
Ta ble 2. Group based de layed neu tron yield of dif fer ent iso topes for fast and ther mal flux
Iso topes Yield Group-1 Group-2 Group-3 Group-4 Group-5 Group-6
235
U vdj(fast) 0.000630 0.003510 0.003100 0.006720 0.002110 0.000430
vdj(th) 0.000520 0.003460 0.003100 0.006240 0.001820 0.000660
239
Pu vdj(fast) 0.000240 0.001760 0.001360 0.002070 0.000650 0.000220
vdj(th) 0.000210 0.001820 0.001290 0.001990 0.000520 0.000270
238
U vdj(fast) 0.000540 0.005640 0.006670 0.015900 0.009270 0.003090
240Pu v
con trib ut ing in power gen er a tion as burn-up in creases and neu tron flux spec trum is also changed. The de -layed neu tron en ergy spec tra cdj(E) de pend upon the iso tope from which the de layed neu trons are emit ted. Due to plutonium con tri bu tion in power gen er a tion, the de layed neu tron yield and en ergy spec tra cdj(E) is changed. There fore with in creas ing burn-up beff is changed and prompt neu tron gen er a tion time is mainly chang ing with changes in av er age in verse ve loc i ties of the neu tron in dif fer ent re gions of the core. The ef fec -tive de layed neu tron frac tion is de creas ing while prompt neu tron gen er a tion time is in creas ing with burn-up; there fore re ac tor re sponse to tran sient is also chang ing with in creas ing burnup. The spa tial and en ergy dis tor tion in the neu tron flux dur ing burnup cy -cle changes the beff and L.
Higher fuel den sity of pro posed core re sults in higher fuel to mod er a tor ra tio in pro posed core as com -pared to the ref er ence op er at ing core of PARR-1. Higher fuel to mod er a tor ra tio in pro posed core causes neu tron en ergy spec trum to be harder [8]. Low av er age in verse ve loc i ties in harder neu tron en ergy spec trum of the pro posed core place prompt neu tron gen er -a tion time on lower side. There fore, prompt neu tron gen er a tion time in the pro posed core is lower than ref -er ence op -er at ing core of PARR-1 at all burn-up steps (tab. 3). How ever, due to smaller size of ref er ence core, in crease in fast non leak age prob a bil ity dom i nates the de crease in fast fis sion fac tor by de layed neu -trons and im por tance of de layed neu -trons is in creased. In gen eral, pro por tion of beff/L is de creas ing with in -creas ing burn-up for both an a lyzed cores as shown in fig. 6.
CON CLU SION
Prompt neu tron gen er a tion time is low, while ef -fec tive de layed neu tron frac tion is high for the smaller sized higher den sity pro posed core as com pared to the larger sized lower den sity ref er ence op er at ing core of PARR-1 by keep ing en rich ment to be con served in both re ac tor cores. Over all ra tio (beff/L) of ki netic pa -ram e ters is de creas ing with in creas ing burn-up for pro posed core of PARR-1.
AU THOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Cal cu la tions were car ried out by A. Mu ham mad and T. Mahmood un der su per vi sion and guide lines of M. Iqbal. All au thors dis cussed the re sult. Manu script was written by A. Mu ham mad and re viewed by T. Mahmood. Fig ures were pre pared by A. Mu ham mad. M. Iqbal checked the manu script and added cor rec -tions.
REF ER ENCES
[1] Lewins, J., Nu clear Re ac tor Ki net ics and Con trol, Pergamon Press, Ox ford, UK, 1978
[2] Schultz, M., Con trol of Nu clear Re ac tors and Power Plants McGraw-Hill, New York, USA, 1961
[3] Wil liams, T., et al., Ex per i men tal In ves ti ga tion of the Ki netic Pa ram e ter (beff/L) in Graph ite-Mod er ated,
LEU Fu eled, Crit i cal Con fig u ra tions, Pro ceed ings, In ter na tional Con fer ence on the Phys ics of Re ac tors (PHYSOR 96), Sep tem ber 16-20, 1996, Mito, Ibaraki, Ja pan, 2, p. E200
[4] Hamid, T., Re ac tor Ki net ics Pa ram e ters as a Func tion of Fuel Burn-Up, PIEAS-445 Re port, Pa ki stan, 1999
[5] Ahmed, R., Aslam, Ahmad, N., Ef fect of HighDen sity Fuel Load ing on Crit i cal ity of Low En riched Ura -nium Fu eled Ma te rial Test Re search Re ac tors, An nals of Nu clear En ergy, 32 (2005), 1, pp. 29-62
[6] Snoj, L., et al., Cal cu la tion of Ki netic Pa ram e ters for Mixed TRIGA Cores with Monte Carlo, An nals of Nu -clear En ergy, 37 (2010), 2, pp. 223-229
Ta ble 3. Burn-up de pend ent ef fec tive de layed neu tron frac tion and prompt neu tron gen er a tion time
Ref er ence op er at ing ore of PARR-1 Pro posed core of PARR-1 Ef fec tive de layed neu tron
frac tion beff
Prompt gen er a tion time
L [s]
Ef fec tive de layed neu tron frac tion beff
Prompt gen er a tion time
L [s]
BOC 0.00730** 4.276×10–5** 0.00753* 3.2517×10–5*
14 full power days
burn-up 0.00728
**
4.3609×10–5** 0.0075*
3.3256×10–5*
35.26 full power
days burn-up 0.00725
***
4.5032×10–5*** 0.00748*
3.4252×10–5*
*pres ent study, **Iqbal et al., 2008
[8], ***Mu ham mad et al., 2011 [11]
Fig ure 6. Ef fec tive de layed neu tron frac tion over prompt neu tron gen er a tion time beff/L as a func tion of
Im prov ing the Per for mance of a Re search Re ac tor's Equi lib rium Core, Nucl Technol Radiat, 28 (2013), 4, pp. 362-369
[9] Iqbal, M., Mahmood, T., Pervez, S., Flow of Ki netic Pa ram e ters in a Typ i cal Swim ming Pool Type Re -search Re ac tor, An nals of Nu clear En ergy, 35 (2008), 3, pp. 518-524
[10] Mu ham mad, F., Majid, A., Ki netic Pa ram e ters of a Ma te rial Test Re search Re ac tor Fu eled with High Den sity U3Si2 Dis per sion Fu els, Prog ress in Nu clear
En ergy, 51 (2009), 1, pp. 141-145
[11] Mu ham mad, A., et al., Cal cu la tion and Mea sure ment of Ki netic Pa ram e ters of Pa ki stan Re search Re ac tor-1 (PARR-1), An nals of Nu clear En ergy, 38 (2011), 1, pp. 44-48
[12] Mahmood, T., et al., Per for mance Eval u a tion/Anal y -sis of Pa ki stan Re search Re ac tor-1 (PARR-1) Cur rent Core Con fig u ra tion, Prog ress in Nu clear En ergy, 53 (2011), 6, pp. 729-735
Mannual, 1993
[15] Fowler, T. B., Vondy, D. R., Cunningham, G. W., Nu -clear Re ac tor Core Anal y sis Code-CI TA TION, USAEC Re port ORNL-TM-2496, Re vi sion 2, Oak Ridge Na tional Lab o ra tory, Oak Ridge, Tenn., USA, 1971
[16] Keepin, G. R., Phys ics of Nu clear Ki net ics, Ad di -son-Wes ley, Read ing, Mass., USA, 1965
[17] Duderstadt, J. J., Ham il ton, L. J., Nu clear Re ac tor Anal y sis, Wiley, New York, USA, 1976
[18] Taubman, C. J., The WIMS69 Group Li brary Tape 166259, AEEWM1324, Atomic En ergy Es tab lish -ment, Winfrith, Dorchester, UK, 1975
Re ceived on July 9, 2014 Ac cepted on De cem ber 8, 2014
Ata MUHAMAD, Masud IGBAL, Tajab MAHMUD
PROU^AVAWE KINETI^KIH PARAMETARA SA IZGARAWEM RADI POBOQ[AWA SVOJSTAVA RAVNOTE@NOG JEZGRA
ISTRA@IVA^KOG REAKTORA
U ovom radu prikazano je istra`ivawe kineti~kih parametara, efektivne frakcije zakasnelih neutrona i vremena nastanka promptnih neutrona, za razli~ite nivoe izgarawa, u ravnote`nom jezgru istra`iva~kog reaktora sa niskooboga}enim uranijumskim gorivom visoke gustine (U3Si2-Al gorivo sa 4.8 g/cm3 uranijuma). Rezultati su upore|eni sa referentnim vrednostima radnog jezgra Pakistanskog istra`iva~kog reaktora-1. Zapa`eno je da se sa porastom izgarawa goriva smawuje efektivna frakcija zakasnelih neutrona, dok vreme nastanka promptnih neutrona raste. Otuda se ukupan odnos beff/L smawuje sa porastom izgarawa. Usled tvrdog spektra, u svim koracima izgarawa vreme nastanka promptnih neutrona L u prou~avanom jezgru kra}e je od onoga u referentnom radnom jezgru. Zapa`eno je da je beff ve}e u prou~avanom jezgru nego u referentnom radnom jezgru usled mawe veli~ine. Prora~uni su obavqeni programima WIMSD/4 i
CI TA TION.